AI and National Security: The New Battlefield
Artificial intelligence is changing how nations protect themselves. It has become essential for cybersecurity, weapon development, border control, and even public discourse. While it offers significant strategic benefits, it also introduces many risks. This article examines how AI is reshaping security, the current outcomes, and the challenging questions these new technologies raise. Cybersecurity: A Fight […] The post AI and National Security: The New Battlefield appeared first on Unite.AI.


Artificial intelligence is changing how nations protect themselves. It has become essential for cybersecurity, weapon development, border control, and even public discourse. While it offers significant strategic benefits, it also introduces many risks. This article examines how AI is reshaping security, the current outcomes, and the challenging questions these new technologies raise.
-
Cybersecurity: A Fight of AI against AI
Most present‑day attacks start in cyberspace. Criminals no longer write every phishing email by hand. They use language models to draft messages that sound friendly and natural. In 2024, a gang used a deep-fake video of a chief financial officer stealing 25 million dollars from his own firm. The video looked so real that an employee followed the fake order without a doubt. Attackers now feed large language models with leaked resumes or LinkedIn data to craft personal bait. Some groups are even using generative AI to create software bugs or write malware snippets.
Defenders are also using AI to shield against these attacks. Security teams feed network logs, user clicks, and global threat reports into AI tools. The software learns “normal” activity and warns when something suspicious happens. When an intrusion is detected, AI systems disconnect a suspected computer to limit damage that would spread if humans reacted slower.
-
Autonomous Weapons
AI also steps onto physical battlefields. In Ukraine, drones use onboard vision to find fuel trucks or radar sites before they explode. The U.S. has used AI to help identify targets for airstrikes in places like Syria. Israel’s army recently used an AI target‑selection platform to sort thousands of aerial images to mark potential militant hideouts. China, Russia, Turkey, and the U.K. have tested “loitering munitions” that circle an area until AI spots a target. These technologies can make military operations more precise and reduce risks for soldiers. But they also bring serious concerns. Who is responsible when an algorithm chooses the wrong target? Some experts fear “flash wars” where machines react too quickly for diplomats to stop them. Many experts are calling for international rules to control autonomous weapons, but states fear falling behind if they pause.
-
Surveillance and Intelligence
Intelligence services once relied on teams of analysts to read reports or watch video feeds. Today they rely on AI to sift millions of images and messages each hour. In some countries, like China, AI tracks citizens’ behavior, from small things like jaywalking to what they do online. Similarly, on the U.S.–Mexico border, solar towers with cameras and thermal sensors scan empty desert. The AI spots a moving figure, labels it human or animal, then alerts patrol agents. This “virtual wall” covers wide ground that humans could never watch alone.
While these tools extend coverage, they also magnify errors. Face‑recognition systems have been shown to misidentify women and people with darker skin at higher rates than white men. A single false match may cause an innocent person to face extra checks or detention. Policymakers ask for audited algorithms, clear appeal paths, and human review before any strong action.
-
Information Warfare
Modern conflicts are fought not only with missiles and code but also with narratives. In March 2024 a fake video showed Ukraine’s president ordering soldiers to surrender; it spread online before fact‑checkers debunked it. During the 2023 Israel–Hamas fighting, AI‑generated fakes favoring one side’s policies flooded social streams, in order to tilt opinion.
False information spreads faster than governments can correct it. This is especially problematic during elections, where AI-generated content is often used to sway voters. Voters find it difficult to distinguish between real and AI-generated images or videos. While governments and tech firms are working on counter‑AI projects to scan the digital fingerprints of AI but the race is tight; creators improve their fakes just as fast as defenders improve their filters.
-
Decision Support
Armies and agencies collect vast amounts of data including hours of drone video, maintenance logs, satellite imagery, and open‑source reports. AI helps by sorting and highlighting relevant information. NATO recently adopted a system inspired by the U.S. Project Maven. It links databases from 30 member states, providing planners with a unified view. The system suggests likely enemy movements and identifies potential supply shortages. The U.S. Special Operations Command uses AI to help draft parts of its annual budget by scanning invoices and recommending reallocations. Similar AI platforms predict engine failures, schedule repairs in advance, and customize flight simulations for individual pilots' needs.
-
Law Enforcement and Border Control
Police forces and immigration officers are using AI for tasks that require constant attention. At busy airports, biometric kiosks confirm identities of travelers to make the process more efficient. Pattern-analysis software picks out travel records that hint at human trafficking or drug smuggling. In 2024, one European partnership used such tools to uncover a ring moving migrants through cargo ships. These tools can make borders safer and help catch criminals. But there are concerns too. Facial recognition sometimes fails for certain classes of people with low representation, which could lead to mistakes. Privacy is another issue. The key question is whether AI should be used to monitor everyone so closely.
The Bottom Line
AI is changing national security in many ways, offering both opportunities and risks. It can protect countries from cyber threats, make military operations more precise, and improve decision-making. But it can also spread lies, invade privacy, or make deadly errors. As AI becomes more common in security, we need to find a balance between using its power for good and controlling its dangers. This means countries must work together and set clear rules for how AI can be used. In the end, AI is a tool, and how we use it will redefine the future of security. We must be careful to use it wisely, so it helps us more than it harms us.
The post AI and National Security: The New Battlefield appeared first on Unite.AI.








































































































































