Hackers Exploit ComfyUI 700+ AI Image Generation Servers to Deploy Malware
A sophisticated malware campaign targeting ComfyUI, a popular AI image generation framework, has successfully compromised at least 695 servers worldwide, security researchers have discovered. The attack represents a significant escalation in threats against AI infrastructure, exploiting vulnerabilities in ComfyUI to deploy a lightweight but highly persistent backdoor dubbed “Pickai.” The campaign first emerged in February […] The post Hackers Exploit ComfyUI 700+ AI Image Generation Servers to Deploy Malware appeared first on Cyber Security News.

A sophisticated malware campaign targeting ComfyUI, a popular AI image generation framework, has successfully compromised at least 695 servers worldwide, security researchers have discovered.
The attack represents a significant escalation in threats against AI infrastructure, exploiting vulnerabilities in ComfyUI to deploy a lightweight but highly persistent backdoor dubbed “Pickai.”
The campaign first emerged in February 2025 when an early version of the malware was uploaded to VirusTotal from Hong Kong, but the full scope of the operation became apparent in March when suspicious activity was detected across multiple geographic regions.
The attackers have demonstrated remarkable persistence and sophistication, utilizing compromised infrastructure including the official website of Rubick.ai, a commercial AI platform serving over 200 major retail brands including Amazon, Myntra, and Hudson Bay.
XLab analysts identified the malware through their Cyber Threat Insight and Analysis System on March 17, 2025, when they flagged suspicious behavior from IP address 185.189.149.151.
The researchers discovered that attackers were leveraging ComfyUI vulnerabilities to distribute ELF executables disguised as configuration files, including config.json, tmux.conf, and vim.json.
The malware’s name “Pickai” reflects its core functionality of stealing sensitive AI-related data, operating as a digital pickpocket within AI development environments.
The global impact of this campaign extends far beyond individual server compromises, with infected systems concentrated primarily in Germany, the United States, and China.
Security researchers obtained partial visibility into the botnet by registering an unclaimed command-and-control domain, revealing traffic spikes exceeding 400 daily active installations during periods when primary C2 servers failed.
Advanced Persistence Mechanisms Ensure Long-Term Compromise
The Pickai malware employs an unusually robust persistence strategy that sets it apart from conventional backdoors.
When operating with root privileges, the malware creates five separate copies of itself across different system directories, each with synchronized modification timestamps matching /bin/sh to blend with legitimate system files.
These copies are strategically placed in locations such as /usr/bin/auditlogd, /usr/sbin/hwstats, /sbin/dmesglog, /var/lib/autoupd, and /var/run/healthmon, masquerading as legitimate system services.
.webp)
Each copy implements dual persistence mechanisms using both init.d and system service frameworks, creating a total of ten different services for root-level infections.
The malware deliberately appends random data to each file copy, ensuring that hash-based detection systems encounter different MD5 signatures for what is essentially the same malicious payload.
For non-root users, Pickai maintains five persistence points using systemd services in user-space directories, demonstrating its adaptability across different privilege levels.
This redundant approach means that incomplete removal attempts will trigger automatic reinfection, making the malware particularly challenging to eradicate from compromised systems.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams! - Interact with malware in the sandbox and find related IOCs. - Request 14-day free trial
The post Hackers Exploit ComfyUI 700+ AI Image Generation Servers to Deploy Malware appeared first on Cyber Security News.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 154]: AI Answers: The Future of AI Agents at Work, Building an AI Roadmap, Choosing the Right Tools, & Responsible AI Use](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20154%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 153]: OpenAI Releases o3-Pro, Disney Sues Midjourney, Altman: “Gentle Singularity” Is Here, AI and Jobs & News Sites Getting Crushed by AI Search](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20153%20cover.png)































































































































































































![GrandChase tier list of the best characters available [June 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33057-1637756796/grandchase-ios-android-3rd-anniversary.jpg?#)














































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





















_Frank_Peters_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

































































































![Samsung’s Galaxy Z Fold 7 looks positively svelte in dummy hands-on [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/Worlds-First-Look-Hands-On-with-the-Galaxy-Z-Fold-7-dummy-1-1-screenshot.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)












![Apple Weighs Acquisition of AI Startup Perplexity in Internal Talks [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97674/97674/97674-640.jpg)
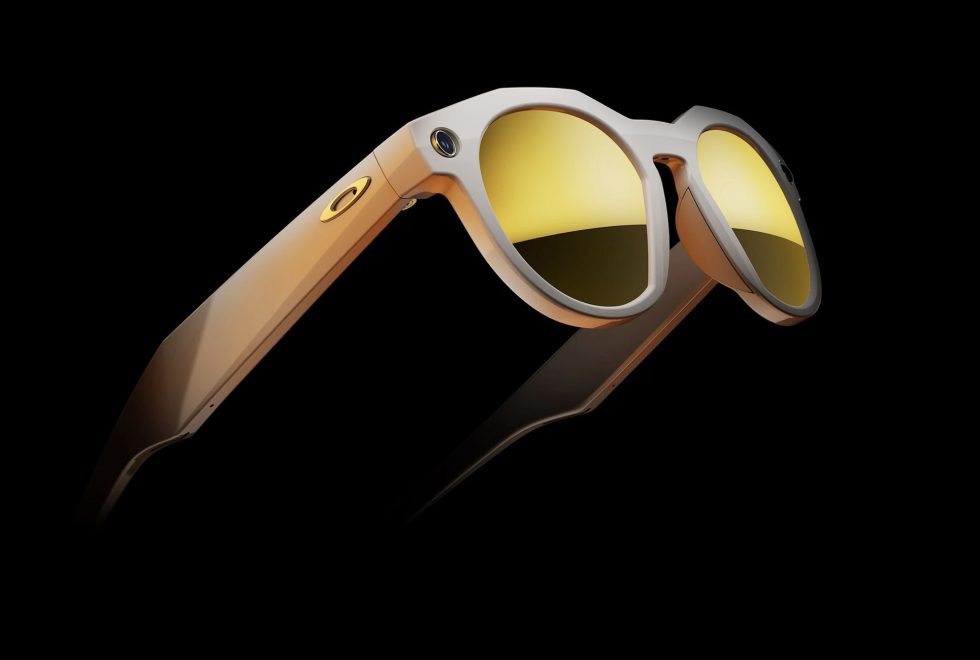
![Oakley and Meta Launch Smart Glasses for Athletes With AI, 3K Camera, More [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97665/97665/97665-640.jpg)

![How to Get Your Parents to Buy You a Mac, According to Apple [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97671/97671/97671-640.jpg)

















![New accessibility settings announced for Steam Big Picture Mode and SteamOS [Beta]](https://www.ghacks.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/New-accessibility-settings-announced-for-Steam-Big-Picture-Mode-and-SteamOS.jpg)