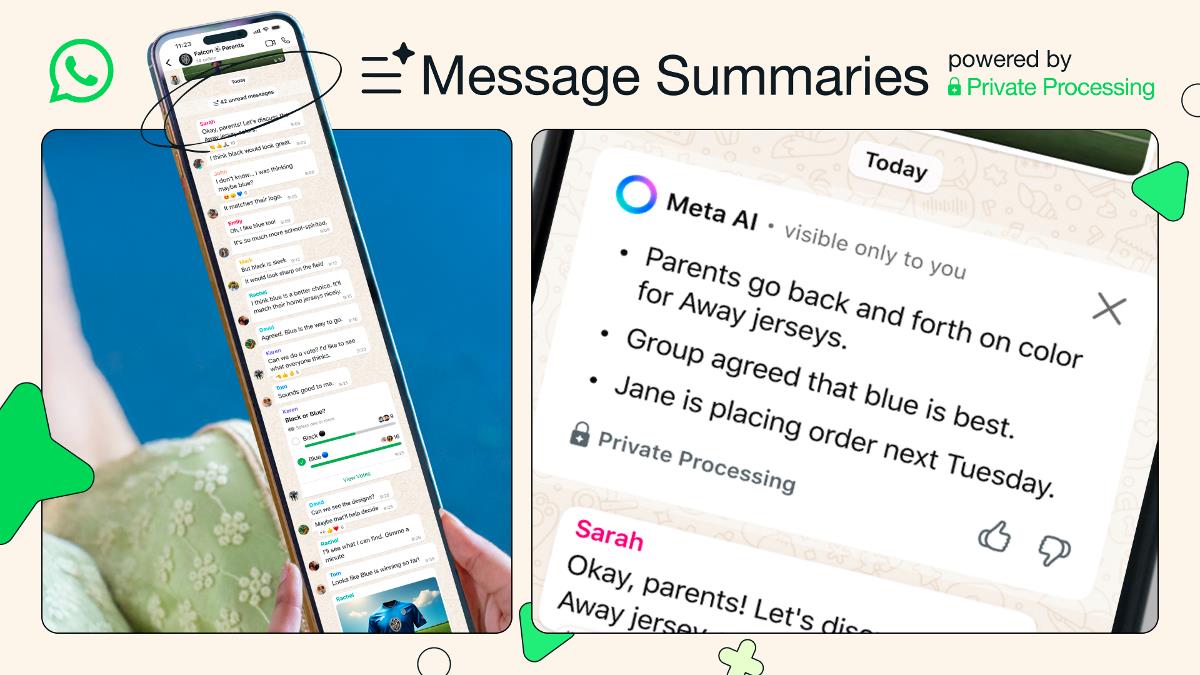
Smart Indulgence: Why Dark Chocolate is the Ultimate Dessert Upgrade
In the world of desserts, chocolate reigns supreme. But not all chocolate is created equal. While milk chocolate and sugary confections dominate the dessert tables, dark chocolate has quietly risen to prominence as a healthier, smarter swap—especially for those post-meal sweet cravings. With its rich flavor, lower sugar content, and surprising array of health benefits, dark chocolate is no longer just a treat; it's a strategic choice for both the palate and the body. So why is dark chocolate the superior pick for post-meal indulgence? Let's unwrap the facts. The Science Behind the Sweet Dark chocolate, especially varieties containing at least 70% cocoa, is loaded with nutrients and powerful antioxidants. Unlike milk chocolate, which often contains more sugar, milk solids, and added fats, dark chocolate preserves more of the cocoa bean's natural properties. This makes it rich in flavonoids—a class of compounds known for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. These flavonoids, particularly epicatechin, have been shown to improve vascular function, lower blood pressure, and support heart health. According to research published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition, moderate consumption of high-cocoa dark chocolate can enhance endothelial function (the performance of the inner lining of blood vessels), leading to better circulation and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. A Better Blood Sugar Response After a meal, reaching for a sugary dessert can send blood sugar levels on a rollercoaster ride. While it may provide a temporary high, it often ends with a crash in energy and cravings for more sugar. Dark chocolate, on the other hand, has a lower glycemic index and contains less added sugar. This means it has a gentler effect on blood glucose levels, helping to prevent spikes and crashes that can contribute to fatigue, mood swings, and long-term metabolic issues. In fact, studies have shown that dark chocolate may help improve insulin sensitivity, which plays a critical role in blood sugar regulation. For those managing type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance, swapping out traditional sweets for a square of dark chocolate could be a significant step toward better metabolic health. Satiety and Mindful Eating Another advantage of dark chocolate is its ability to promote satiety. Thanks to its rich, intense flavor, even a small piece can feel satisfying. Unlike sugary desserts that may tempt you to overindulge, dark chocolate encourages slower, more mindful eating. Its dense texture and slightly bitter edge trigger different taste receptors and promote a more thoughtful experience, often leading to less consumption overall. As a result, people are less likely to overeat, which is crucial for weight management and avoiding the habit of unnecessary snacking post-meal. Mood Enhancement Without the Crash We all know the comforting feeling of biting into something sweet after a stressful day. While milk chocolate and desserts can offer a temporary mood lift, their high sugar content can contribute to anxiety, irritability, and even depressive symptoms when consumed in excess. Dark chocolate, however, stimulates the production of endorphins—our body’s natural “feel good” chemicals—without overloading the system with sugar. It also contains small amounts of theobromine and caffeine, providing a gentle mental boost and helping to reduce fatigue without the jittery aftermath associated with stronger stimulants. Dark chocolate is also a source of magnesium, a mineral linked to improved mood, reduced anxiety, and better sleep. For people experiencing stress or hormonal changes (such as during PMS), this mineral-rich treat can be especially helpful. A