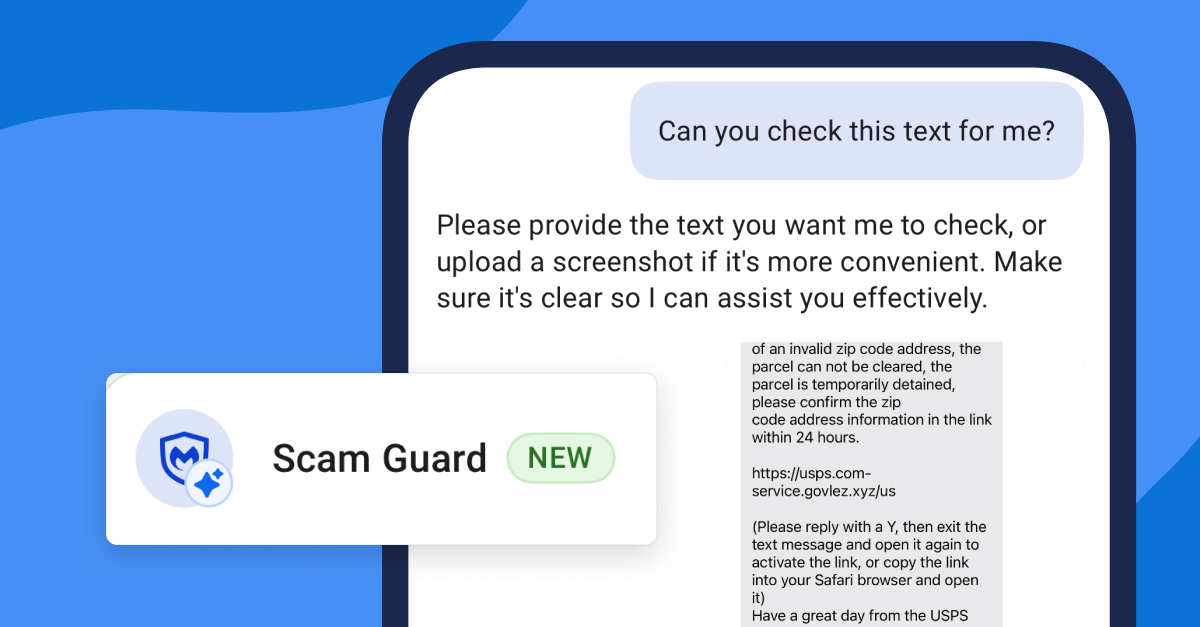
Beware of Weaponized AI Tool Installers That Infect Your Devices With Ransomware
Cybercriminals are increasingly exploiting the growing popularity of artificial intelligence tools by distributing sophisticated malware disguised as legitimate AI solution installers. This emerging threat landscape has seen malicious actors create convincing replicas of popular AI platforms, using these deceptive packages to deploy devastating ransomware and destructive malware onto unsuspecting victims’ systems. The proliferation of AI […] The post Beware of Weaponized AI Tool Installers That Infect Your Devices With Ransomware appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Cybercriminals are increasingly exploiting the growing popularity of artificial intelligence tools by distributing sophisticated malware disguised as legitimate AI solution installers.
This emerging threat landscape has seen malicious actors create convincing replicas of popular AI platforms, using these deceptive packages to deploy devastating ransomware and destructive malware onto unsuspecting victims’ systems.
The proliferation of AI across various business sectors has created an attractive attack vector for threat actors who employ sophisticated techniques including search engine optimization poisoning to manipulate search rankings.
These malicious campaigns cause fraudulent websites and download links to appear prominently in search results, effectively deceiving businesses and individuals seeking genuine AI solutions.
The attackers distribute their weaponized installers through multiple channels including Telegram, social media platforms, and professionally designed fake websites that closely mirror legitimate AI service providers.
.webp)
Cisco Talos researchers identified multiple distinct threats masquerading as AI solutions currently circulating in the wild, including the CyberLock and Lucky_Gh0$t ransomware families, along with a newly discovered destructive malware dubbed “Numero.”
.webp)
These threats specifically target industries where AI tools are particularly popular, including business-to-business sales domains and technology and marketing sectors, indicating that organizations in these verticals face heightened risk exposure.
The scope of this threat extends beyond simple file encryption, with some variants exhibiting purely destructive behavior designed to render infected systems completely unusable.
The legitimate AI tools being impersonated are widely recognized platforms with substantial user bases, making the deception particularly effective against potential victims who may lower their guard when downloading what appears to be software from trusted sources.
CyberLock Ransomware Deployment Mechanism
The CyberLock ransomware exemplifies the sophisticated technical approach employed by these AI-impersonating threats.
.webp)
The malware operates through a multi-stage deployment process that begins with a .NET executable loader containing embedded PowerShell scripts as resource files.
When victims execute the seemingly legitimate “NovaLeadsAI.exe” installer, the loader extracts and deploys the ransomware payload using the following code structure:-
Assembly executingAssembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
using (Stream manifestResourceStream = executingAssembly.GetManifestResourceStream("NovaLeadsAI.ps1"))
using (StreamReader streamReader = new StreamReader(manifestResourceStream, Encoding.UTF8))
string text4 = streamReader.ReadToEnd();The PowerShell-based ransomware immediately conceals its presence by hiding the console window through Windows API calls to GetConsoleWindow and ShowWindow functions.
CyberLock demonstrates advanced capabilities including privilege escalation, where it automatically re-executes itself with administrative rights if not already running in an elevated context.
The malware targets an extensive range of file types across logical partitions C:, D:, and E:, encrypting files using AES encryption while appending the “.Cyberlock” extension.
After completing the encryption process, CyberLock employs the built-in Windows cipher.exe utility with the “/w” option to securely wipe free disk space, effectively hindering forensic recovery efforts and eliminating traces of the original unencrypted files.
Celebrate 9 years of ANY.RUN! Unlock the full power of TI Lookup plan (100/300/600/1,000+ search requests), and your request quota will double.
The post Beware of Weaponized AI Tool Installers That Infect Your Devices With Ransomware appeared first on Cyber Security News.














































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 151]: Anthropic CEO: AI Will Destroy 50% of Entry-Level Jobs, Veo 3’s Scary Lifelike Videos, Meta Aims to Fully Automate Ads & Perplexity’s Burning Cash](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20151%20cover.png)





































































































































































































































































_Andrea_Danti_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)












































































































![Apple AI Launch in China Delayed Amid Approval Roadblocks and Trade Tensions [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97500/97500/97500-640.jpg)