Space-Based Datacenters Take The Cloud into Orbit
Where’s the best place for a datacenter? It’s an increasing problem as the AI buildup continues seemingly without pause. It’s not just a problem of NIMBYism; earthly power grids are …read more


Where’s the best place for a datacenter? It’s an increasing problem as the AI buildup continues seemingly without pause. It’s not just a problem of NIMBYism; earthly power grids are having trouble coping, to say nothing of the demand for cooling water. Regulators and environmental groups alike are raising alarms about the impact that powering and cooling these massive AI datacenters will have on our planet.
While Sam Altman fantasizes about fusion power, one obvious response to those who say “think about the planet!” is to ask, “Well, what if we don’t put them on the planet?” Just as Gerald O’Niell asked over 50 years ago when our technology was merely industrial, the question remains:
“Is the surface of a planet really the right place for expanding technological civilization?”
O’Neill’s answer was a resounding “No.” The answer has not changed, even though our technology has. Generative AI is the latest and greatest technology on offer, but it turns out it may be the first one to make the productive jump to Earth Orbit. Indeed, it already has, but more on that later, because you’re probably scoffing at such a pie-in-the-sky idea.
There are three things needed for a datacenter: power, cooling, and connectivity. The people at companies like Starcloud, Inc, formally Lumen Orbit, make a good, solid case that all of these can be more easily met in orbit– one that includes hard numbers.
Sure, there’s also more radiation on orbit than here on earth, but our electronics turn out to be a lot more resilient than was once thought, as all the cell-phone cubesats have proven. Starcloud budgets only 1 kg of sheilding per kW of compute power in their whitepaper, as an example. If we can provide power, cooling, and connectivity, the radiation environment won’t be a showstopper.
Power
There’s a great big honkin’ fusion reactor already available for anyone to use to power their GPUs: the sun. Of course on Earth we have tricky things like weather, and the planet has an annoying habit of occluding the sun for half the day but there are no clouds in LEO. Depending on your choice of orbit, you do have that annoying 45 minutes of darkness– but a battery to run things for 45 minutes is not a big UPS, by professional standards. Besides, the sun-synchronous orbits are right there, just waiting for us to soak up that delicious, non-stop solar power.

Sun-synchronous orbits (SSOs) are polar orbits that precess around the Earth once every sidereal year, so that they always maintain the same angle to the sun. For example, you might have an SSO that crosses the equator 12 times a day, each time at local 15:00, or 10:43, any other time set by the orbital parameters. With SSOs, you don’t have to worry about ever losing solar power to some silly, primitive, planet-bound concept like nighttime.
Without the atmosphere in the way, solar panels are also considerably more effective per unit area, something the Space Solar Power people have been pointing out since O’Neill’s day. The problem with Space Solar Power has always been the efficiencies and regulatory hurdles of beaming the power back to Earth– but if you use the power to train an AI model, and send the data down, that’s no longer an issue. Given that the 120 kW array on ISS has been trouble-free for decades now, we can consider it a solved problem. Sure, solar panels degrade, but the rate is in fractions of a percent per year, and it happens on Earth too. By the time solar panel replacement is likely to be the rest of the hardware is likely to be totally obsolete.
Cooling
This is where skepticism creeps in. After all, cooling is the greatest challenge with high performance computing hardware here on earth, and heat rejection is the great constraint of space operations. The “icy blackness of space” you see in popular culture is as realistic as warp drive; space is a thermos, and shedding heat is no trivial issue. It is also, from an engineering perspective, not a complex issue. We’ve been cooling spacecraft and satellites using radiators to shed heat via infrared emission for decades now. It’s pretty easy to calculate that if you have X watts of heat to reject at Y degrees, you will need a radiator of area Z. The Stephan-Boltzmann Law isn’t exactly rocket science.

