Appliances Powered by Wireless Charging Technology: A Glimpse into the Future of Cord-Free Convenience
In an era of smart homes and seamless connectivity, wireless charging technology has emerged as a game-changer. What began as a convenient way to charge smartphones has now evolved into a powerful innovation influencing a wide range of household appliances. The prospect of a home where devices power up without cords, clutter, or manual intervention is no longer a distant dream—it’s a rapidly approaching reality. Wireless charging, also known as inductive charging, is revolutionizing how appliances function and interact within the modern home. From kitchen gadgets to vacuum cleaners, the adoption of this technology is growing steadily, offering benefits like enhanced convenience, reduced wear and tear, and greater design flexibility. In this blog, we’ll explore how wireless charging is reshaping everyday appliances, its underlying technology, and what the future holds for cord-free living. Understanding Wireless Charging Technology At its core, wireless charging operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. A transmitter coil, usually embedded in a charging base, generates a magnetic field when electricity flows through it. A corresponding receiver coil in the appliance picks up this magnetic field and converts it back into electrical energy, which then charges the appliance’s battery. There are two major types of wireless charging methods: Inductive Charging – This is the most common method used in consumer electronics and small appliances. It requires close proximity between the transmitter and receiver, typically through direct contact or very short distances. Resonant Charging – This method allows for greater spatial freedom, transmitting power over several centimeters or even a few meters. It’s more flexible and is being researched for larger devices or those with varying alignment. Household Appliances Embracing Wireless Charging The adoption of wireless charging is no longer limited to smartphones and wearables. A growing number of home appliances are being designed to utilize this technology for improved user experience and greater efficiency. 1. Robotic Vacuum Cleaners One of the earliest adopters in the home appliance segment, robotic vacuum cleaners like the Roomba have utilized wireless charging for years. These devices automatically return to their docking stations when they need to recharge. The base station contains a transmitter coil that charges the device without physical plug-in mechanisms, offering a hands-free experience. 2. Kitchen Appliances Wireless charging is making its way into the kitchen, with companies experimenting with countertops embedded with charging pads. Imagine placing your blender, coffee maker, or electric kettle directly onto your kitchen counter, and it begins charging without the need for a power socket. Inductive cooking surfaces—already popular in high-tech kitchens—are also being integrated with wireless charging capabilities to power other devices while the cooktop is in use or idle. 3. Personal Care Devices Electric toothbrushes, hair trimmers, and facial cleansing devices are increasingly leveraging inductive charging. The cordless nature not only improves safety—especially in wet environments like bathrooms—but also reduces the inconvenience of handling charging cables. 4. Smart Home Assistants and Speakers Voice-activated assistants and wireless speakers are also beginning to integrate wireless charging, ensuring they remain operational even when moved between rooms, provided a charging base or pad is available nearby. 5. Power Tools and Lawn Equipment While still in early stages, brands are exploring wireless charging docks for tools such as drills or garden trimmers. This reduces downtime by allowing devices to charge between uses without the need for cable management. Advantages of Wireless Charging in Appliances Wireless charging brings a host of benefits that align perfectly with modern lifestyle expectations: • Convenience The most apparent advantage is ease of use. Appliances can be charged simply by placing them on a compatible surface, reducing the need for cords and manual intervention. • Safety In environments like kitchens and bathrooms, wireless charging reduces the risk of electric shock by eliminating exposed connectors. • Durability Without constant plugging and unplugging, wear and tear on both the appliance and its charging port is minimized, potentially extending the device’s lifespan. • Aesthetics Cord-free designs are sleeker and allow for greater flexibility in product design and placement, contributing to the minimalist aesthetic favored in modern interiors. • Automation and Integration Wireless charging enables greater integration into smart home ecosystems. Devices can be programmed to automatically charge during off-peak hours or coordinate with other smart appliances for optimized energy use. Challenges and Considerations Despite the promise of wir

