New Phishing Attack Abusing Blob URLs to Bypass SEGs and Evade Analysis
Cybersecurity experts have identified a sophisticated phishing technique that exploits blob URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) to evade detection by Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) and security analysis tools. This emerging attack method leverages the unique properties of blob URIs, which are designed to display temporary data that can only be accessed by the browser that generated […] The post New Phishing Attack Abusing Blob URLs to Bypass SEGs and Evade Analysis appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Cybersecurity experts have identified a sophisticated phishing technique that exploits blob URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) to evade detection by Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) and security analysis tools.
This emerging attack method leverages the unique properties of blob URIs, which are designed to display temporary data that can only be accessed by the browser that generated it.
Unlike standard phishing sites that can be crawled and analyzed, blob URI-based attacks create credential harvesting pages that exist solely in the victim’s browser memory, making them nearly invisible to traditional security measures.
The attack begins with a seemingly innocuous email containing links to legitimate, allowlisted websites rather than directly to malicious domains.
This initial misdirection helps the phishing attempt bypass email security filters that typically block messages with suspicious links.
Upon reaching these intermediary pages, victims are then redirected through a series of steps that ultimately generate a local blob URI containing the actual phishing content.
Cofense researchers identified this technique starting in mid-2022 and have observed its growing adoption among threat actors.
According to their analysis, this method is particularly effective because the final credential phishing page exists only in the victim’s browser, leaving no external URL for security tools to scan or block.
This technical limitation creates a significant blind spot in conventional phishing detection systems.
.webp)
The infection chain follows a sophisticated multi-stage process. After the initial email bypasses the SEG, users are directed to legitimate services such as Microsoft OneDrive.
.webp)
What appears to be a standard login page or document access screen is actually a carefully crafted redirection mechanism.
When victims click to “Sign in” or “View document,” they are seamlessly directed to a threat actor-controlled HTML page that generates a blob URI locally in the victim’s browser.
.webp)
The resulting phishing page, rendered from the blob URI (typically appearing as “blob:https://domain.com/random-string” in the address bar), presents convincing login forms mimicking services like Microsoft 365 or OneDrive.
Despite existing only in the local browser memory, these pages contain hidden functionality to exfiltrate captured credentials to remote servers controlled by the attackers.
This technique represents a concerning evolution in phishing tactics, as it effectively circumvents both technological defenses and standard user awareness training that emphasizes checking URL validity before entering credentials.
Are you from the SOC and DFIR Teams? – Analyse Real time Malware Incidents with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.
The post New Phishing Attack Abusing Blob URLs to Bypass SEGs and Evade Analysis appeared first on Cyber Security News.












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)















































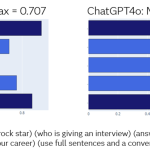
















































































































































































































_incamerastock_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)



























































































![Senators reintroduce App Store bill to rein in ‘gatekeeper power in the app economy’ [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/app-store-senate.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)