Nutritional Edge Beyond antioxidants and mood-boosting compounds, dark chocolate is packed with nutrients like iron, copper, magnesium, and manganese. These micronutrients support everything from oxygen transport to bone health and immune function. Here’s a quick look at what a standard 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of 70–85% dark chocolate provides: Iron: 19% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) Magnesium: 16% of the RDI Copper: 25% of the RDI Manganese: 27% of the RDI Plus: small amounts of potassium, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium Compare that to a frosted cupcake or a sugary donut, and dark chocolate clearly offers more than just empty calories. Environmentally and Ethically Conscious Another reason to make the dark chocolate switch? It can be the more ethical and environmentally sustainable choice. Many high-quality dark chocolate brands now prioritize fair trade practices, organic farming, and sustainable sourcing methods. Choosing these brands helps support cocoa farmers and reduce environmental harm, making your dessert both delicious and socially responsible. Look for certifications like Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or USDA Organic when shopping for dark chocolate to ensure you're maki

In the world of desserts, chocolate reigns supreme. But not all chocolate is created equal. While milk chocolate and sugary confections dominate the dessert tables, dark chocolate has quietly risen to prominence as a healthier, smarter swap—especially for those post-meal sweet cravings. With its rich flavor, lower sugar content, and surprising array of health benefits, dark chocolate is no longer just a treat; it's a strategic choice for both the palate and the body.
So why is dark chocolate the superior pick for post-meal indulgence? Let's unwrap the facts.
The Science Behind the Sweet
Dark chocolate, especially varieties containing at least 70% cocoa, is loaded with nutrients and powerful antioxidants. Unlike milk chocolate, which often contains more sugar, milk solids, and added fats, dark chocolate preserves more of the cocoa bean's natural properties. This makes it rich in flavonoids—a class of compounds known for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
These flavonoids, particularly epicatechin, have been shown to improve vascular function, lower blood pressure, and support heart health. According to research published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition, moderate consumption of high-cocoa dark chocolate can enhance endothelial function (the performance of the inner lining of blood vessels), leading to better circulation and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
A Better Blood Sugar Response
After a meal, reaching for a sugary dessert can send blood sugar levels on a rollercoaster ride. While it may provide a temporary high, it often ends with a crash in energy and cravings for more sugar. Dark chocolate, on the other hand, has a lower glycemic index and contains less added sugar. This means it has a gentler effect on blood glucose levels, helping to prevent spikes and crashes that can contribute to fatigue, mood swings, and long-term metabolic issues.
In fact, studies have shown that dark chocolate may help improve insulin sensitivity, which plays a critical role in blood sugar regulation. For those managing type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance, swapping out traditional sweets for a square of dark chocolate could be a significant step toward better metabolic health.
Satiety and Mindful Eating
Another advantage of dark chocolate is its ability to promote satiety. Thanks to its rich, intense flavor, even a small piece can feel satisfying. Unlike sugary desserts that may tempt you to overindulge, dark chocolate encourages slower, more mindful eating.
