Damaging the Peroxidase-Like Task associated with nGO, MoS2 along with WS2 Nanozymes through the use of Steel Cations.
This study's participation in clinicaltrials.gov is documented. We are interested in the characteristics of the clinical trial, NCT04024605. Though readily digestible, the flaxseed protein in biscuits was marked by lysine inadequacy and poor lysine digestibility, which both negatively impacted DIAAS and boosted deamination. Comparatively, rapeseed's digestibility was moderate, but it had no limiting indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), hence its excellent DIAAS value and minimal deamination. This study's registration is documented at clinicaltrials.gov. NCT04024605 represents a particular clinical trial. Within our prior research, elevated expression of the Spfoxl-2 transcript was observed within the Scylla paramamosain gonads; this led to the identification of potential target genes in the ovary. Our initial study, using RNA interference (RNAi) and RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq), aimed to analyze potential target genes within the testis and subsequently compare the findings with those obtained from the ovary. A significant finding from the Spfoxl-2 silencing experiment in the testis was the differential expression of 7892 unigenes, many of which are conserved genes associated with testicular development, including those from the Dmrt, Sox, Caspase, Cdk, Kinesin, Fox families, and others. Further research indicated the prevalence of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) within key spermatogenesis pathways, including DNA replication, the cell cycle, spliceosome function, homologous recombination, meiosis, and apoptosis. Potential target genes, compared across ovaries and testes, showed 135 shared genes, a subset of which are associated with immune responses. Based on our current knowledge, this work was the initial report to expose the functions of foxl-2 in crustacean testes, achieved through the analysis of the transcriptome. By identifying key genes and pathways central to the testicular development of S. paramamosain, a groundbreaking molecular understanding of foxl-2's function in this context is also established. In murine models of paraquat (PQ)-induced Parkinson's disease (PD), prior research has shown neuroinflammation's association with dopaminergic neuron loss, though the underlying mechanisms of this relationship are not fully understood. The current study explored the impact of microglia-induced inflammation on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the associated processes. For six weeks, C57BL/6 mice were injected intraperitoneally with PQ twice weekly, and then were further treated either with intraperitoneal minocycline once every two days, or no additional treatment. The factors examined included microglial activation, the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, the expression levels of tight junction proteins and matrix metalloproteinase, alongside the loss of dopaminergic neurons and the assessment of resulting neurological deficits. PQ-induced nigral microglial activation in mice was effectively suppressed by minocycline. Minocycline treatment led to a considerable attenuation of the PQ-induced escalation of brain EB content and the pronounced overexpression of zonula occludin-1 (ZO-1), claudin-5, and occludin. Minocycline's intervention, specifically targeting microglial activation, substantially alleviated the loss of dopaminergic neurons and neurological impairments in mice subjected to PQ exposure. The downregulation of MMP-2/9 expression in PQ-lesioned mice was observed following microglial inactivation. Potential protection against dopaminergic neurodegeneration through suppression of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and reduction of blood-brain barrier breakdown in a mouse model of PQ-induced Parkinson's disease was suggested by these findings; MMP-2/9's involvement merits future verification. Crucial human-body components, peptides, demonstrate their importance in a wide array of chemistry applications. In light of their biocompatibility, the utilization of these structures within drug delivery systems stands out as a key application. Diphenylalanine (FF) peptide-based systems, being the smallest dipeptide group within the -amyloid polypeptide sequence, are favored in novel targeted drug systems due to their biocompatible nature, excellent thermal stability, and substantial ionic strength properties in water. Lung cancer patients may be treated with epirubicin, an isomeric form of doxorubicin. Strategies to decrease both the side effects and the doses administered of epirubicin are currently being explored. This study involved the creation and analysis of tert-butyloxycarbonyl-protected diphenylalanine (Boc)-FF particles loaded with epirubicin, subsequently assessing their effects on cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLC), specifically A549 cells. As determined by the study, epirubicin-loaded Boc-FF dipeptides led to a substantial decrease in cell viability, an elevation in oxidative stress, and a concomita

This study's participation in clinicaltrials.gov is documented. We are interested in the characteristics of the clinical trial, NCT04024605.
Though readily digestible, the flaxseed protein in biscuits was marked by lysine inadequacy and poor lysine digestibility, which both negatively impacted DIAAS and boosted deamination. Comparatively, rapeseed's digestibility was moderate, but it had no limiting indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), hence its excellent DIAAS value and minimal deamination. This study's registration is documented at clinicaltrials.gov. NCT04024605 represents a particular clinical trial.
