How JavaScript helped me find a Car
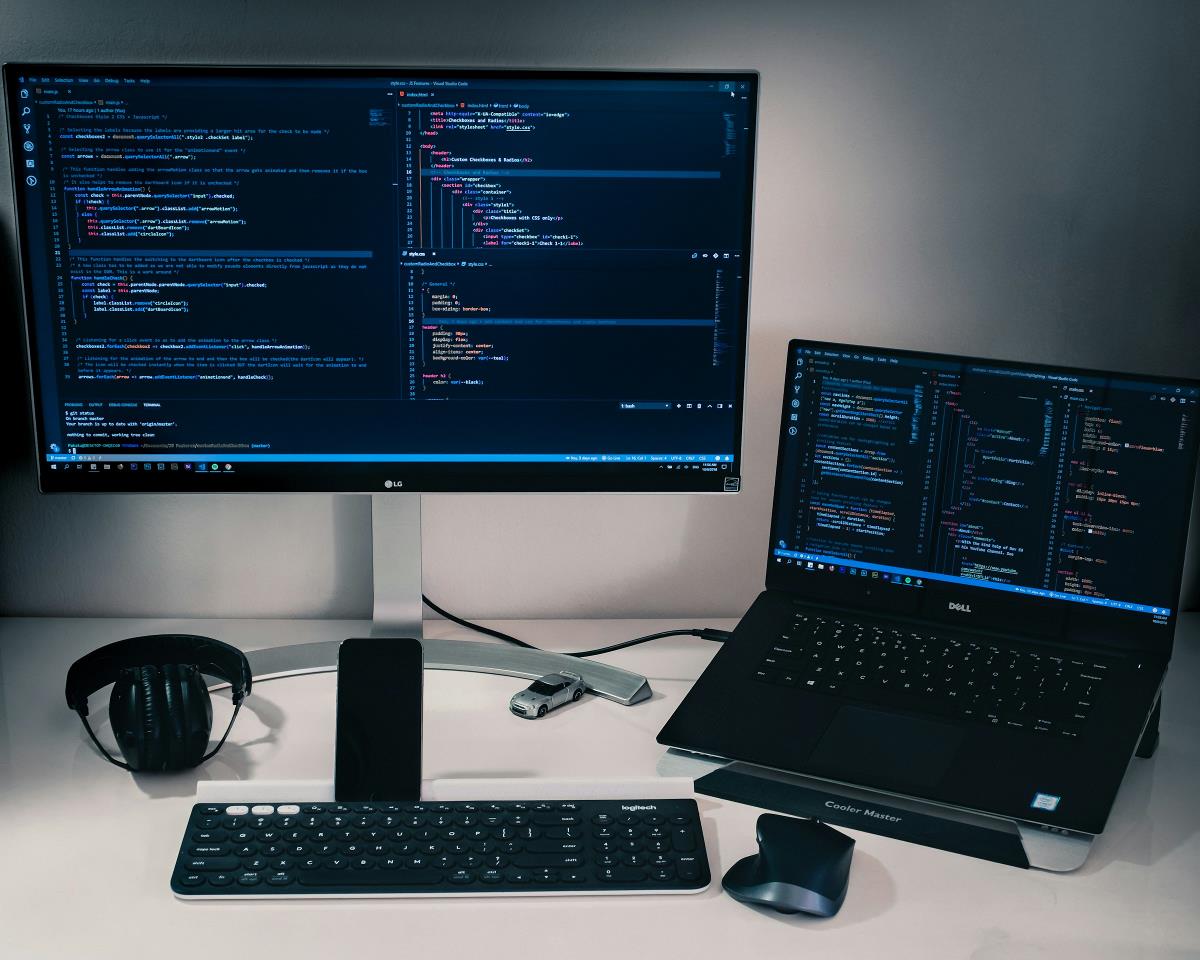
I'm looking for a Jetta, and of course, I want to make sure I get the best option. Instead of manually checking car dealers' websites, I'm writing ETLs to collect car data, save it as JSON, and use a Next.js app to display the results. Architecture I'm going to write one ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) per website (source). Extract This step involves opening the website and retrieving the data. Sometimes it's in HTML, sometimes in JSON. Transform I'm interested in the following properties: title price year link vin mileage Each website may have a different structure, but the goal is to extract these values. Load For this demo, I'm keeping it simple by saving a JSON file per site. In a real-world setup, the data would be stored in a database. Aggregator This script will combine all the JSON files into a single one, simulating what a database would do in a real example. Next.js A basic web app to display the data in a table-like format with simple filters. Example Let's take a look at the following dealer's website: Notice how the website displays the properties I'm interested in. Fortunately, at the time of writing, this site returns a JSON response, which makes it easy to traverse and extract car data. The ETL looks like this: const fs = require("fs"); const extract = async (url) => { const response = await fetch(url); return await response.json(); }; const transform = (data) => { return data.DisplayCards.map((VehicleCard) => { return { title: VehicleCard.VehicleName, price: VehicleCard.VehicleInternetPrice, year: VehicleCard.VehicleYear, link: VehicleCard.VehicleDetailUrl, vin: VehicleCard.VehicleVin, mileage: VehicleCard.Mileage, }; }); }; const load = (cars, name) => { fs.writeFileSync(`./_sites/${name}.json`, JSON.stringify(cars)); }; const main = async () => { const site = { url: "https://www.vwoaklawn.com/api/vhcliaa/vehicle-pages/cosmos/srp/vehicles/25795/2631261?st=Price+asc&Make=Volkswagen&mileagerange=0-50000&host=www.vwoaklawn.com&baseFilter=dHlwZT0ndSc=&displayCardsShown=NaN", }; const data = await extract(site.url); const cars = transform(data); load(cars, "vwoaklawn"); }; Site_A.json After running the ETL, I’ll get a JSON file like this: [ { "title": "Volkswagen Jetta 1.4T SE", "price": 19640, "year": 2021, "link": "https://www.cityvwofchicago.com/inventory/certified-used-2021-volkswagen-jetta-1-4t-se-fwd-4d-sedan-3vwc57bu4mm003393/", "vin": "3VWC57BU4MM003393", "mileage": 27203 }, ... ] Aggregator This helper combines all the Site_N.json files into a single cars.json file, which will be used by the web application. Next.js A simple web app that displays cars.json. The page looks like this: Demo Make sure to check out the Website and take a look at the Codebase. So now, I know which Jetta to get

