Application Framework: Cross-App Navigation Practice in HarmonyOS
Application Framework: Cross-App Navigation Practice Concept and Scenarios of Cross-App Navigation Typical Scenario Implementation: Social Sharing Typical Scenario Implementation: Ad Redirection Typical Scenario Implementation: Special Text Recognition Common Issues Summary Concept and Scenarios of Cross-App Navigation Concept of Cross-App Navigation Cross-app navigation refers to the process of navigating from the currently used app (caller) to another app (target) for continued business operations. Caller and Target: In the app launch process, when app A launches app B, app A is the caller, and app B is the target. import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; const link = 'https://appgallery.huawei.com/app/detail?id=com.huawei.hmsapp.books' @Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Column() { Text('Caller') Button('Go to App Market').onClick(()=> { let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext context.openLink(link) }) } .height('100%') .width('100%') } } Cross-App Navigation in Daily Life Links shared in social media that direct to specific content pages in the original app. Video app splash screen ads that redirect to a specific product details page. Calendar invitation links that directly add events to the system calendar. Typical Scenario 1: Social Sharing Redirection Share content links containing App Linking through the system share panel to friends, achieving a one-click direct access to the original content. Typical Scenario 2: Ad Redirection Use App Linking to accurately redirect from an advertisement link to a specific app page, increasing marketing conversion rates. Typical Scenario 3: Special Text Recognition Redirection Utilize the system’s text recognition capabilities to identify special texts and directly redirect to functionality from text. Cross-App Navigation Implementation Plan Based on the determinability of the target app, cross-app navigation can be divided into two categories: Launch a specific app: Directly navigate to a designated app and its specific page (e.g., app A redirects to product detail page in app B). Launch a specific type of app: Let the system recommend an app capable of carrying out a task based on the function intent, allowing the user to choose. For example, when navigating, the user can select any map app. Launch a Specific App Launching a specific app refers to scenarios where the target app is explicitly specified for navigation. The system offers two main implementation methods: 1. App Linking (App Linking and Deep Linking) App Linking: Achieves more secure and reliable navigation via domain verification and HTTPS protocols. When the target app is not installed, it can open a web page, providing a better user experience. Deep Linking: Easier to implement but carries the risk of being impersonated by malicious sources. Compared to Deep Linking, App Linking has the following advantages: Security: Ensures only legitimate apps are launched through end-to-cloud security authorization and domain validation. Direct Experience: No secondary confirmation is needed, allowing a direct jump to a specific page in the app. Direct to App Market: When the app is not installed, it can redirect to the app market's app detail page. Deferred Link: Supports restoring the previous navigation intent after app installation. App Linking is more recommended. 2. System App Redirection The system provides several capabilities and interfaces to allow developers to quickly implement redirection to system apps, such as settings, app market, wallet, phone, calendar, contacts, etc., while ensuring access security. Refer to "Launching System Apps" for details. Launch a Specific Type of App In some scenarios, developers wish to implement functionality based on user intent rather than a specific app, such as using any supported map app for navigation. In such cases, developers do not specify a specific app. Instead, the system queries all apps on the device that match the criteria, and the user selects which app to use for the task. Typical Scenario Implementation: Social Sharing Scenario Description Scenario 1: Target App Installed When the user clicks a shared link, the system directly launches the target app and navigates to the content detail page without going through a browser, enabling one-click access and greatly enhancing convenience and conversion rates. Scenario 2: Target App Not Installed, Direct to App Market Configured When the user hasn't installed the target app and the developer has configured the direct link to the app market, clicking the link will directly redirect to the app market's app detail page. After installation, the app will automatically navigate to the original shared content via def
Application Framework: Cross-App Navigation Practice
- Concept and Scenarios of Cross-App Navigation
- Typical Scenario Implementation: Social Sharing
- Typical Scenario Implementation: Ad Redirection
- Typical Scenario Implementation: Special Text Recognition
- Common Issues
- Summary
Concept and Scenarios of Cross-App Navigation
Concept of Cross-App Navigation
Cross-app navigation refers to the process of navigating from the currently used app (caller) to another app (target) for continued business operations.
- Caller and Target: In the app launch process, when app A launches app B, app A is the caller, and app B is the target.
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
const link = 'https://appgallery.huawei.com/app/detail?id=com.huawei.hmsapp.books'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Column() {
Text('Caller')
Button('Go to App Market').onClick(()=> {
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext
context.openLink(link)
})
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
}
Cross-App Navigation in Daily Life
- Links shared in social media that direct to specific content pages in the original app.
