'The Models Were Right!' Astronomers Locate Universe's 'Missing' Matter
It's not dark matter, writes Space.com. But astronomers have discovered "a vast tendril of hot gas linking four galaxy clusters and stretching out for 23 million light-years, 230 times the length of our galaxy. "With 10 times the mass of the Milky Way, this filamentary structure accounts for much of the universe's 'missing matter,' the search for which has baffled scientists for decades...." [I]t is "ordinary matter" made up of atoms, composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons (collectively called baryons) which make up stars, planets, moons, and our bodies. For decades, our best models of the universe have suggested that a third of the baryonic matter that should be out there in the cosmos is missing. This discovery of that missing matter suggests our best models of the universe were right all along. It could also reveal more about the "Cosmic Web," the vast structure along which entire galaxies grew and gathered during the earlier epochs of our 13.8 billion-year-old universe.... The newly observed filament isn't just extraordinary in terms of its mass and size; it also has a temperature of a staggering 18 million degrees Fahrenheit (10 million degrees Celsius). That's around 1,800 times hotter than the surface of the sun... The team's research was published on Thursday (June 19) in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. Models of the cosmos (including the standard model of cosmology) "have long posited the idea that the missing baryonic matter of the universe is locked up in vast filaments of gas stretching between the densest pockets of space..." the article points out. But now thanks to Suzaku, a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) satellite, and the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton, "a team of astronomers has for the first time been able to determine the properties of one of these filaments, which links four galactic clusters in the local universe." Team leader Konstantinos Migkas (of the Netherlands' Leiden Observatory) explained the significance of their finding. "For the first time, our results closely match what we see in our leading model of the cosmos — something that's not happened before." "It seems that the simulations were right all along." Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.




















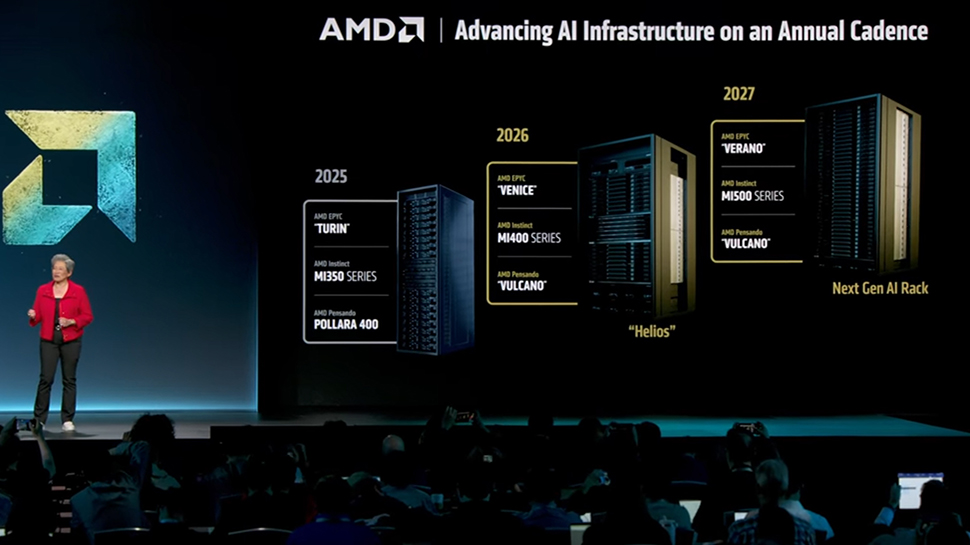
















































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 154]: AI Answers: The Future of AI Agents at Work, Building an AI Roadmap, Choosing the Right Tools, & Responsible AI Use](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20154%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 153]: OpenAI Releases o3-Pro, Disney Sues Midjourney, Altman: “Gentle Singularity” Is Here, AI and Jobs & News Sites Getting Crushed by AI Search](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20153%20cover.png)

























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] The Chief AI Officer’s Handbook, Natural Language Processing with Python & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)









































































![GrandChase tier list of the best characters available [June 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33057-1637756796/grandchase-ios-android-3rd-anniversary.jpg?#)




































































_Frank_Peters_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)






























































































![Apple tells students ‘how to convince your parents to get you a Mac’ [Update: Removed]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/screenshot-2025-06-20-at-09.14.21.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)















![Apple Weighs Acquisition of AI Startup Perplexity in Internal Talks [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97674/97674/97674-640.jpg)
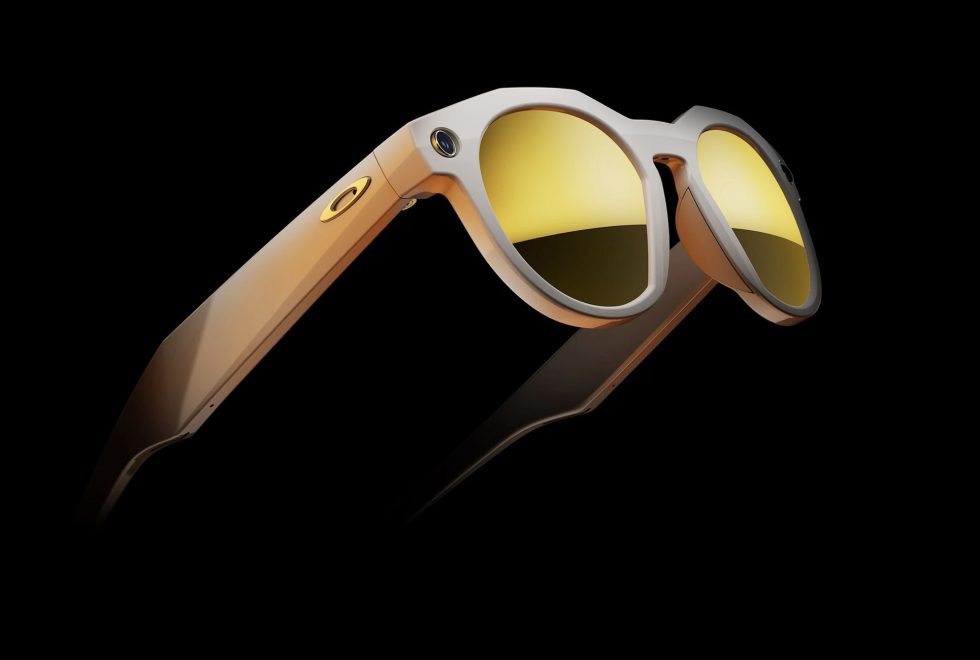
![Oakley and Meta Launch Smart Glasses for Athletes With AI, 3K Camera, More [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97665/97665/97665-640.jpg)

![How to Get Your Parents to Buy You a Mac, According to Apple [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97671/97671/97671-640.jpg)

















![New accessibility settings announced for Steam Big Picture Mode and SteamOS [Beta]](https://www.ghacks.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/New-accessibility-settings-announced-for-Steam-Big-Picture-Mode-and-SteamOS.jpg)