What is OrbitDB? The Open Source Business Model, Funding, and Community
Abstract OrbitDB is a revolutionary decentralized database built atop IPFS that reshapes data storage in blockchain ecosystems. In this post, we explore its background, architecture, open source funding model, and community-driven governance. We dive into practical applications, challenges, and future trends. By comparing OrbitDB with related decentralized projects and touching on innovative funding strategies inspired by MIT’s open source philosophy, we demonstrate how OrbitDB is fueling a decentralized future in technology. Furthermore, this article is enriched with tables, bullet lists, and useful links—such as the Original Article and authoritative sources—to provide both technical insights and practical guidance. Introduction In a world where data privacy and security are paramount, decentralized solutions like OrbitDB are rapidly evolving to meet modern digital challenges. OrbitDB, a blockchain database that uses the power of the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), stands at the forefront of this revolution. Its open source business model and community-supported funding strategy embody principles long championed by institutions like MIT. This post explores the comprehensive world of OrbitDB—from its origins to its technical features and future prospects—making it accessible for both technical experts and enthusiasts in blockchain and open source development. Background and Context History and Evolution OrbitDB emerged as a response to traditional data storage vulnerabilities. Conventional centralized databases often face risks like single points of failure, limited transparency, and demanding maintenance costs. OrbitDB was designed to address these issues by leveraging a peer-to-peer architecture built on IPFS. This design decentralizes the storage process, ensuring data integrity, enhanced privacy, and security. Key Milestones: Decentralized Data Storage: OrbitDB revolutionized the storage paradigm by embracing decentralized hash tables and blockchain verification. Open Source Funding: Inspired by MIT’s open source strategies, OrbitDB has attracted community support, academic grants, and sponsorship funds. Community-Driven Development: Continuous contributions from developers, biotech researchers, and blockchain innovators have molded OrbitDB into a versatile database solution. Ecosystem and Definitions Decentralization: The process of distributing authority and functionality away from a central location to enhance resilience and transparency. IPFS: The InterPlanetary File System is a peer-to-peer protocol used to store and share data in a distributed fashion. Blockchain Database: A database time-stamped and cryptographically secured using blockchain principles, ensuring immutability and verifiability. Open Source Funding: A collaborative funding model that relies on community contributions, decentralized finance (DeFi) mechanisms, and grants—as opposed to traditional venture capital. Together, these elements create an innovative ecosystem where OrbitDB serves as both a technical solution and a case study in digital collaboration. Core Concepts and Features OrbitDB incorporates several core features that distinguish it in the blockchain and open source communities: Decentralized Architecture Peer-to-Peer Communication: OrbitDB ignites data sharing by eliminating centralized servers, providing true data ownership. Fault Tolerance: Its distributed hash table ensures that even if one node fails, the data remains accessible. Immutable Records: Every transaction logged on OrbitDB is cryptographically verifiable, ensuring data integrity. Open Source Funding and Business Model OrbitDB thrives through a vibrant financial ecosystem: Community Contributions: Developers and tech enthusiasts fund and support the project via donation campaigns, sponsorships, and crowdfunding. Grants and Sponsorships: Academic institutions and tech giants alike have recognized the merit of open source innovation by offering grants. For example, similar initiatives can be found in communities such as open source funding best practices. Decentralized Governance: Decision-making in OrbitDB is shared amongst community members, reducing the risk of centralized manipulation. Table: Key Features of OrbitDB Feature Description Decentralization Data is distributed via a peer-to-peer network, reducing reliance on centralized servers. Security Uses cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms to secure data on the blockchain. Scalability The architecture supports real-time synchronization and efficient data replication over vast networks. Openness The open source model allows global contributions, accelerating innovation and sustainability. Community Governance Decisions are made collaboratively, fostering transparency and shared ownership. Integration with Blockchain and IPFS Orbit