In an era of smart homes and seamless connectivity, wireless charging technology has emerged as a game-changer. What began as a convenient way to charge smartphones has now evolved into a powerful innovation influencing a wide range of household appliances. The prospect of a home where devices power up without cords, clutter, or manual intervention is no longer a distant dream—it’s a rapidly approaching reality.
Wireless charging, also known as inductive charging, is revolutionizing how appliances function and interact within the modern home. From kitchen gadgets to vacuum cleaners, the adoption of this technology is growing steadily, offering benefits like enhanced convenience, reduced wear and tear, and greater design flexibility. In this blog, we’ll explore how wireless charging is reshaping everyday appliances, its underlying technology, and what the future holds for cord-free living.
Understanding Wireless Charging Technology
At its core, wireless charging operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. A transmitter coil, usually embedded in a charging base, generates a magnetic field when electricity flows through it. A corresponding receiver coil in the appliance picks up this magnetic field and converts it back into electrical energy, which then charges the appliance’s battery.
There are two major types of wireless charging methods:
Inductive Charging – This is the most common method used in consumer electronics and small appliances. It requires close proximity between the transmitter and receiver, typically through direct contact or very short distances.
Resonant Charging – This method allows for greater spatial freedom, transmitting power over several centimeters or even a few meters. It’s more flexible and is being researched for larger devices or those with varying alignment.
Household Appliances Embracing Wireless Charging
The adoption of wireless charging is no longer limited to smartphones and wearables. A growing number of home appliances are being designed to utilize this technology for improved user experience and greater efficiency.
1. Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
One of the earliest adopters in the home appliance segment, robotic vacuum cleaners like the Roomba have utilized wireless charging for years. These devices automatically return to their docking stations when they need to recharge. The base station contains a transmitter coil that charges the device without physical plug-in mechanisms, offering a hands-free experience.
2. Kitchen Appliances
Wireless charging is making its way into the kitchen, with companies experimenting with countertops embedded with charging pads. Imagine placing your blender, coffee maker, or electric kettle directly onto your kitchen counter, and it begins charging without the need for a power socket.
Inductive cooking surfaces—already popular in high-tech kitchens—are also being integrated with wireless charging capabilities to power other devices while the cooktop is in use or idle.
3. Personal Care Devices
Electric toothbrushes, hair trimmers, and facial cleansing devices are increasingly leveraging inductive charging. The cordless nature not only improves safety—especially in wet environments like bathrooms—but also reduces the inconvenience of handling charging cables.
4. Smart Home Assistants and Speakers
Voice-activated assistants and wireless speakers are also beginning to integrate wireless charging, ensuring they remain operational even when moved between rooms, provided a charging base or pad is available nearby.
5. Power Tools and Lawn Equipment
While still in early stages, brands are exploring wireless charging docks for tools such as drills or garden trimmers. This reduces downtime by allowing devices to charge between uses without the need for cable management.
Advantages of Wireless Charging in Appliances
Wireless charging brings a host of benefits that align perfectly with modern lifestyle expectations:
• Convenience
The most apparent advantage is ease of use. Appliances can be charged simply by placing them on a compatible surface, reducing the need for cords and manual intervention.
• Safety
In environments like kitchens and bathrooms, wireless charging reduces the risk of electric shock by eliminating exposed connectors.
• Durability
Without constant plugging and unplugging, wear and tear on both the appliance and its charging port is minimized, potentially extending the device’s lifespan.
• Aesthetics
Cord-free designs are sleeker and allow for greater flexibility in product design and placement, contributing to the minimalist aesthetic favored in modern interiors.
• Automation and Integration
Wireless charging enables greater integration into smart home ecosystems. Devices can be programmed to automatically charge during off-peak hours or coordinate with other smart appliances for optimized energy use.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promise of wireless charging, the technology is not without its challenges.
Charging Speed: Wireless charging typically takes longer than wired charging. While advancements are being made, high-powered appliances may still require faster, more efficient methods.
Heat Generation: Inductive charging can produce excess heat, which might affect sensitive electronic components if not managed properly.
Standardization: There is a lack of uniform standards across manufacturers, which can limit interoperability between appliances and charging stations.
Cost: Incorporating wireless charging into appliances can increase production costs, which may be passed on to consumers.
The Future of Wireless Charging in Appliances
The future looks promising as technology continues to evolve. Emerging developments in resonant charging, radio frequency (RF) charging, and magnetic resonance aim to extend charging ranges and improve energy efficiency. Tech giants and appliance manufacturers are collaborating to create standards and improve interoperability.
A particularly exciting development is furniture-integrated wireless charging, such as kitchen islands or bathroom vanities with built-in charging capabilities. Similarly, multi-device pads could soon charge multiple appliances simultaneously, just as wireless chargers now do for phones and smartwatches.
Furthermore, as smart homes become more interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT), appliances will be able to monitor their own power needs and automatically recharge when necessary—ensuring uninterrupted service and smarter energy management.
Conclusion
Wireless charging technology is transforming household appliances by bringing unparalleled convenience, safety, and design innovation. While the technology is still maturing in terms of speed and scalability, the direction is clear: a cord-free, smarter future for the modern home.
As wireless charging becomes more efficient and widespread, we can expect more appliances to adopt it—not just for the convenience of users, but also for improved sustainability and seamless integration into smart living environments. The homes of tomorrow are being built today, one wire-free device at a time.










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)














































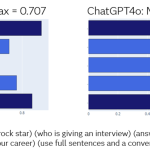


























































































































































































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
























_Michael_Burrell_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)