- Video app splash screen ads that redirect to a specific product details page.
- Calendar invitation links that directly add events to the system calendar.
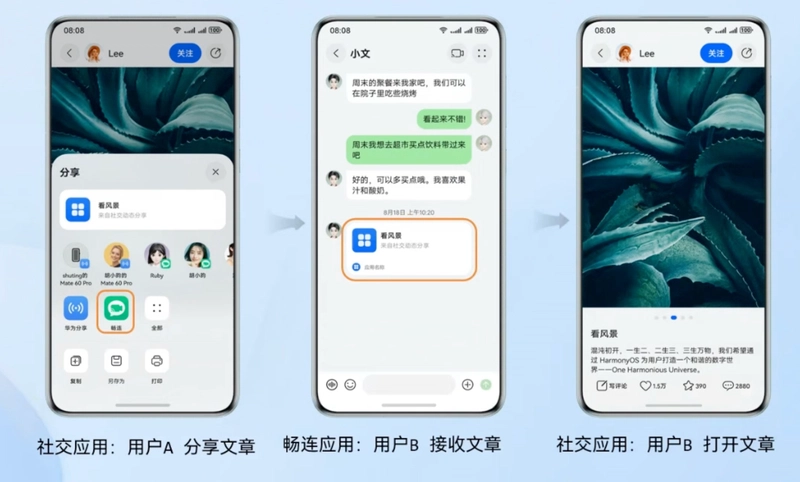
Typical Scenario 1: Social Sharing Redirection
Share content links containing App Linking through the system share panel to friends, achieving a one-click direct access to the original content.
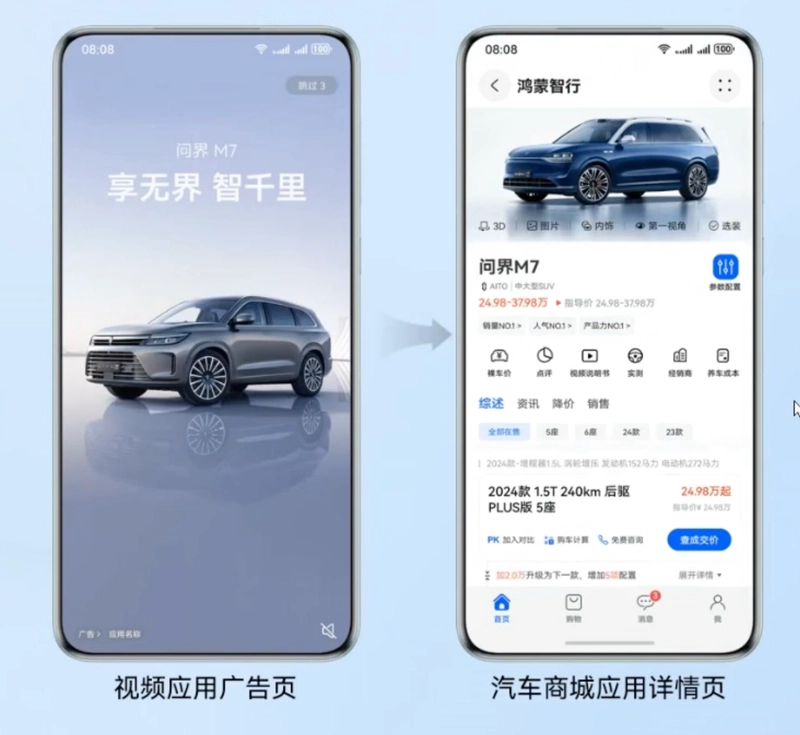
Typical Scenario 2: Ad Redirection
Use App Linking to accurately redirect from an advertisement link to a specific app page, increasing marketing conversion rates.
Typical Scenario 3: Special Text Recognition Redirection
Utilize the system’s text recognition capabilities to identify special texts and directly redirect to functionality from text.

Cross-App Navigation Implementation Plan
Based on the determinability of the target app, cross-app navigation can be divided into two categories:
- Launch a specific app: Directly navigate to a designated app and its specific page (e.g., app A redirects to product detail page in app B).
- Launch a specific type of app: Let the system recommend an app capable of carrying out a task based on the function intent, allowing the user to choose. For example, when navigating, the user can select any map app.
Launch a Specific App
Launching a specific app refers to scenarios where the target app is explicitly specified for navigation. The system offers two main implementation methods:
1. App Linking (App Linking and Deep Linking)
- App Linking: Achieves more secure and reliable navigation via domain verification and HTTPS protocols. When the target app is not installed, it can open a web page, providing a better user experience.
