Understanding DNS: The Internet's Phone Book and Why It's Critical for Web Browsing
Have you ever wondered how typing a website address magically takes you to the right page? Behind the scenes, a vital system called DNS (Domain Name System) makes this possible. Think of DNS as the internet's address book — a translator that connects human-friendly URLs like www.graphitedge.com.au to the numerical IP addresses computers understand. What is DNS? DNS stands for Domain Name System. It's essentially a network of servers that translate domain names (like graphitedge.com.au) into IP (Internet Protocol) addresses, which are strings of numbers that identify devices on a network. For example, the IP address for a website might look like 192.168.1.1 or, in modern cases, a longer string like 2606:4700:4700::1111 (IPv6). Why Do We Need DNS? DNS solves a fundamental problem of accessibility. While computers rely on IP addresses to locate each other on the internet, these addresses are difficult for humans to remember. Without DNS, you'd need to memorize complex number sequences for every website you want to visit. DNS acts as an intermediary, allowing us to use readable domain names while computers handle the technical details in the background. How Does DNS Work? The process of resolving a domain name involves several steps: You Type a URL into Your Browser When you enter www.graphitedge.com.au, your browser first checks if it already knows the IP address (this is called caching).[rest of the content remains the same] Querying a Recursive Resolver If your browser doesn't have the IP address cached, it sends a request to a DNS resolver, typically provided by your ISP or services like Google Public DNS or Cloudflare. Contacting the Root Servers The resolver asks one of the 13 sets of root servers worldwide, which direct it to the next step. Asking the TLD Servers TLD servers manage domain extensions like .com, .org, or .au. For www.graphitedge.com.au, the resolver contacts the .au TLD server. Getting the Final Answer The authoritative server for graphitedge.com.au provides the IP address, which is then sent back to your browser to load the website. Why Should You Care About DNS? Understanding DNS is crucial for several reasons: Performance: Using fast DNS services like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8) can improve your browsing speed. Security: Criminals can exploit DNS vulnerabilities through attacks like DNS spoofing. Secure DNS services, such as DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH), help protect against these threats. Reliability: When DNS servers fail, you may experience website outages. Having backup DNS providers can help mitigate this risk. Privacy: DNS queries can reveal your browsing history, even in incognito mode. Privacy-focused DNS services ensure your data isn't logged or shared. What Happens When DNS Fails? When DNS services go down, several critical problems occur: Browsers can't translate domain names into IP addresses Email services stop working properly Web applications become unreachable Only direct IP address access would work (if you know them) Best Practices for DNS Management Use reliable DNS providers Configure backup DNS servers Implement DNS caching Keep local DNS records for critical services Monitor DNS health regularly Conclusion DNS plays an indispensable role in web browsing, acting as the backbone of the internet's navigation system. By understanding its basics, you can make informed choices about your online security, privacy, and performance. Just as you wouldn't want to memorize phone numbers for every person you know, DNS ensures you don't have to memorize IP addresses for every website you visit. This article was originally published on Graphitedge, where we demystify web development concepts with clear, practical explanations. What's your experience with DNS? Have you ever encountered DNS-related issues, or do you use any alternative DNS providers? Share your stories and let's learn from each other's experiences in the comments below! Want more tutorials that break down web concepts into clear, practical explanations? Visit us at Graphitedge.
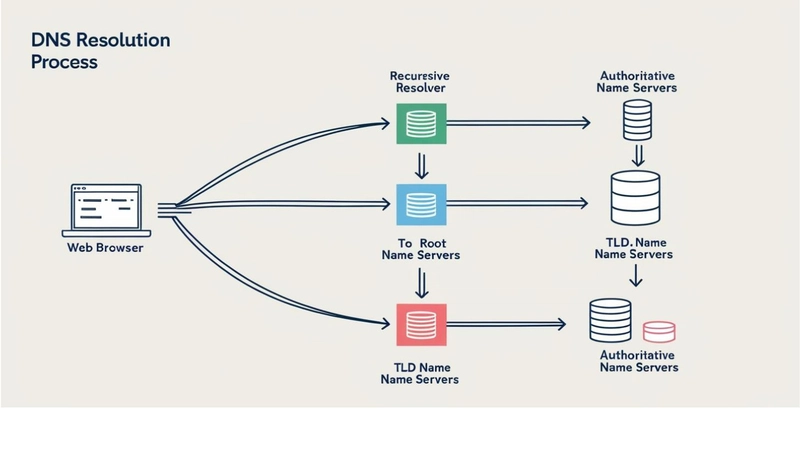
Have you ever wondered how typing a website address magically takes you to the right page? Behind the scenes, a vital system called DNS (Domain Name System) makes this possible. Think of DNS as the internet's address book — a translator that connects human-friendly URLs like www.graphitedge.com.au to the numerical IP addresses computers understand.
