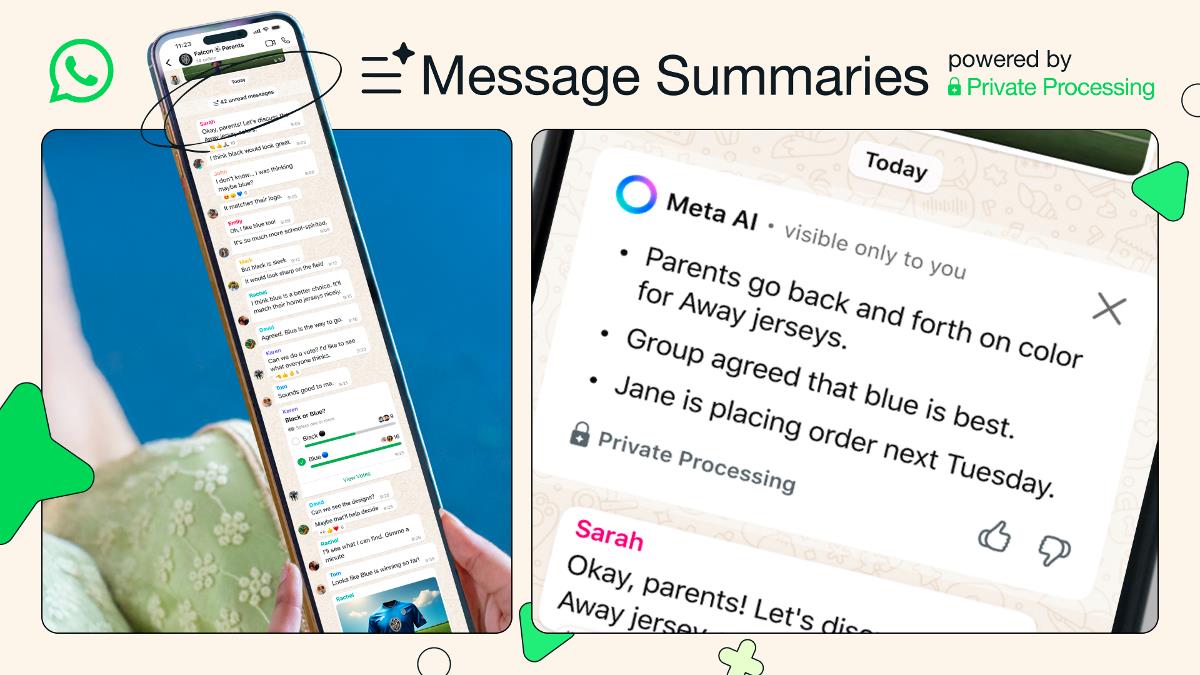
Mastering Cloud Costs: A Practical Guide to Sustainable Cloud Spending
Mastering Cloud Costs: A Practical Guide to Sustainable Cloud Spending # Mastering Cloud Costs: A Practical Guide to Sustainable Cloud Spending Cloud computing offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability, but managing costs can be a significant challenge. Uncontrolled spending can quickly spiral out of hand due to factors like idle resources, over-provisioning, and inefficient data transfers. This post provides a practical, step-by-step approach to optimizing your cloud costs across AWS, Azure, and GCP, regardless of your organization's size. The key principles remain consistent: visibility, accountability, and efficiency. Why Cloud Cost Optimization Matters Ignoring cloud costs can lead to unpleasant surprises. Proactive cost optimization offers several key advantages: Avoid Unexpected Bills: Instead of reacting to alarming invoices, stay ahead of the curve and prevent unexpected spikes in spending. Maximize ROI: Optimize your cloud usage to extract maximum value from your investment. Enable FinOps: Foster collaboration between engineering, finance, and operations teams for a unified approach to cost management. Promote Sustainable Operations: Cost efficiency often aligns with energy efficiency, contributing to a more sustainable IT footprint. A Step-by-Step Approach to Cloud Cost Optimization Now, let's dive into the practical steps you can take to optimize your cloud spending. Gain Visibility Into Your Spending: Before you can optimize, you need to understand where your money is going. * **AWS:** Utilize AWS Cost Explorer, AWS Budgets, and AWS Cost and Usage Reports. * **Azure:** Leverage Azure Cost Management + Billing. * **GCP:** Use Cloud Billing Reports and GCP Cost Table Reports. **Pro Tip:** Set up automated alerts (using AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or GCP Monitoring) to receive real-time notifications about unusual spending patterns. Think of these alerts as your early warning system. Right-Size Your Resources: Over-provisioning is a major cost culprit. Let's address this: * Use auto-scaling groups for EC2/VM instances to dynamically adjust resources based on demand. Imagine it as having a flexible workforce—you only pay for the employees you need at any given time. * Regularly monitor CPU, memory, and disk usage to identify underutilized resources. * Use optimization tools to pinpoint underutilized instances: * `aws compute-optimizer` (AWS) * Azure Advisor (Azure) * GCP Recommender (GCP) **Automation Tip:** Integrate auto-remediation scripts or utilize Terraform with policies that enforce right-sizing during resource provisioning. Automation is your friend here! Leverage Reserved Instances and Savings Plans: Committing to longer-term contracts can significantly reduce your costs. * Instead of paying on-demand prices, consider 1- or 3-year commitments. * **AWS:** Savings Plans, Reserved Instances * **Azure:** Reserved Virtual Machine Instances * **GCP:** Committed Use Discounts These plans can offer savings of 30–72% compared to on-demand pricing. It's like getting a bulk discount at the grocery store! Eliminate Idle and "Zombie" Resources: These often-overlooked resources silently drain your budget: * Unattached EBS volumes (AWS) * Idle IP addresses (AWS, GCP) * Stopped VMs with persistent disks (Azure, GCP) * Forgotten Load Balancers or Elastic IPs * Stale snapshots or backups **Cleanup Automation Tools:** * `aws-nuke` (AWS) * `gcloud cleanup` (GCP) * Azure CLI scripts with `az resource list` (Azure) Optimize Storage and Data Transfer: Moving data across regions or between providers can be surprisingly expensive. * Use CloudFront (AWS), Azure CDN, or GCP Cloud CDN to cache frequently accessed content, reducing the need for repeated data transfers. * Move infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage tiers like S3 Glacier (AWS), Azure Archive, or Nearline Storage (GCP). * Implement object lifecycle rules to automatically transition or delete stale data. This is like decluttering your digital attic! * [AWS S3 Lifecycle Docs](link_to_aws_s3_lifecycle_docs) Consolidate and Modernize Architectures: Refining your architecture can lead to substantial cost savings. * Adopt serverless computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Cloud Functions) where appropriate. * Containerize applications with Kubernetes or managed container services (ECS/EKS/GKE) for improved resource utilization. * Migrate to managed databases (RDS, CosmosDB, Cloud SQL) to reduce operational overhead. **Bonus Tools:** * KubeCost: Analyze Kubernetes cluster costs. * Infracost: Estimate Terraform infrastructure costs. Implement Cost Governance Policies: Establish clear policies to maintain control over spending. * **Use Resource Tags:** Enforce tagging conventions to track costs by environment, team, and project. * **Create Budgets per Team/Project:** Set spending limits to prevent overruns. * *

Mastering Cloud Costs: A Practical Guide to Sustainable Cloud Spending
# Mastering Cloud Costs: A Practical Guide to Sustainable Cloud Spending
Cloud computing offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability, but managing costs can be a significant challenge. Uncontrolled spending can quickly spiral out of hand due to factors like idle resources, over-provisioning, and inefficient data transfers. This post provides a practical, step-by-step approach to optimizing your cloud costs across AWS, Azure, and GCP, regardless of your organization's size. The key principles remain consistent: visibility, accountability, and efficiency.
Why Cloud Cost Optimization Matters
Ignoring cloud costs can lead to unpleasant surprises. Proactive cost optimization offers several key advantages:
- Avoid Unexpected Bills: Instead of reacting to alarming invoices, stay ahead of the curve and prevent unexpected spikes in spending.
- Maximize ROI: Optimize your cloud usage to extract maximum value from your investment.
- Enable FinOps: Foster collaboration between engineering, finance, and operations teams for a unified approach to cost management.
- Promote Sustainable Operations: Cost efficiency often aligns with energy efficiency, contributing to a more sustainable IT footprint.
A Step-by-Step Approach to Cloud Cost Optimization
Now, let's dive into the practical steps you can take to optimize your cloud spending.
- Gain Visibility Into Your Spending: Before you can optimize, you need to understand where your money is going.
* **AWS:** Utilize AWS Cost Explorer, AWS Budgets, and AWS Cost and Usage Reports.
* **Azure:** Leverage Azure Cost Management + Billing.
* **GCP:** Use Cloud Billing Reports and GCP Cost Table Reports.
**Pro Tip:** Set up automated alerts (using AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or GCP Monitoring) to receive real-time notifications about unusual spending patterns. Think of these alerts as your early warning system.
- Right-Size Your Resources: Over-provisioning is a major cost culprit. Let's address this:
* Use auto-scaling groups for EC2/VM instances to dynamically adjust resources based on demand. Imagine it as having a flexible workforce—you only pay for the employees you need at any given time.
* Regularly monitor CPU, memory, and disk usage to identify underutilized resources.
* Use optimization tools to pinpoint underutilized instances:
* `aws compute-optimizer` (AWS)
* Azure Advisor (Azure)
* GCP Recommender (GCP)
**Automation Tip:** Integrate auto-remediation scripts or utilize Terraform with policies that enforce right-sizing during resource provisioning. Automation is your friend here!
- Leverage Reserved Instances and Savings Plans: Committing to longer-term contracts can significantly reduce your costs.
