Russian Hackers Leverage Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to Scaleway Object Storage
In a sophisticated cybersecurity attack uncovered this week, Russian threat actors have been observed exploiting multiple cloud service providers to deliver the notorious Lumma Stealer malware. The campaign utilizes legitimate cloud infrastructure—including Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Scaleway Object Storage, and Tigris—to host malicious content that targets privileged users across various organizations. Security experts warn this […] The post Russian Hackers Leverage Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to Scaleway Object Storage appeared first on Cyber Security News.

In a sophisticated cybersecurity attack uncovered this week, Russian threat actors have been observed exploiting multiple cloud service providers to deliver the notorious Lumma Stealer malware.
The campaign utilizes legitimate cloud infrastructure—including Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Scaleway Object Storage, and Tigris—to host malicious content that targets privileged users across various organizations.
Security experts warn this represents a growing trend of threat actors leveraging trusted cloud platforms to bypass traditional security controls.
.webp)
The attackers employ social engineering tactics that lure victims through disguised free game downloads and fake reCAPTCHA verification pages.
These deceptive elements are strategically hosted across different cloud providers, creating a distributed attack infrastructure that proves difficult to detect and mitigate.
Once users interact with these seemingly legitimate elements, they unknowingly initiate a complex infection chain that ultimately delivers the Lumma Stealer malware.
CATO Networks researchers identified the campaign through their threat intelligence operations, noting the sophisticated use of multiple cloud providers as a deliberate tactic to enhance the attack’s resilience.
“By distributing malicious components across Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Scaleway, and Tigris, the attackers create redundancy that helps them maintain persistence even if one hosting location is discovered and blocked,” explained Guile Domingo, SOC Analyst at Cato Networks.
The attack’s technical sophistication is evident in its multi-stage approach. Initial compromise begins when users encounter malicious links, often through phishing emails or compromised websites.
These links direct victims to cloud-hosted content that appears legitimate but contains hidden malicious code.
The attackers specifically target privileged users who may have access to valuable organizational data or credentials, making this campaign particularly dangerous for enterprises.
Analysis of the attack infrastructure reveals an extensive network of malicious domains and URLs spread across multiple cloud providers.
Particularly concerning is the attackers’ ability to maintain persistent access to victims’ systems through advanced techniques like DLL search order hijacking, which allows the malware to establish itself securely on infected systems.
Infection Mechanism: The Path to Compromise
The infection process begins when victims interact with either disguised free game downloads or fake reCAPTCHA verification forms.
.webp)
The game download scenario involves a seemingly legitimate software installation that secretly delivers malicious components.
The user believes they’re downloading popular gaming software, but instead receive an archive containing the Lumma Stealer malware.
.webp)
Similarly, the fake reCAPTCHA challenges hosted in Tigris Object Storage trick users into engaging with malicious content.
URLs such as “fly.storage.tigris.showing-next-go.html” and similarly structured addresses on Oracle Cloud (objectstorage.ap-seoul-1.oraclecloud.com) and Scaleway (datastream-dist.s3.pl-waw.scw.cloud) host these verification challenges that ultimately lead to malware infection.
When users interact with these elements, the system downloads a ZIP archive (identified as “DOwnl0@d Comp!3t3 L@t3st PC Setup.zip”) containing a signed executable (“setup[.]exe”).
This legitimate-appearing executable then executes the Lumma Stealer from memory, allowing it to harvest credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and other sensitive information without being detected by traditional security solutions.
The attackers further enhance their chances of success by using DLL search order hijacking via a malicious MpGear.dll file.
This technique ensures the malware loads automatically when certain legitimate applications are launched, providing persistence on infected systems and allowing continuous data exfiltration over extended periods.
Security professionals recommend implementing advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying suspicious cloud-hosted content, maintaining strict access controls for privileged users, and deploying comprehensive endpoint protection solutions to mitigate the risk posed by this and similar campaigns.
Equip your SOC team with deep threat analysis for faster response -> Get Extra














































































































































































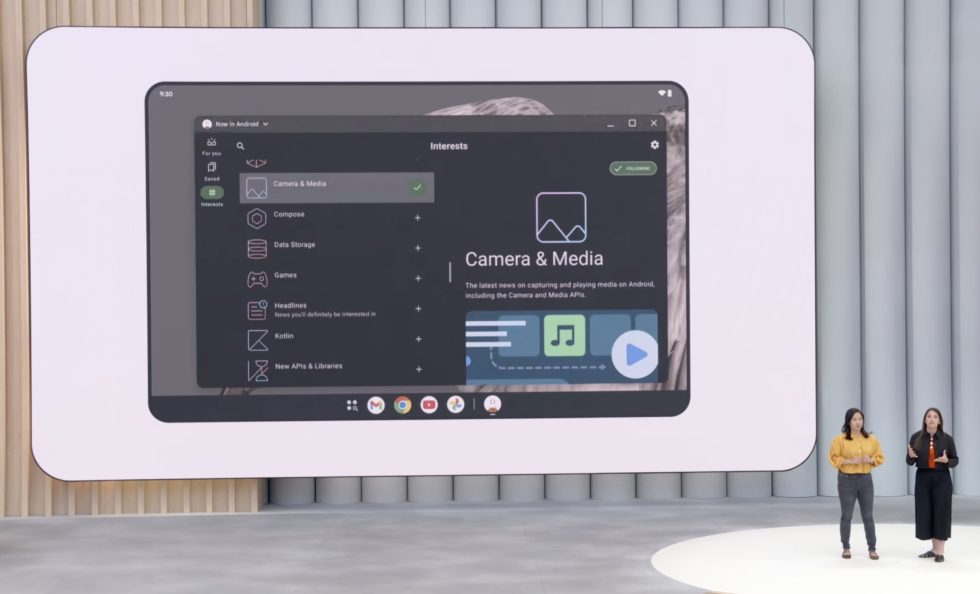
![[The AI Show Episode 148]: Microsoft’s Quiet AI Layoffs, US Copyright Office’s Bombshell AI Guidance, 2025 State of Marketing AI Report, and OpenAI Codex](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20148%20cover%20%281%29.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)





















































































































![[DEALS] Babbel Language Learning: Lifetime Subscription (All Languages) (71% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)




































































































![Borderlands 4 Boss Says 'A Real Fan' Will Pay $80 For Games [Update]](https://i.kinja-img.com/image/upload/c_fill,h_675,pg_1,q_80,w_1200/086e4654c281e40d12b833591d2c6fdc.jpg)










































_Olekcii_Mach_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)































































































![Nomad levels up its best-selling charger with new 100W slim adapter [Hands-on]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/05/100w-FI.jpg.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)



![Google just showed off Android Auto’s upcoming light theme [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/05/android-auto-light-theme-documentation-2.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Accelerates Smart Glasses for 2026, Cancels Watch With Camera [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97408/97408/97408-640.jpg)
![Jony Ive and OpenAI Working on AI Device With No Screen [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97401/97401/97401-640.jpg)

![Anthropic Unveils Claude 4 Models That Could Power Apple Xcode AI Assistant [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97407/97407/97407-640.jpg)