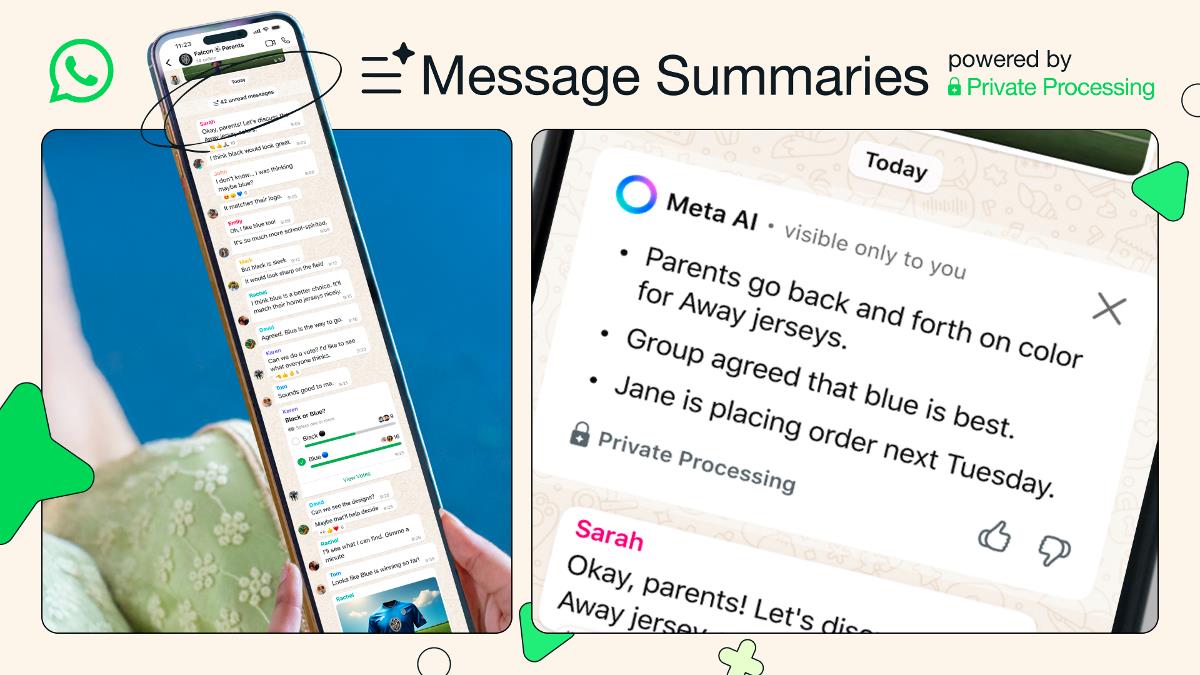
Agentic AI vs Generative AI: Key Differences & Use Cases
As Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet, stated, "AI is probably the most important thing humanity has ever worked on." As artificial intelligence moves from experimentation into everyday reality, one crucial distinction is beginning to reshape how we think about its role in the world: the divide between Agentic and Generative AI. Both represent remarkable breakthroughs, but they are built for different purposes. Generative AI is taking the spotlight with its ability to create original text, images, and even music. Meanwhile, Agentic AI quietly redefines autonomy in business operations, enabling systems to make decisions, adapt to changing environments, and execute complex tasks without constant human oversight. As businesses increasingly turn to AI to enhance innovation, automate processes, and drive smarter operations, understanding the strengths and limits of each AI type is no longer optional. In this blog, we’ll break down the core differences between Generative AI vs Agentic AI, highlight what makes each unique, and help you decide which approach best fits your needs. What is Agentic AI? Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to operate independently, with the ability to pursue assigned goals and make decisions without requiring continuous human guidance. Unlike traditional AI, which often relies on predefined rules or fixed responses, Agentic AI demonstrates proactive behavior: it adapts to changing environments, adjusts its strategies to meet objectives, and continuously learns from real-world interactions. This ability enables Agentic AI to operate as autonomous agents, handling complex tasks and continuously improving their performance over time. Key features of Agentic AI Autonomous decision making: Agentic AI can autonomously make decisions without the need for human intervention. Through agentic automation, it can process data, evaluate potential risks, and determine the most effective course of action to accomplish its goals. Goal-oriented: Agentic AI operates based on defined goals instead of relying on pre-programmed rules. It can break down the assigned goals into actionable steps, prioritize tasks, and adapt its actions dynamically to stay aligned with its intended outcomes. Self-Learning Capabilities: Agentic AI continuously enhances its performance by learning from real-world interactions and the results of its actions. It adjusts its strategies based on new data, feedback, and changing environments, allowing it to handle increasingly complex tasks with greater efficiency. Proactive problem-solving: Instead of waiting for explicit commands, Agentic AI anticipates challenges, analyzes situations, and initiates solutions to keep progressing toward its goals. Use cases for Agentic AI Customer Support Automation: Traditional customer support chatbots often struggled with limited understanding and needed frequent human help. Agentic AI changes this by autonomously interpreting customer intent and emotions, enabling faster and more accurate issue resolution. Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization: Agentic AI enhances supply chain management by continuously monitoring operations, predicting disruptions, and adjusting logistics strategies to maintain efficiency and reduce costs. Healthcare Workflow Management: Agentic AI is streamlining healthcare administration by automating patient scheduling, resource allocation, and treatment workflows. These systems adjust dynamically based on patient needs, improving operational efficiency and patient outcomes. Software Development & QA Agents: Beyond generating code, Agentic AI identifies bugs, refines testing strategies, and suggests