Within our prior research, elevated expression of the Spfoxl-2 transcript was observed within the Scylla paramamosain gonads; this led to the identification of potential target genes in the ovary. Our initial study, using RNA interference (RNAi) and RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq), aimed to analyze potential target genes within the testis and subsequently compare the findings with those obtained from the ovary. A significant finding from the Spfoxl-2 silencing experiment in the testis was the differential expression of 7892 unigenes, many of which are conserved genes associated with testicular development, including those from the Dmrt, Sox, Caspase, Cdk, Kinesin, Fox families, and others. Further research indicated the prevalence of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) within key spermatogenesis pathways, including DNA replication, the cell cycle, spliceosome function, homologous recombination, meiosis, and apoptosis. Potential target genes, compared across ovaries and testes, showed 135 shared genes, a subset of which are associated with immune responses. Based on our current knowledge, this work was the initial report to expose the functions of foxl-2 in crustacean testes, achieved through the analysis of the transcriptome. By identifying key genes and pathways central to the testicular development of S. paramamosain, a groundbreaking molecular understanding of foxl-2's function in this context is also established.
In murine models of paraquat (PQ)-induced Parkinson's disease (PD), prior research has shown neuroinflammation's association with dopaminergic neuron loss, though the underlying mechanisms of this relationship are not fully understood. The current study explored the impact of microglia-induced inflammation on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the associated processes. For six weeks, C57BL/6 mice were injected intraperitoneally with PQ twice weekly, and then were further treated either with intraperitoneal minocycline once every two days, or no additional treatment. The factors examined included microglial activation, the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, the expression levels of tight junction proteins and matrix metalloproteinase, alongside the loss of dopaminergic neurons and the assessment of resulting neurological deficits. PQ-induced nigral microglial activation in mice was effectively suppressed by minocycline. Minocycline treatment led to a considerable attenuation of the PQ-induced escalation of brain EB content and the pronounced overexpression of zonula occludin-1 (ZO-1), claudin-5, and occludin. Minocycline's intervention, specifically targeting microglial activation, substantially alleviated the loss of dopaminergic neurons and neurological impairments in mice subjected to PQ exposure. The downregulation of MMP-2/9 expression in PQ-lesioned mice was observed following microglial inactivation. Potential protection against dopaminergic neurodegeneration through suppression of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and reduction of blood-brain barrier breakdown in a mouse model of PQ-induced Parkinson's disease was suggested by these findings; MMP-2/9's involvement merits future verification.
Crucial human-body components, peptides, demonstrate their importance in a wide array of chemistry applications. In light of their biocompatibility, the utilization of these structures within drug delivery systems stands out as a key application. Diphenylalanine (FF) peptide-based systems, being the smallest dipeptide group within the -amyloid polypeptide sequence, are favored in novel targeted drug systems due to their biocompatible nature, excellent thermal stability, and substantial ionic strength properties in water. Lung cancer patients may be treated with epirubicin, an isomeric form of doxorubicin. Strategies to decrease both the side effects and the doses administered of epirubicin are currently being explored. This study involved the creation and analysis of tert-butyloxycarbonyl-protected diphenylalanine (Boc)-FF particles loaded with epirubicin, subsequently assessing their effects on cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLC), specifically A549 cells. As determined by the study, epirubicin-loaded Boc-FF dipeptides led to a substantial decrease in cell viability, an elevation in oxidative stress, and a concomitant increase in DNA damage and apoptosis. The study highlights the potential of epirubicin-loaded Boc-FF particles as an alternative drug delivery system for NSCLC, owing to their advantageous physiological, chemical, and biological activity.
In a broad sense, the link between predicted functional effects of missense mutations within genes known to be involved in human illnesses and the severity of observed disease symptoms is often weak. This study in pigs sought to determine if missense single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) impacting genes associated with lipid metabolism correlate with lipid characteristics. In silico analyses of functional mutations revealed that nine of seventy-two nominally associated SNPs demonstrated a high or very high degree of consistency, yet displayed no association with anticipated lipid traits contingent upon inactivation of the relevant gene, according to association analysis. Although the scarcity of endophenotypes and the limited size of particular genotype sets could partially restrict the current study's reach, the data we have gathered signify that modern bioinformatic tools have a restrained capacity to project the repercussions of missense mutations upon complex phenotypes.