I'm looking for a Jetta, and of course, I want to make sure I get the best option. Instead of manually checking car dealers' websites, I'm writing ETLs to collect car data, save it as JSON, and use a Next.js app to display the results.
Architecture
I'm going to write one ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) per website (source).
Extract
This step involves opening the website and retrieving the data. Sometimes it's in HTML, sometimes in JSON.
Transform
I'm interested in the following properties:
title
price
year
link
vin
mileage
Each website may have a different structure, but the goal is to extract these values.
Load
For this demo, I'm keeping it simple by saving a JSON file per site. In a real-world setup, the data would be stored in a database.
Aggregator
This script will combine all the JSON files into a single one, simulating what a database would do in a real example.
Next.js
A basic web app to display the data in a table-like format with simple filters.
Example
Let's take a look at the following dealer's website:
Notice how the website displays the properties I'm interested in. Fortunately, at the time of writing, this site returns a JSON response, which makes it easy to traverse and extract car data. The ETL looks like this:
const fs = require("fs");
const extract = async (url) => {
const response = await fetch(url);
return await response.json();
};
const transform = (data) => {
return data.DisplayCards.map((VehicleCard) => {
return {
title: VehicleCard.VehicleName,
price: VehicleCard.VehicleInternetPrice,
year: VehicleCard.VehicleYear,
link: VehicleCard.VehicleDetailUrl,
vin: VehicleCard.VehicleVin,
mileage: VehicleCard.Mileage,
};
});
};
const load = (cars, name) => {
fs.writeFileSync(`./_sites/${name}.json`, JSON.stringify(cars));
};
const main = async () => {
const site = {
url: "https://www.vwoaklawn.com/api/vhcliaa/vehicle-pages/cosmos/srp/vehicles/25795/2631261?st=Price+asc&Make=Volkswagen&mileagerange=0-50000&host=www.vwoaklawn.com&baseFilter=dHlwZT0ndSc=&displayCardsShown=NaN",
};
const data = await extract(site.url);
const cars = transform(data);
load(cars, "vwoaklawn");
};
Site_A.json
After running the ETL, I’ll get a JSON file like this:
[
{
"title": "Volkswagen Jetta 1.4T SE",
"price": 19640,
"year": 2021,
"link": "https://www.cityvwofchicago.com/inventory/certified-used-2021-volkswagen-jetta-1-4t-se-fwd-4d-sedan-3vwc57bu4mm003393/",
"vin": "3VWC57BU4MM003393",
"mileage": 27203
},
...
]
Aggregator
This helper combines all the Site_N.json files into a single cars.json file, which will be used by the web application.
Next.js
A simple web app that displays cars.json. The page looks like this:
Demo
Make sure to check out the Website and take a look at the Codebase.
So now, I know which Jetta to get






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)











































































































































































































































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
























_Michael_Burrell_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)