Its dense texture and slightly bitter edge trigger different taste receptors and promote a more thoughtful experience, often leading to less consumption overall. As a result, people are less likely to overeat, which is crucial for weight management and avoiding the habit of unnecessary snacking post-meal.
Mood Enhancement Without the Crash
We all know the comforting feeling of biting into something sweet after a stressful day. While milk chocolate and desserts can offer a temporary mood lift, their high sugar content can contribute to anxiety, irritability, and even depressive symptoms when consumed in excess.
Dark chocolate, however, stimulates the production of endorphins—our body’s natural “feel good” chemicals—without overloading the system with sugar. It also contains small amounts of theobromine and caffeine, providing a gentle mental boost and helping to reduce fatigue without the jittery aftermath associated with stronger stimulants.
Dark chocolate is also a source of magnesium, a mineral linked to improved mood, reduced anxiety, and better sleep. For people experiencing stress or hormonal changes (such as during PMS), this mineral-rich treat can be especially helpful.
A Nutritional Edge
Beyond antioxidants and mood-boosting compounds, dark chocolate is packed with nutrients like iron, copper, magnesium, and manganese. These micronutrients support everything from oxygen transport to bone health and immune function.
Here’s a quick look at what a standard 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of 70–85% dark chocolate provides:
Iron: 19% of the recommended daily intake (RDI)
Magnesium: 16% of the RDI
Copper: 25% of the RDI
Manganese: 27% of the RDI
Plus: small amounts of potassium, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium
Compare that to a frosted cupcake or a sugary donut, and dark chocolate clearly offers more than just empty calories.
Environmentally and Ethically Conscious
Another reason to make the dark chocolate switch? It can be the more ethical and environmentally sustainable choice. Many high-quality dark chocolate brands now prioritize fair trade practices, organic farming, and sustainable sourcing methods. Choosing these brands helps support cocoa farmers and reduce environmental harm, making your dessert both delicious and socially responsible.
Look for certifications like Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or USDA Organic when shopping for dark chocolate to ensure you're making an ethical choice.
How to Make the Switch
If you’re used to milk chocolate or traditional desserts, transitioning to dark chocolate can take a little adjustment. Start by choosing a dark chocolate that contains around 60–70% cocoa and work your way up as your palate adapts.
Here are some practical tips for integrating dark chocolate into your post-meal routine:
Portion Control: Break off one or two squares after dinner—just enough to satisfy your craving without overdoing it.
Pair It Well: Enjoy with a handful of almonds, a glass of red wine, or fresh berries for a balanced and decadent finish.
Choose Wisely: Read labels and avoid brands with excessive added sugars, artificial flavors, or hydrogenated oils.
Mindful Eating: Let the chocolate melt slowly on your tongue. Appreciate the complexity of flavor—bitter, fruity, earthy notes—that high-quality dark chocolate offers.
Final Thoughts
Dark chocolate proves that smart indulgence doesn’t mean sacrificing pleasure. By choosing this rich, satisfying treat over traditional sweets, you’re not just feeding a craving—you’re supporting your heart, your brain, and your overall wellness.
So the next time you finish a meal and reach for something sweet, consider swapping the cookie or candy bar for a few squares of dark chocolate. It’s a small change that delivers big benefits—making every bite a win for your health and your taste buds.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)































































































































































































































































_incamerastock_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)



























































































![Senators reintroduce App Store bill to rein in ‘gatekeeper power in the app economy’ [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/app-store-senate.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)