Google fixes another actively exploited vulnerability in Chrome, so update now!
Google has released an important update for Chrome, patching one actively exploited zero-day and two other security flaws

Google has released an update for the Chrome browser to patch an actively exploited flaw.
The update brings the Stable channel to versions 137.0.7151.68/.69 for Windows and Mac and 137.0.7151.68 for Linux.
The easiest way to update Chrome is to allow it to update automatically, but you can end up lagging behind if you never close your browser or if something goes wrong—such as an extension stopping you from updating the browser.
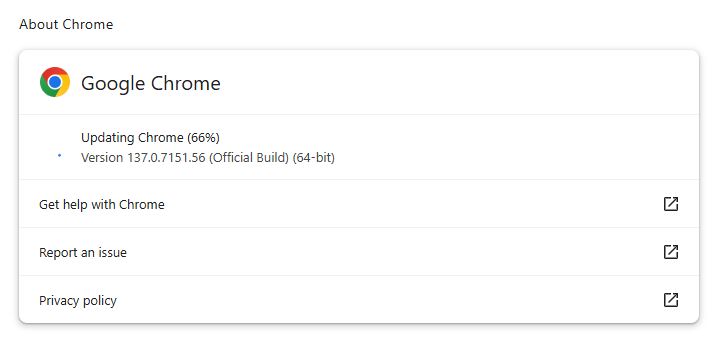
To manually get the update, click the “more menu” (three stacked dots) > Settings > About Chrome. If there is an update available, Chrome will notify you and start downloading it. Then all you have to do is relaunch the browser in order for the update to complete, and for you to be safe from the vulnerability.
This update is crucial since it addresses an actively exploited vulnerability which could allow an attacker to exploit a specially crafted HTML page (website).
Technical details
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025-5419 is an out-of-bounds read and write in Google Chrome’s “V8,” which is the engine that Google developed for processing JavaScript. Prior to Google Chrome version 137.0.7151.68, this vulnerability allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page.
V8 has been a significant source of security problems in the past.
An out-of-bounds read and write vulnerability means that the attacker can manipulate parts of the device’s memory that should be out of their reach. Such a flaw in a program allows it to read or write outside the bounds the program sets, enabling attackers to manipulate other parts of the memory allocated to more critical functions. Attackers can write code to a part of the memory where the system executes it with permissions that the program and user should not have.
Google knows that attackers currently exploit CVE-2025-5419 in the wild, but released no details yet on who exploits the flaw, how they do it in real-world attacks, or who the targets are in those attacks. However, the Google Threat Analysis Group (TAG) team, which discovered the exploit, focuses on spyware and nation-state attackers who abuse zero days for espionage purposes.
This Chrome update also patches a medium-severity, use-after-free flaw (CVE-2025-5068) in the open-source rendering engine Blink and one internally discovered vulnerability.
We don’t just report on browser vulnerabilities. Malwarebytes’ Browser Guard protects your browser against malicious websites and credit card skimmers, blocks unwanted ads, and warns you about relevant data breaches and scams.












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 151]: Anthropic CEO: AI Will Destroy 50% of Entry-Level Jobs, Veo 3’s Scary Lifelike Videos, Meta Aims to Fully Automate Ads & Perplexity’s Burning Cash](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20151%20cover.png)

























































































































![[DEALS] FileJump 2TB Cloud Storage: Lifetime Subscription (85% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)





















































































































































































































































![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'The Wild Ones' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97515/97515/97515-640.jpg)