Abstract
OrbitDB is a revolutionary decentralized database built atop IPFS that reshapes data storage in blockchain ecosystems. In this post, we explore its background, architecture, open source funding model, and community-driven governance. We dive into practical applications, challenges, and future trends. By comparing OrbitDB with related decentralized projects and touching on innovative funding strategies inspired by MIT’s open source philosophy, we demonstrate how OrbitDB is fueling a decentralized future in technology. Furthermore, this article is enriched with tables, bullet lists, and useful links—such as the Original Article and authoritative sources—to provide both technical insights and practical guidance.
Introduction
In a world where data privacy and security are paramount, decentralized solutions like OrbitDB are rapidly evolving to meet modern digital challenges. OrbitDB, a blockchain database that uses the power of the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), stands at the forefront of this revolution. Its open source business model and community-supported funding strategy embody principles long championed by institutions like MIT. This post explores the comprehensive world of OrbitDB—from its origins to its technical features and future prospects—making it accessible for both technical experts and enthusiasts in blockchain and open source development.
Background and Context
History and Evolution
OrbitDB emerged as a response to traditional data storage vulnerabilities. Conventional centralized databases often face risks like single points of failure, limited transparency, and demanding maintenance costs. OrbitDB was designed to address these issues by leveraging a peer-to-peer architecture built on IPFS. This design decentralizes the storage process, ensuring data integrity, enhanced privacy, and security.
Key Milestones:
- Decentralized Data Storage: OrbitDB revolutionized the storage paradigm by embracing decentralized hash tables and blockchain verification.
- Open Source Funding: Inspired by MIT’s open source strategies, OrbitDB has attracted community support, academic grants, and sponsorship funds.
- Community-Driven Development: Continuous contributions from developers, biotech researchers, and blockchain innovators have molded OrbitDB into a versatile database solution.
Ecosystem and Definitions
Decentralization: The process of distributing authority and functionality away from a central location to enhance resilience and transparency.
IPFS: The InterPlanetary File System is a peer-to-peer protocol used to store and share data in a distributed fashion.
Blockchain Database: A database time-stamped and cryptographically secured using blockchain principles, ensuring immutability and verifiability.
Open Source Funding: A collaborative funding model that relies on community contributions, decentralized finance (DeFi) mechanisms, and grants—as opposed to traditional venture capital.
Together, these elements create an innovative ecosystem where OrbitDB serves as both a technical solution and a case study in digital collaboration.
Core Concepts and Features
OrbitDB incorporates several core features that distinguish it in the blockchain and open source communities:
Decentralized Architecture
- Peer-to-Peer Communication: OrbitDB ignites data sharing by eliminating centralized servers, providing true data ownership.
- Fault Tolerance: Its distributed hash table ensures that even if one node fails, the data remains accessible.
- Immutable Records: Every transaction logged on OrbitDB is cryptographically verifiable, ensuring data integrity.
Open Source Funding and Business Model
OrbitDB thrives through a vibrant financial ecosystem:
- Community Contributions: Developers and tech enthusiasts fund and support the project via donation campaigns, sponsorships, and crowdfunding.
- Grants and Sponsorships: Academic institutions and tech giants alike have recognized the merit of open source innovation by offering grants. For example, similar initiatives can be found in communities such as open source funding best practices.
- Decentralized Governance: Decision-making in OrbitDB is shared amongst community members, reducing the risk of centralized manipulation.
Table: Key Features of OrbitDB
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Decentralization | Data is distributed via a peer-to-peer network, reducing reliance on centralized servers. |
| Security | Uses cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms to secure data on the blockchain. |
| Scalability | The architecture supports real-time synchronization and efficient data replication over vast networks. |
| Openness | The open source model allows global contributions, accelerating innovation and sustainability. |
| Community Governance | Decisions are made collaboratively, fostering transparency and shared ownership. |
Integration with Blockchain and IPFS
OrbitDB’s reliance on IPFS allows seamless integration with blockchain applications. Its architecture supports various digital use cases, ensuring that even decentralized apps (dApps) can operate without bottlenecks or reliance on central authorities.
Applications and Use Cases
OrbitDB has shown remarkable versatility across industries. Here are some practical examples:
1. Decentralized Social Media Platforms
Developers have harnessed OrbitDB to build secure and censorship-resistant social media platforms. By combining OrbitDB with decentralized identity management, user privacy is maintained while ensuring content immutability.
2. Real-Time Financial Data Tracking
In the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector, OrbitDB has been deployed for real-time transaction logging and tracking. Its immutable ledger offers a verifiable audit trail that is crucial for compliance and transparency in financial services.
3. Decentralized Content Distribution
By integrating with IPFS, OrbitDB powers content distribution networks that prevent data monopolies and censorship. This method is vital for digital content creators seeking to maintain complete control over their work.