![Top Features of Vision-Based Workplace Safety Tools [2025]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/379e66_7e75a4bcefe14e4fbc100abdff83bed3~mv2.jpg/v1/fit/w_1000,h_884,al_c,q_80/file.png?#)































![[The AI Show Episode 152]: ChatGPT Connectors, AI-Human Relationships, New AI Job Data, OpenAI Court-Ordered to Keep ChatGPT Logs & WPP’s Large Marketing Model](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20152%20cover.png)



































































































































































.jpg?#)











































![MindsEye From Ex-GTA Producer Is A Day-One Car Wreck [Update]](https://i.kinja-img.com/image/upload/c_fill,h_675,pg_1,q_80,w_1200/aa09b256615c422f7d1e1535d023e578.png)






















.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


















































































































![PSA: iOS 26 Spatial Scenes will work on iPhones 12 and up [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/spatial-photos-ios26.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
![Apple categorically denies Siri vaporware claims, and offers a better explanation [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/Apple-categorically-denies-Siri-vaporware-claims-and-offers-a-better-explanation.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
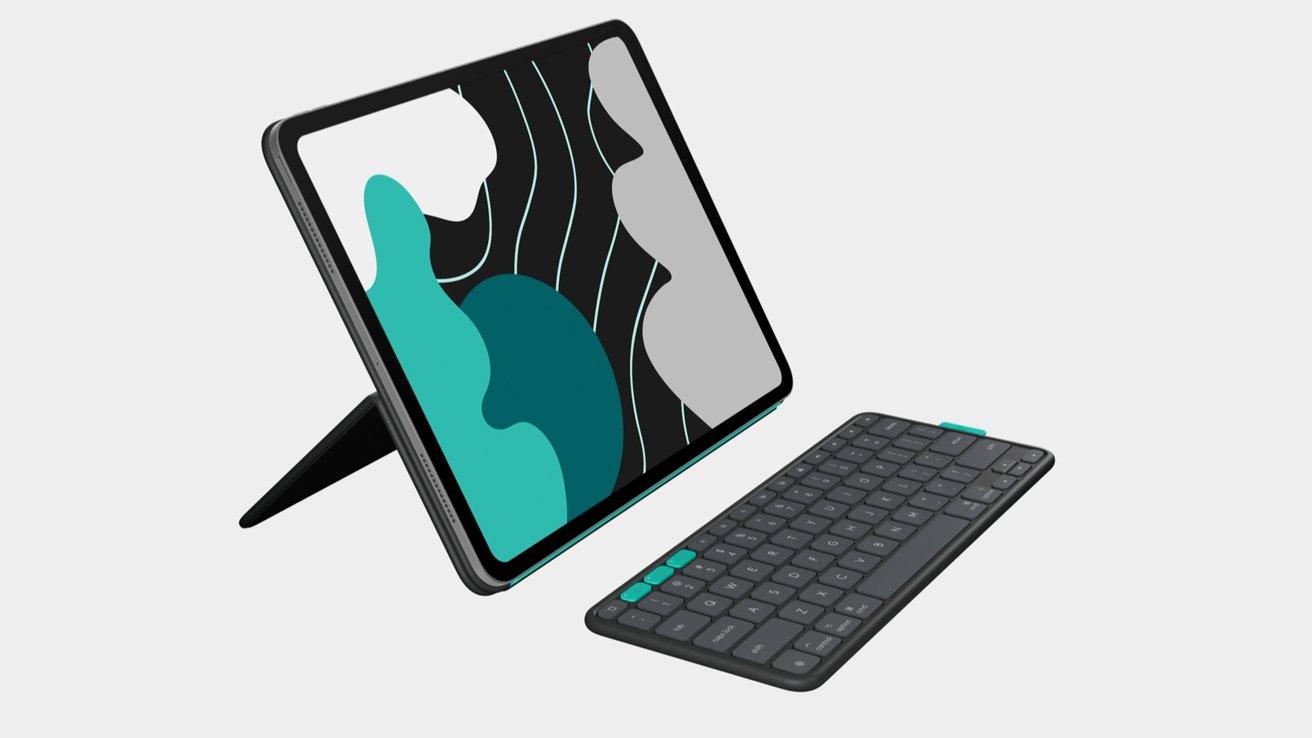
![This new iPad keyboard was purpose-built for versatility and portability – Logitech Flip Folio [Hands-on]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/Logitech-FI.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
![Nothing confirms it was almost called ‘Essential’ instead [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/nothing-essential-3.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)














![Apple Shares Teaser Trailer for 'The Lost Bus' Starring Matthew McConaughey [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97582/97582/97582-640.jpg)