improvements, adjusting as project requirements evolve without manual oversight. Financial Services: Agentic AI can detect fraudulent activities, analyze risks, and drive smart decision-making across loan processing, investment management, and regulatory compliance. In addition, Agentic AI is adopted across the travel and hospitality sector to deliver personalized guest experiences and streamline operations. It also plays a critical role in cybersecurity by detecting threats early and enabling faster, more autonomous responses. What is Generative AI? Generative AI is a subfield of artificial intelligence focused on creating new content such as text, images, audio, video, or code by learning patterns and structures from large datasets. These systems use machine learning models, especially deep learning and neural networks, to analyze existing data and then generate original outputs in response to user prompts. Some examples of Generative AI include chatbots such as ChatGPT and Gemini, as well as image generators like DALL-E and Midjourney. Key features of Generative AI Content creation: Generative AI is highly effective at creating original content in multiple formats, such as text, images, audio, and video. It leverages deep lea

As Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet, stated, "AI is probably the most important thing humanity has ever worked on."
As artificial intelligence moves from experimentation into everyday reality, one crucial distinction is beginning to reshape how we think about its role in the world: the divide between Agentic and Generative AI.
Both represent remarkable breakthroughs, but they are built for different purposes. Generative AI is taking the spotlight with its ability to create original text, images, and even music. Meanwhile, Agentic AI quietly redefines autonomy in business operations, enabling systems to make decisions, adapt to changing environments, and execute complex tasks without constant human oversight.
As businesses increasingly turn to AI to enhance innovation, automate processes, and drive smarter operations, understanding the strengths and limits of each AI type is no longer optional.
In this blog, we’ll break down the core differences between Generative AI vs Agentic AI, highlight what makes each unique, and help you decide which approach best fits your needs.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to operate independently, with the ability to pursue assigned goals and make decisions without requiring continuous human guidance.
Unlike traditional AI, which often relies on predefined rules or fixed responses, Agentic AI demonstrates proactive behavior: it adapts to changing environments, adjusts its strategies to meet objectives, and continuously learns from real-world interactions.
This ability enables Agentic AI to operate as autonomous agents, handling complex tasks and continuously improving their performance over time.
Key features of Agentic AI
Autonomous decision making: Agentic AI can autonomously make decisions without the need for human intervention. Through agentic automation, it can process data, evaluate potential risks, and determine the most effective course of action to accomplish its goals.
Goal-oriented: Agentic AI operates based on defined goals instead of relying on pre-programmed rules. It can break down the assigned goals into actionable steps, prioritize tasks, and adapt its actions dynamically to stay aligned with its intended outcomes.
Self-Learning Capabilities: Agentic AI continuously enhances its performance by learning from real-world interactions and the results of its actions. It adjusts its strategies based on new data, feedback, and changing environments, allowing it to handle increasingly complex tasks with greater efficiency.