Bullet List: Practical Benefits of OrbitDB Applications
- Security: Each transaction is cryptographically signed, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Transparency: Immutable logs provide verifiable audit trails.
- Resilience: Distributed infrastructure minimizes single points of failure.
- Interoperability: Easily integrates with other decentralized systems and blockchain networks.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower overhead compared to centralized cloud services.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its innovative design, OrbitDB and similar decentralized databases face several challenges:
Technical Challenges
- Scalability Under Heavy Load: While the architecture is designed for scalability, large-scale applications must tackle challenges related to network latency and storage replication.
- Complexity of Consensus Mechanisms: Ensuring data consistency across a highly distributed network can be complex and may require advanced consensus protocols.
- Integration Hurdles: Bridging OrbitDB with legacy systems or traditional centralized applications might involve compatibility issues and require additional middleware.
Adoption and Community Challenges
- Awareness and Expertise: Many enterprises remain unfamiliar with decentralized database architectures, limiting its wider adoption.
- Funding Volatility: Since the funding model largely depends on community contributions, financial stability might be challenged during market downturns.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving regulations in the blockchain and data privacy space can create hurdles for decentralized projects.
Future Outlook and Innovations
The future of OrbitDB is promising, with innovative features on the horizon:
1. Advanced Cryptographic Protocols
Researchers are exploring enhancements such as secure multi-party computation and zero-knowledge proofs to further secure data exchanges without sacrificing transparency.
2. Enhanced Consensus Mechanisms
Future iterations may incorporate more efficient consensus protocols to ensure that OrbitDB not only scales seamlessly, but also maintains high throughput during peak usage. These innovations will likely draw parallels with advancements in projects such as Arbitrum and Ethereum interoperability.
3. Broader Ecosystem Integration
OrbitDB will increasingly integrate with various decentralized platforms and corporate systems. Partnerships with academic institutions and industry leaders indicate that further research and improved interoperability are on the horizon. For instance, notable discussions on decentralized funding trends can be explored in open source funding for tech projects.
4. Tokenized Funding Models
With the evolution of NFTs and token economics, tokenized funding models may provide new avenues to ensure sustainable growth. Projects in this area—similar to those detailed in NFT tokenomics—offer alternative strategies for fundraising and incentivizing community contributions.
Dev.to Link Insights
For additional perspectives, check out insightful discussions on open source and blockchain funding models on Dev.to such as Open Source Funding for Educational Resources and Blockchain Based Project Funding and Navigating Open Source Licensing in the Blockchain Era. These articles offer complementary insights and practical strategies relevant to OrbitDB’s future.
Summary
OrbitDB is more than just a decentralized blockchain database—it is a pioneering example of an open source-driven approach to data storage. Its robust integration with IPFS, community-centric funding model, and decentralized governance structure ensure data integrity, security, and resilience. While challenges related to scalability and regulatory environments remain, continuous innovations in cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and tokenized funding models present a bright future.
Key Takeaways:
- Decentralized Technology: OrbitDB eliminates single points of failure by using a peer-to-peer network.
- Open Source Funding: Community contributions, grants, and sponsorships drive its development.
- Applications: Use cases range from decentralized social media to real-time financial tracking.
- Challenges: Technical and adoption challenges remain, but ongoing innovations will address these issues.
- Future Prospects: Enhanced cryptographic protocols and collaborative integration with blockchain ecosystems will further strengthen OrbitDB's position.
As the world continues to shift toward decentralization, innovative projects like OrbitDB provide a blueprint for sustainable, community-driven technology. By embracing open source philosophy and decentralized governance, OrbitDB is well-positioned to shape the future of data storage, blockchain integrity, and digital innovation.
For more detailed insights on OrbitDB’s dynamic ecosystem and funding strategies, please refer to the Original Article and explore additional resources like the OrbitDB Official Website.
This comprehensive discussion also touches upon related themes in NFT marketing and decentralized financial solutions—areas that are increasingly interconnected with the evolution of projects like OrbitDB. As technology converges and communities grow, the interplay between open source funding and blockchain innovation is certain to foster a more transparent and resilient digital future.














































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)
















































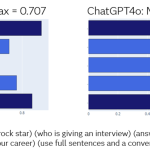























































































































































































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)

























_Michael_Burrell_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)