The focus of this paper was the adsorption of the trimethylthiazoline (TMT) molecule onto the human olfactory receptor OR5K1 and the mouse olfactory receptor Olfr175. This work's core contribution was to analyze the stereochemical and energetic aspects of OR5K1 and Olfr175 activation triggered by trimethylthiazoline. This analysis was based on docking simulations of the molecules within the respective human and mouse olfactory binding pockets, employing the grand canonical ensemble in statistical physics. The human olfactory receptor OR5K1's interaction with trimethylthiazoline, as indicated by both experimental data and advanced statistical physics models, is effectively depicted by a monolayer model with a single energy value. In contrast, the interaction of trimethylthiazoline with the mouse receptor Olfr175 appears best represented by a two-energy monolayer model. Further investigation of the odorant revealed that it was lodged through a multi-stage docking procedure and positioned non-parallel on OR5K1 and Olfr175, as the number of TMT molecules per binding site, 'n', was larger than 1. The proposed models were employed to assess the size distributions of human and mouse olfactory receptor binding sites relative to TMT. These distributions ranged from 0.30 to 20 nanometers, with a maximum at approximately 175 nanometers for OR5K1, and from 1 to 25 nanometers, having a peak around 4.25 nanometers for Olfr175. It was determined, from the calculated molar adsorption energies, to be under 11 kJ/mol, that physical adsorption occurred in the two olfactory systems. Understanding the olfactory process in general is facilitated by calculating adsorption energy distributions relative to TMT, identifying olfactory bands (i. OR5K1 exhibited adsorption energy distribution bands between 0 and 1050 kJ/mol, and Olfr175 between 3 and 1250 kJ/mol, respectively. Observing the thermodynamic functions governing the adsorption process, such as adsorption entropy, Gibbs free enthalpy, and internal energy, one can conclude that the disorder peak of the two olfactory systems was reached when the concentration at equilibrium became equivalent to the concentration at half-saturation. Calculated Gibbs free enthalpy and internal energy values were negative, suggesting an exothermic and spontaneous nature for the adsorption process central to the olfactory mechanism.