Proactive problem-solving: Instead of waiting for explicit commands, Agentic AI anticipates challenges, analyzes situations, and initiates solutions to keep progressing toward its goals.
Use cases for Agentic AI
Customer Support Automation: Traditional customer support chatbots often struggled with limited understanding and needed frequent human help. Agentic AI changes this by autonomously interpreting customer intent and emotions, enabling faster and more accurate issue resolution.
Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization: Agentic AI enhances supply chain management by continuously monitoring operations, predicting disruptions, and adjusting logistics strategies to maintain efficiency and reduce costs.
Healthcare Workflow Management: Agentic AI is streamlining healthcare administration by automating patient scheduling, resource allocation, and treatment workflows. These systems adjust dynamically based on patient needs, improving operational efficiency and patient outcomes.
Software Development & QA Agents: Beyond generating code, Agentic AI identifies bugs, refines testing strategies, and suggests improvements, adjusting as project requirements evolve without manual oversight.
Financial Services: Agentic AI can detect fraudulent activities, analyze risks, and drive smart decision-making across loan processing, investment management, and regulatory compliance.
In addition, Agentic AI is adopted across the travel and hospitality sector to deliver personalized guest experiences and streamline operations. It also plays a critical role in cybersecurity by detecting threats early and enabling faster, more autonomous responses.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a subfield of artificial intelligence focused on creating new content such as text, images, audio, video, or code by learning patterns and structures from large datasets.
These systems use machine learning models, especially deep learning and neural networks, to analyze existing data and then generate original outputs in response to user prompts. Some examples of Generative AI include chatbots such as ChatGPT and Gemini, as well as image generators like DALL-E and Midjourney.
Key features of Generative AI
Content creation: Generative AI is highly effective at creating original content in multiple formats, such as text, images, audio, and video. It leverages deep learning models to interpret prompts, produce cohesive outputs, and replicate human-like creativity on a large scale.
Data analysis: Beyond content generation, Generative AI can also synthesize large datasets to find patterns, extract insights, and create summaries. This capability enables faster decision-making by transforming complex information into actionable knowledge.
Personalization: Generative AI can tailor content, recommendations, or interactions based on individual preferences and behaviors. It adapts outputs to match user needs, creating more engaging, customized experiences across platforms.
Customizability: Users can fine-tune Generative AI models to meet specific goals or brand requirements. Whether adjusting the style, tone, or focus of outputs, these models offer flexibility to fit different industries and contexts.
Multi-modal capabilities: Generative AI is capable of handling multiple data types simultaneously, integrating text, images, audio, and video into unified outputs. This allows for richer, more dynamic content generation that bridges different media forms.
Use cases for Generative AI
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Generative AI powers more natural and dynamic conversations in chatbots and virtual assistants. It helps these systems understand user intent, generate human-like responses, and handle a wider range of customer queries without relying solely on pre-programmed scripts.
Content creation for Design: It supports designers by generating marketing visuals, social media graphics, website layouts, and branding elements. Creative prompts are quickly turned into multiple design variations, accelerating both ideation and production.
Education and Learning Assistance: In education, Generative AI crafts personalized learning materials, develops tutoring programs, and creates interactive assessments. Content is adapted dynamically to fit each learner’s style, making learning more accessible and engaging.
Product design and development: Across product teams, AI design tools powered by Generative AI spark innovation by producing design concepts, prototypes, and user-centric feature ideas. It enables quicker iterations, wider exploration, and greater efficiency in development processes.
Beyond these areas, Generative AI is also widely used in marketing and sales to create personalized campaigns, generate promotional content, and optimize customer engagement strategies.
Agentic AI vs Generative AI: A detailed comparison
Can you identify the key differences between Agentic AI and Generative AI? If you are wondering what is Agentic AI vs Generative AI, the core differences lie in their purpose, level of autonomy, applications, and limitations.
Take a look at the comparison below to better understand how these two powerful types of AI differ.
1. Primary Purpose
Agentic AI focuses on autonomously executing tasks to solve real-world problems. It operates with a goal-driven approach, handling everything from planning to execution while minimizing the need for constant human intervention.