What is DNS?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It's essentially a network of servers that translate domain names (like graphitedge.com.au) into IP (Internet Protocol) addresses, which are strings of numbers that identify devices on a network. For example, the IP address for a website might look like 192.168.1.1 or, in modern cases, a longer string like 2606:4700:4700::1111 (IPv6).
Why Do We Need DNS?
DNS solves a fundamental problem of accessibility. While computers rely on IP addresses to locate each other on the internet, these addresses are difficult for humans to remember. Without DNS, you'd need to memorize complex number sequences for every website you want to visit. DNS acts as an intermediary, allowing us to use readable domain names while computers handle the technical details in the background.
How Does DNS Work?
The process of resolving a domain name involves several steps:
- You Type a URL into Your Browser
-
When you enter
www.graphitedge.com.au, your browser first checks if it already knows the IP address (this is called caching).[rest of the content remains the same]- Querying a Recursive Resolver
-
If your browser doesn't have the IP address cached, it sends a request to a DNS resolver, typically provided by your ISP or services like Google Public DNS or Cloudflare.
- Contacting the Root Servers
-
The resolver asks one of the 13 sets of root servers worldwide, which direct it to the next step.
- Asking the TLD Servers
-
TLD servers manage domain extensions like
.com,.org, or.au. Forwww.graphitedge.com.au, the resolver contacts the.auTLD server.- Getting the Final Answer
The authoritative server for
graphitedge.com.auprovides the IP address, which is then sent back to your browser to load the website.
Why Should You Care About DNS?
Understanding DNS is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance: Using fast DNS services like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8) can improve your browsing speed.
- Security: Criminals can exploit DNS vulnerabilities through attacks like DNS spoofing. Secure DNS services, such as DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH), help protect against these threats.
- Reliability: When DNS servers fail, you may experience website outages. Having backup DNS providers can help mitigate this risk.
- Privacy: DNS queries can reveal your browsing history, even in incognito mode. Privacy-focused DNS services ensure your data isn't logged or shared.
What Happens When DNS Fails?
When DNS services go down, several critical problems occur:
- Browsers can't translate domain names into IP addresses
- Email services stop working properly
- Web applications become unreachable
- Only direct IP address access would work (if you know them)
Best Practices for DNS Management
- Use reliable DNS providers
- Configure backup DNS servers
- Implement DNS caching
- Keep local DNS records for critical services
- Monitor DNS health regularly
Conclusion
DNS plays an indispensable role in web browsing, acting as the backbone of the internet's navigation system. By understanding its basics, you can make informed choices about your online security, privacy, and performance. Just as you wouldn't want to memorize phone numbers for every person you know, DNS ensures you don't have to memorize IP addresses for every website you visit.
This article was originally published on Graphitedge, where we demystify web development concepts with clear, practical explanations.
What's your experience with DNS? Have you ever encountered DNS-related issues, or do you use any alternative DNS providers? Share your stories and let's learn from each other's experiences in the comments below!
Want more tutorials that break down web concepts into clear, practical explanations? Visit us at Graphitedge.










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)
































































































































































































































































_incamerastock_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)


























































































![Nothing Phone (3) has a 50MP ‘periscope’ telephoto lens – here are the first samples [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/nothing-phone-3-telephoto.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)