Even better, unlike on Earth where you have changeable things like seasons and heat waves, in a SSO you need only account for throttling– and if your data center is profitable, you won’t be doing much of that. So while you need a cooling system, it won’t be difficult to design. Liquid or two-phase cooling on server hardware? Not new. Plumbing cooling a loop to a radiator in the vacuum of space? That’s been part of satellite busses for years.
Aside from providing you with a stable thermal environment, the other advantage of an SSO is that if one chooses the dawn/dusk orbit along the terminator, while the solar panels always face the sun, the radiators can always face black space, letting them work to their optimal potential. This would also simplify the satellite bus, as no motion system would be required to keep the solar panels and radiators aligned into/out of the sun. Conceivably the whole thing could be stabilized by gravity gradient, minimizing the need to use reaction wheels.
Connectivity
One word: Starlink. That’s not to say that future data centers will necessarily be hooking into the Starlink network, but high-bandwidth operations on orbit are already proven, as long as you consider 100 gigabytes per second sufficient bandwidth. An advantage not often thought of for this sort of space-based communications is that the speed of light in a vacuum is about 31% faster than glass fibers, while the circumference of a low Earth orbit is much less than 31% greater than the circumference of the planet. That reduces ping times between elements of free-flying clusters or clusters and whatever communications satellite is overhead of the user. It is conceivable, but by no means a sure thing, that a user in the EU might have faster access to orbital data than they would to a data center in the US.
The Race
This hypothetical European might want to use European-owned servers. Well, the European Commission is on it; in the ASCEND study (Advanced Space Cloud for European Net zero Emission and Data sovereignty) you can tell from the title they put as much emphasis on keeping European data European as they do on the environmental aspects mentioned in the introduction. ASCEND imagines a 32-tonne, 800 kW data center lofted by a single super-heavy booster (sadly not Ariane 6), and proposes it could be ready by the 2030s. There’s no hint in this proposal that the ASCEND Consortium or the EC would be willing to stop at one, either. European efforts have already put AI in orbit, with missions like PhiSat2 using on-board AI image processing for Earth observation.


The Americans, of course, are leaving things to private enterprise. Axiom Space has leveraged their existing relationship with NASA to put hardware on ISS for testing purposes, staring with an AWS snowcone in 2022, which they claimed was the first flight-test of cloud computing. Axiom has also purchased space on the Kepler Relay Network satellites set to launch late 2025. Aside from the 2.5 Gb/s optical link from Kepler, exactly how much compute power is going into these is not clear. A standalone data center is expected to follow in 2027, but again, what hardware will be flying is not stated.
There are other American companies chasing venture capital for this purpose, like Google-founder-backed Relativity Space or the wonderfully-named Starcloud mentioned above. Starcloud’s whitepaper is incredibly ambitious, talking about building an up to 5 GW cluster whose double-sided solar/radiator array would be by far the largest object ever built in orbit at 4 km by 4 km. (Only a few orders of magnitude bigger than ISS. Not big deal.) At least it is a modular plan, that could be built up over time, and they are planning to start with a smaller standalone proof-of-concept, Starcloud-2, in 2026.


Once they get up there, the American and European AIs are are going to find someone else has already claimed the high ground, and that that someone else speaks Chinese. A startup called ADA Space launched 12 satellites in May 2025 to begin building out the world’s first orbital supercomputer, called the Three Body Computing Constellation. (You can’t help but love the poetry of Chinese naming conventions.)
Unlike the American startups, they aren’t shy about its capabilities: 100 Gb/s optical datalinks, with the most powerful satellite in the constellation capable of 744 trillion operations per second. (TOPS, not FLOPS. FLOPS specifically refers to floating point operations, whereas TOPS could be any operation but usually refers to operations on 8-bit integers.)
For comparison, Microsoft requires an “AI PC” like the copilot laptops to have 40 TOPS of AI-crunching capacity. The 12 satellites must not be identical, as the constellation together has a quoted capability of 5 POPS (peta-operations per second), and a storage capacity of 30 TB. That’s seems pretty reasonable for a proof-of-concept. You don’t get a sense of the ambition behind it until you hear that these 12 are just the first wave of a planned 2,800 satellites. Now that’s what I’d call a supercluster!