Due to its classification within the Cryptophyta and the Rhodomonas genus, Rhodomonas salina plays a crucial role in both aquaculture live feed and the production of phycoerythrin (PE). Extracted from Rhodomonas salina in this investigation, PE displayed a molecular weight near 24 kDa, an absorbance maximum at 545 nm, and a purity of up to 661, a quality exceeding reagent grade requirements indicated by an OD545/OD280 ratio above 4. To determine the immunomodulatory effect of PE on the A549 human lung cancer cell line, an evaluation of its influence on anticancer activity and its related mechanisms was undertaken. Biochemical assays, coupled with western blot analysis, provided a means for confirming the immune mechanisms. The results clearly indicated a dose-dependent and significant reduction in A549 cell proliferation after a 24-hour period of exposure to PE. A consequence of PE was the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). The subsequent analysis demonstrated a remarkable augmentation of cleaved caspase-3 and p53 protein levels through the use of PE. In parallel, the BCL-2 family was affected, demonstrating changes such as a substantial increase in Bim and Bak, and a decrease in Bcl-2 levels. The experiment demonstrated a lack of alteration in Bax expression levels; an interesting finding. The biological underpinnings of PE's capacity to induce apoptosis demonstrated activation of the ERK/Bak and JNK/caspase-3 signaling pathways. z-4-hydroxytamoxifen This research highlights PE's anticancer properties, observed within Rhodomonas salina, potentially serving a role in cancer prevention and introducing it as a novel immunostimulant for the pharmaceutical sector.z-4-hydroxytamoxifen










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)

















































































































![[DEALS] 1min.AI: Lifetime Subscription (82% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)














































































































































_incamerastock_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
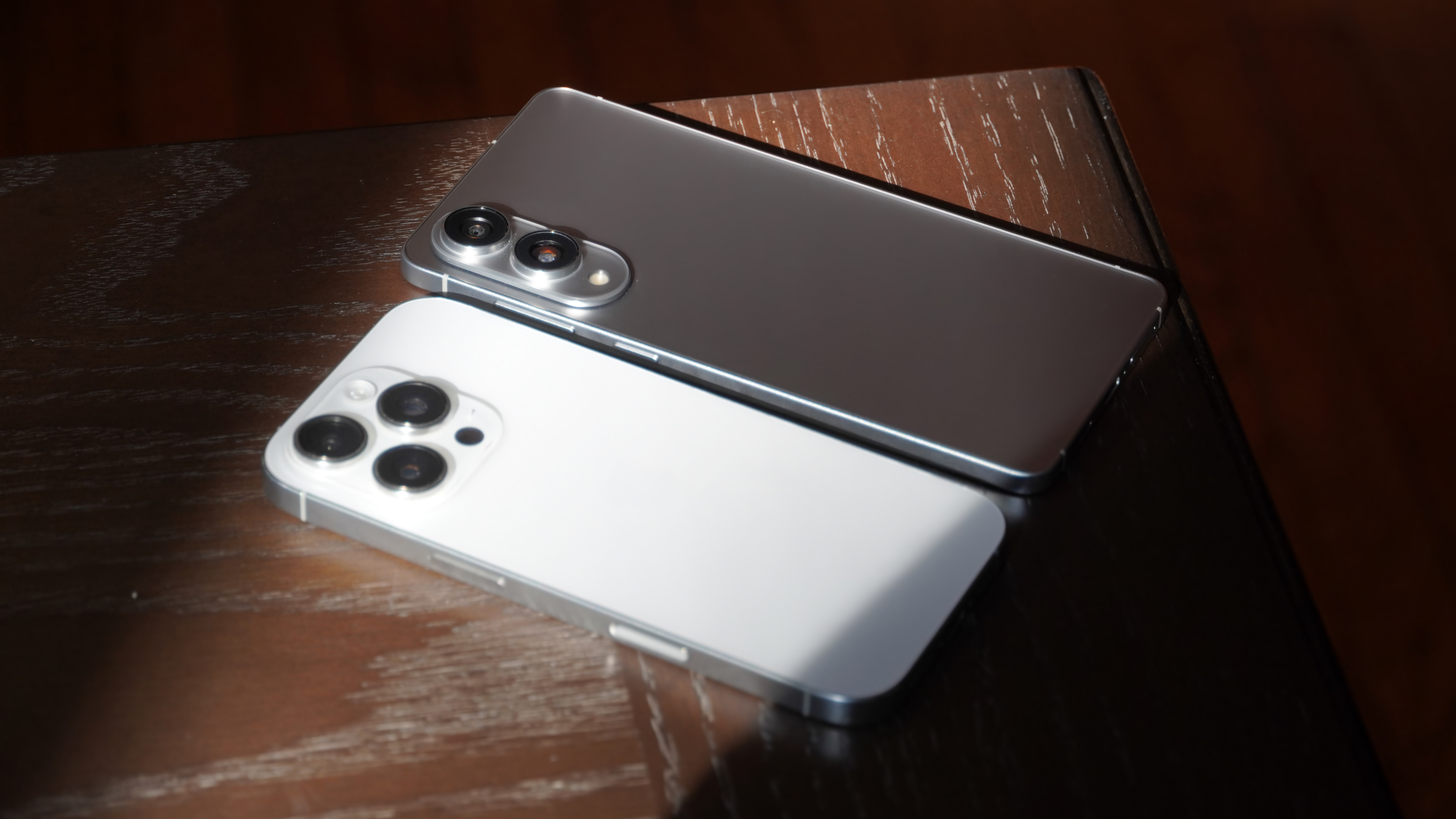


























































































![Nothing Phone (3) has a 50MP ‘periscope’ telephoto lens – here are the first samples [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/nothing-phone-3-telephoto.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)