Generative AI, on the other hand, centers around creating original content such as text, images, videos, or code. It relies on learned data models to respond to input prompts by generating new outputs that follow established patterns.
2. Level of Autonomy
Agentic AI is characterized by a high level of autonomy, capable of independently initiating actions, adapting to environmental changes, and pursuing goals without requiring continuous human guidance.
Generative AI, by contrast, functions with a more limited degree of autonomy. It primarily depends on user prompts to function and does not initiate new actions unless externally triggered.
3. Applications
Agentic AI is widely applied in fields that require autonomous decision-making, such as customer support automation, supply chain optimization, and workflow management. It effectively handles complex tasks that previously demanded significant human supervision.
Generative AI excels in creative domains like content production, graphic design, code generation, and writing assistance. Businesses leverage it to accelerate ideation and the development of creative assets across various industries.
4. Limitations
Agentic AI systems are complex to build and maintain, requiring strong technological infrastructure and strict governance frameworks to ensure safety, accuracy, and scalability.
Generative AI, although easier to implement, still heavily relies on the quality of its input data and training datasets. If not carefully managed, it may produce biased or inaccurate outputs, limiting its overall reliability.
Conclusion
As we’ve covered, Generative AI and Agentic AI each serve a distinct purpose and are not necessarily a "one or the other" choice. When used strategically, both can significantly optimize efficiency, creativity, and innovation for businesses.
In the design field, this combination becomes even more powerful. Generative AI accelerates ideation by creating diverse visual concepts and content, while Agentic AI acts more like a digital assistant, streamlining workflows and keeping projects aligned with client goals. Together, they help design teams move faster, think more creatively, and deliver with greater precision.
If you are looking for guidance on how to integrate Agentic AI and Generative AI into your product or service experiences, Lollypop is here to support!
As a global AI-Powered UI/UX Design Agency, we go beyond visuals by combining design thinking with the latest AI advancements to deliver experiences that are intelligent, adaptive, and future-ready.
Get in touch with us for a FREE consultation and discover how we can help you unlock the full potential of AI-powered design and drive real business impact.
You may want to read more: Transforming the Future of UX Through AI Conversational Interfaces
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can Agentic AI and Generative AI work together?
Yes, Agentic AI and Generative AI can work together effectively to boost overall performance. While Generative AI focuses on creating content, ideas, and solutions, Agentic AI autonomously plans, makes decisions, and carries out tasks based on those outputs. Together, they can enhance both creativity and operational efficiency across various industries.
2. What is the difference between Agentic AI vs AI Agents?
Agentic AI refers to the broader concept of AI systems that act autonomously, set goals, and make independent decisions. AI agents are specific implementations of this concept — individual programs or systems built to perform particular tasks using agentic principles. In short, AI agents are practical examples of Agentic AI in action.
3. How is Agentic AI different from RPA?
While both Agentic AI and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) aim to automate tasks, they operate very differently. RPA follows predefined rules and scripts to complete repetitive processes, often without adapting to new situations. Agentic AI, in contrast, can make context-aware decisions, adapt to changes, and pursue goals dynamically without being limited to fixed workflows.














































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)































































































































































































































































_incamerastock_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)




























































































![Senators reintroduce App Store bill to rein in ‘gatekeeper power in the app economy’ [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/06/app-store-senate.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)