High-performance computing in space? It’s no AI hallucination, it’s already here. There is a network forming in the sky. A sky-net, if you will, and I for one welcome our future AI overlords. They already have the high ground, so there’s no point fighting now. Hopefully this datacenter build-out will just be the first step on the road Gerry O’Neill and his students envisioned all those years ago: a road that ends with Earth’s surface as parkland, and civilization growing onwards and upwards. Ad astra per AI? There are worse futures.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 153]: OpenAI Releases o3-Pro, Disney Sues Midjourney, Altman: “Gentle Singularity” Is Here, AI and Jobs & News Sites Getting Crushed by AI Search](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20153%20cover.png)






















































































































![[DEALS] Internxt Cloud Storage Lifetime Subscription (20TB) (89% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



















































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





















![GrandChase tier list of the best characters available [June 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33057-1637756796/grandchase-ios-android-3rd-anniversary.jpg?#)






































































_Paul_Markillie_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)































































































![Nothing Phone (3) has ‘Glyph Matrix’ lights in corner, leaked design was likely wrong [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/nothing-phone-3-glyph-matrix-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
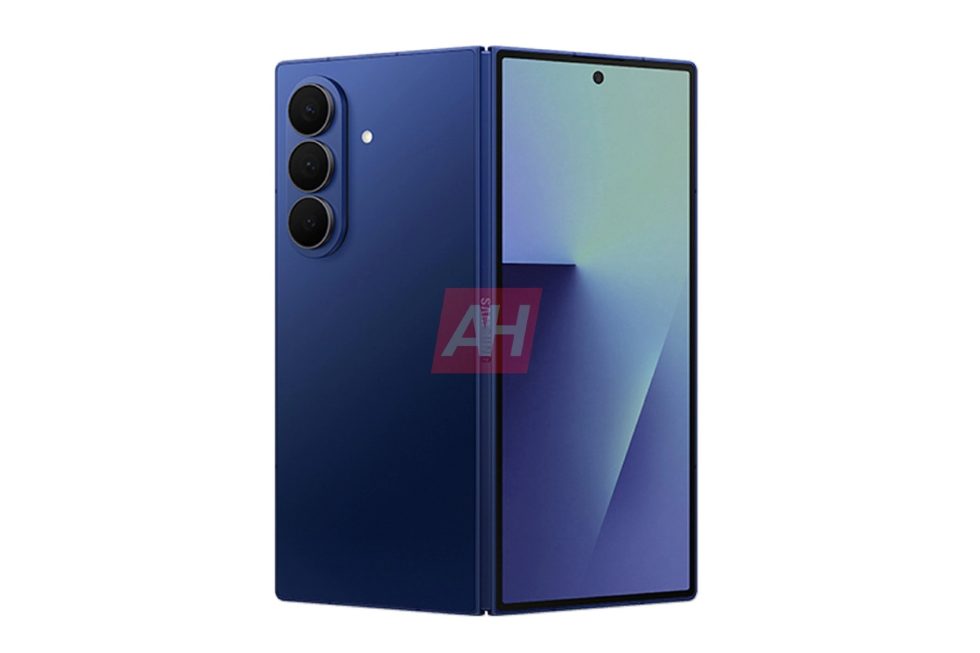
![Galaxy Z Fold 7 leaks in first official-looking renders with thin design, slick blue color [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/galaxy-z-fold-7-leak-ah-9.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![iPhone 18 Pro Models to Feature Under-Display Face ID, Keep Same Display Sizes [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97657/97657/97657-640.jpg)
![Apple M4 Mac Mini Drops to Just $469 — Save $130 [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97659/97659/97659-640.jpg)

![Apple Shares New Shot on iPhone Film: 'Big Man' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97654/97654/97654-640.jpg)