* Instead of paying on-demand prices, consider 1- or 3-year commitments.
* **AWS:** Savings Plans, Reserved Instances
* **Azure:** Reserved Virtual Machine Instances
* **GCP:** Committed Use Discounts
These plans can offer savings of 30–72% compared to on-demand pricing. It's like getting a bulk discount at the grocery store!
- Eliminate Idle and "Zombie" Resources: These often-overlooked resources silently drain your budget:
* Unattached EBS volumes (AWS)
* Idle IP addresses (AWS, GCP)
* Stopped VMs with persistent disks (Azure, GCP)
* Forgotten Load Balancers or Elastic IPs
* Stale snapshots or backups
**Cleanup Automation Tools:**
* `aws-nuke` (AWS)
* `gcloud cleanup` (GCP)
* Azure CLI scripts with `az resource list` (Azure)
- Optimize Storage and Data Transfer: Moving data across regions or between providers can be surprisingly expensive.
* Use CloudFront (AWS), Azure CDN, or GCP Cloud CDN to cache frequently accessed content, reducing the need for repeated data transfers.
* Move infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage tiers like S3 Glacier (AWS), Azure Archive, or Nearline Storage (GCP).
* Implement object lifecycle rules to automatically transition or delete stale data. This is like decluttering your digital attic!
* [AWS S3 Lifecycle Docs](link_to_aws_s3_lifecycle_docs)
- Consolidate and Modernize Architectures: Refining your architecture can lead to substantial cost savings.
* Adopt serverless computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Cloud Functions) where appropriate.
* Containerize applications with Kubernetes or managed container services (ECS/EKS/GKE) for improved resource utilization.
* Migrate to managed databases (RDS, CosmosDB, Cloud SQL) to reduce operational overhead.
**Bonus Tools:**
* KubeCost: Analyze Kubernetes cluster costs.
* Infracost: Estimate Terraform infrastructure costs.
- Implement Cost Governance Policies: Establish clear policies to maintain control over spending.
* **Use Resource Tags:** Enforce tagging conventions to track costs by environment, team, and project.
* **Create Budgets per Team/Project:** Set spending limits to prevent overruns.
* **Enable Chargeback/Showback Models:** Improve accountability by assigning costs to specific teams or projects.
* **Schedule Resources:** Use scheduling tools (Instance Scheduler (AWS), Logic Apps (Azure), Cloud Scheduler (GCP)) to shut down non-production environments during off-peak hours.
Example: Deep Dive Into CloudWatch Costs
Let's examine how to analyze AWS CloudWatch costs using the AWS CLI:
aws ce get-cost-and-usage \
--time-period Start=2025-04-01,End=$(date +%F) \
--granularity MONTHLY \
--metrics "UnblendedCost" \
--filter '{
"Dimensions": {
"Key": "SERVICE",
"Values": ["AmazonCloudWatch"]
}
}' \
--group-by '[{"Type": "DIMENSION", "Key": "USAGE_TYPE"}]' \
--region ap-south-1
This command reveals specific CloudWatch usage types (e.g., APN1-CW:Requests, APN2-CW:Requests) contributing to costs. Optimization steps might include reducing custom metrics, deleting unused dashboards, aggregating metrics to longer intervals, and using embedded metrics format instead of verbose JSON logs.
Additional Resources
- AWS Well-Architected Cost Optimization Pillar
- GCP Cost Optimization Best Practices
- Azure Cost Optimization Techniques
Conclusion
Cloud cost optimization is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. By combining diligent monitoring, automation, and robust governance, you can significantly reduce cloud spending and improve the efficiency of your systems. Embrace cost awareness as a core principle within your DevOps and SRE teams. Start with visibility, implement small changes, and iterate continuously towards a more cost-effective cloud strategy. Remember, small consistent improvements add up to big savings!











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)































































































































































































































































_incamerastock_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)



























































































![Senators reintroduce App Store bill to rein in ‘gatekeeper power in the app economy’ [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/app-store-senate.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)