Creating a Somatosensory Pathway From Human Stem Cells
Human biology is very much like that of other mammals, and yet so very different in areas where it matters. One of these being human neurology, with aspects like the …read more


Human biology is very much like that of other mammals, and yet so very different in areas where it matters. One of these being human neurology, with aspects like the human brain and the somatosensory pathways (i.e. touch etc.) being not only hard to study in non-human animal analogs, but also (genetically) different enough that a human test subject is required. Over the past years the use of human organoids have come into use, which are (parts of) organs grown from human pluripotent stem cells and thus allow for ethical human experimentation.
For studying aspects like the somatosensory pathways, multiple of such organoids must be combined, with recently [Ji-il Kim] et al. as published in Nature demonstrating the creation of a so-called assembloid. This four-part assembloid contains somatosensory, spinal, thalamic and cortical organoids, covering the entirety of such a pathway from e.g. one’s skin to the brain’s cortex where the sensory information is received.
Such assembloids are – much like organoids – extremely useful for not only studying biological and biochemical processes, but also to research diseases and disorders, including tactile deficits as previously studied in mouse models by e.g. [Lauren L. Orefice] et al. caused by certain genetic mutations in Mecp2 and other genes, as well as genes like SCN9A that can cause clinical absence of pain perception.
Using these assembloids the development of these pathways can be studied in great detail and therapies developed and tested.








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)
























































































































![From Accountant to Data Engineer with Alyson La [Podcast #168]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1744420903260/fae4b593-d653-41eb-b70b-031591aa2f35.png?#)


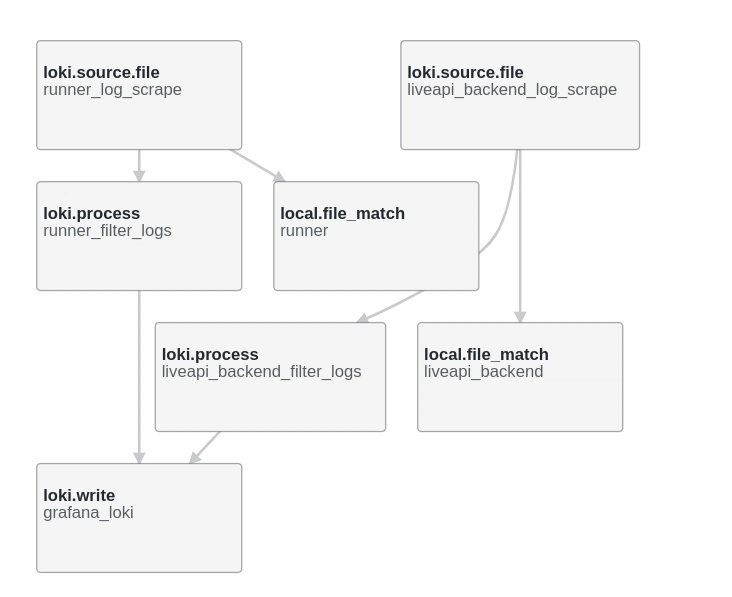

































































































.png?#)















































































































































![Apple Posts Full First Episode of 'Your Friends & Neighbors' on YouTube [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96990/96990/96990-640.jpg)

![Apple May Implement Global iPhone Price Increases to Mitigate Tariff Impacts [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96987/96987/96987-640.jpg)