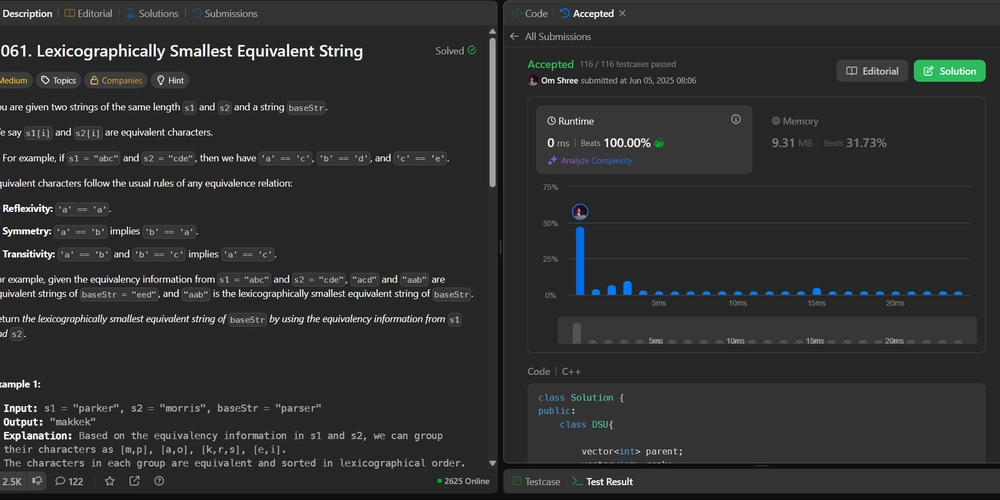
Google Chrome 0-Day Vulnerability Exploited in the Wild to Execute Arbitrary Code
Google has released an emergency security update for Chrome after confirming that a critical zero-day vulnerability is being actively exploited by attackers in the wild. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-5419, allows threat actors to execute arbitrary code on victims’ systems through out-of-bounds read and write operations in Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. The tech giant pushed […] The post Google Chrome 0-Day Vulnerability Exploited in the Wild to Execute Arbitrary Code appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Google has released an emergency security update for Chrome after confirming that a critical zero-day vulnerability is being actively exploited by attackers in the wild.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-5419, allows threat actors to execute arbitrary code on victims’ systems through out-of-bounds read and write operations in Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine.
The tech giant pushed Chrome version 137.0.7151.68/.69 for Windows and Mac users, and 137.0.7151.68 for Linux systems, with the update rolling out globally over the coming days and weeks.
Google has explicitly stated that “an exploit for CVE-2025-5419 exists in the wild,” marking this as a high-priority security issue requiring immediate user attention.
Chrome 0-Day Vulnerability Exploited
CVE-2025-5419 was discovered and reported by Clement Lecigne and Benoît Sevens from Google’s Threat Analysis Group on May 27, 2025. The vulnerability stems from memory corruption issues in V8, Chrome’s JavaScript and WebAssembly engine, which processes code from websites and web applications.
Out-of-bounds memory access vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous as they can allow attackers to read sensitive data or write malicious code to system memory.
Recognizing the severity of the threat, Google implemented emergency mitigation measures on May 28, 2025, pushing a configuration change across all Chrome platforms to help protect users before the full patch became available.
This rapid response demonstrates the critical nature of the vulnerability and the active threat it poses to Chrome users worldwide.
The security update also addresses a second vulnerability, CVE-2025-5068, a use-after-free flaw in Blink, Chrome’s rendering engine. Security researcher Walkman reported this medium-severity vulnerability on April 7, 2025, and carries a $1,000 bounty reward.
While less critical than the zero-day, use-after-free vulnerabilities can still lead to memory corruption and potential code execution.
Google has maintained its policy of restricting access to detailed vulnerability information until the majority of users have updated their browsers.
This approach prevents malicious actors from reverse-engineering patches to develop new exploits while users remain on vulnerable versions.
The company credits its comprehensive security testing infrastructure for detecting many vulnerabilities before they reach stable releases.
Google employs advanced tools, including AddressSanitizer, MemorySanitizer, UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer, Control Flow Integrity, libFuzzer, and AFL, to identify potential security issues during development.
Chrome users should immediately update their browsers by navigating to Settings > About Chrome, which will automatically download and install the latest version.
Given the active exploitation of CVE-2025-5419, users are strongly recommended to treat this update as urgent. Users can verify their Chrome version matches 137.0.7151.68 or higher to ensure protection against these vulnerabilities.
Organizations should prioritize deploying this update across their networks to prevent potential compromise through malicious websites targeting the zero-day vulnerability.
Live Credential Theft Attack Unmask & Instant Defense – Free Webinar
The post Google Chrome 0-Day Vulnerability Exploited in the Wild to Execute Arbitrary Code appeared first on Cyber Security News.










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 151]: Anthropic CEO: AI Will Destroy 50% of Entry-Level Jobs, Veo 3’s Scary Lifelike Videos, Meta Aims to Fully Automate Ads & Perplexity’s Burning Cash](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20151%20cover.png)




































































































































































































































































_Andrea_Danti_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)












































































































![Apple AI Launch in China Delayed Amid Approval Roadblocks and Trade Tensions [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97500/97500/97500-640.jpg)