- Deep Linking: Easier to implement but carries the risk of being impersonated by malicious sources.
Compared to Deep Linking, App Linking has the following advantages:
- Security: Ensures only legitimate apps are launched through end-to-cloud security authorization and domain validation.
- Direct Experience: No secondary confirmation is needed, allowing a direct jump to a specific page in the app.
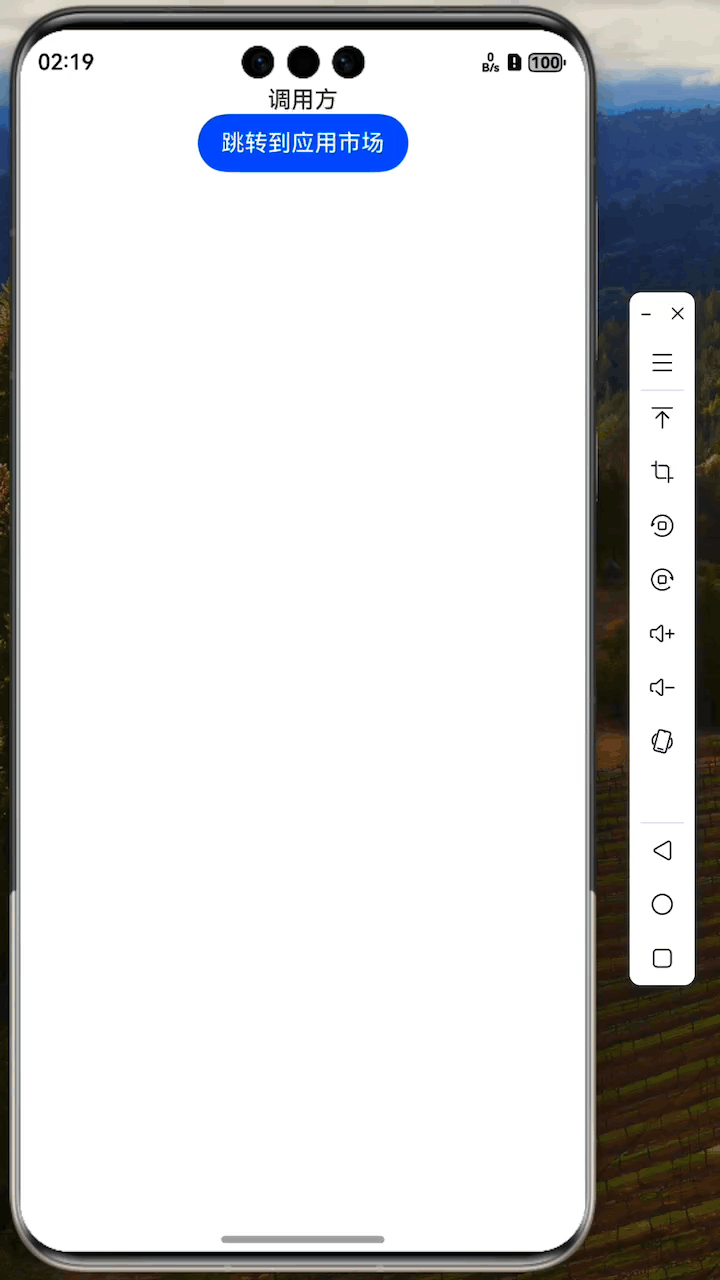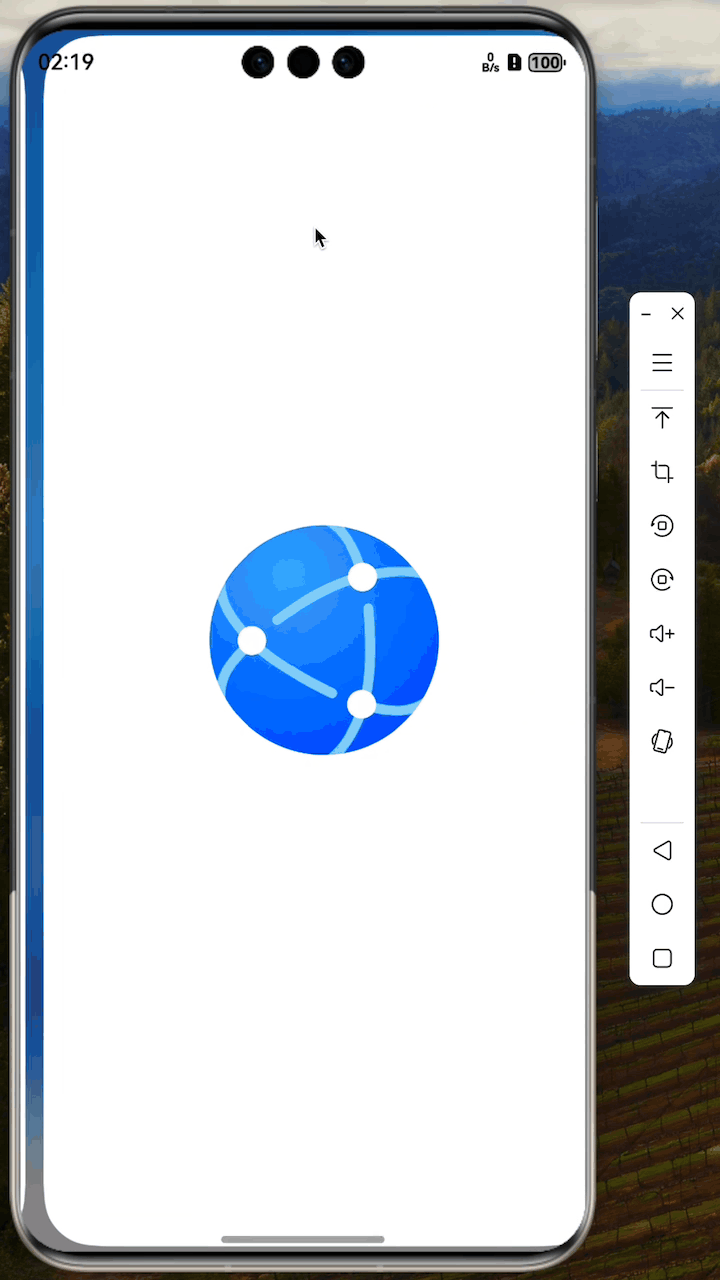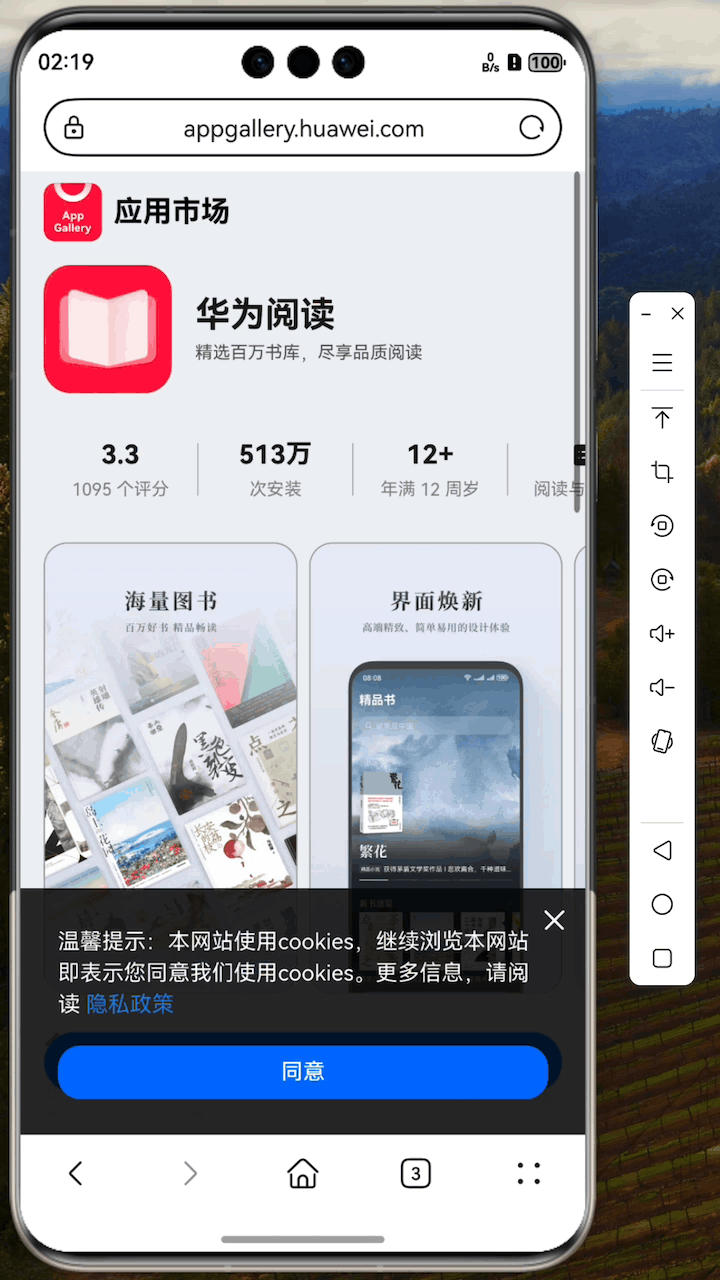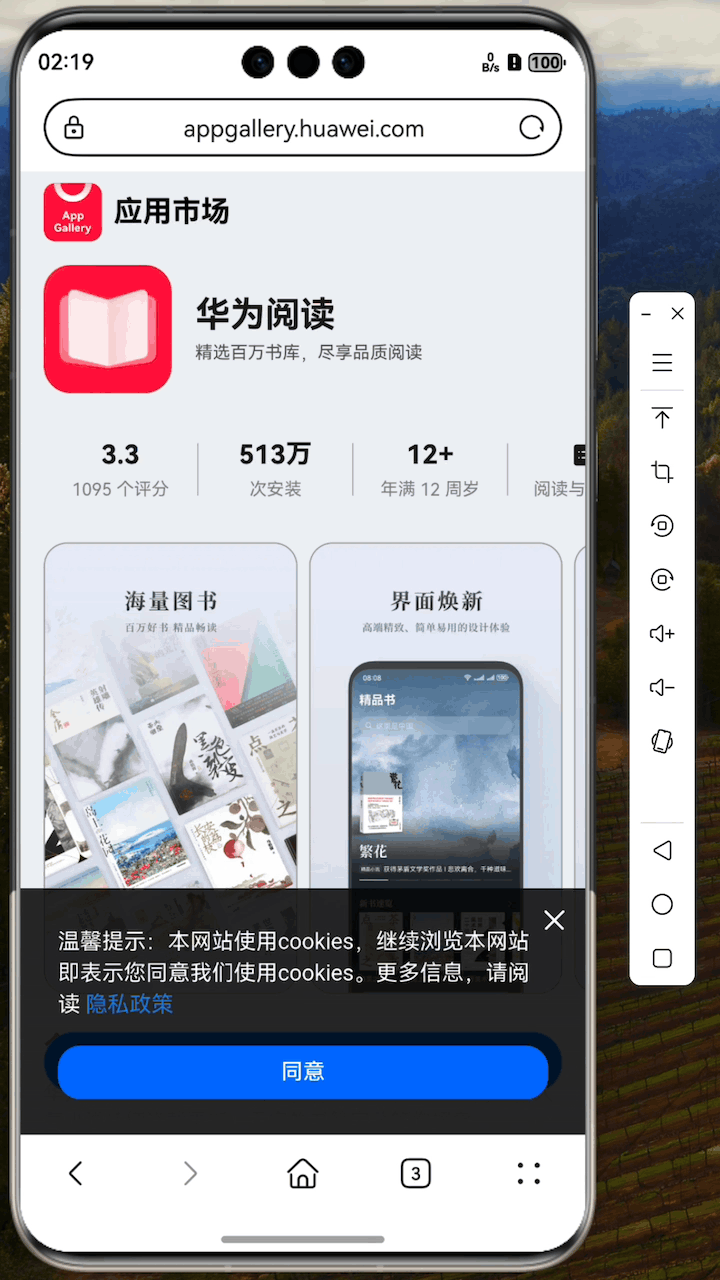
- Direct to App Market: When the app is not installed, it can redirect to the app market's app detail page.
-
Deferred Link: Supports restoring the previous navigation intent after app installation.

- App Linking is more recommended.
2. System App Redirection
The system provides several capabilities and interfaces to allow developers to quickly implement redirection to system apps, such as settings, app market, wallet, phone, calendar, contacts, etc., while ensuring access security. Refer to "Launching System Apps" for details.

Launch a Specific Type of App
In some scenarios, developers wish to implement functionality based on user intent rather than a specific app, such as using any supported map app for navigation.
In such cases, developers do not specify a specific app. Instead, the system queries all apps on the device that match the criteria, and the user selects which app to use for the task.
Typical Scenario Implementation: Social Sharing
Scenario Description
Scenario 1: Target App Installed
When the user clicks a shared link, the system directly launches the target app and navigates to the content detail page without going through a browser, enabling one-click access and greatly enhancing convenience and conversion rates.
Scenario 2: Target App Not Installed, Direct to App Market Configured
When the user hasn't installed the target app and the developer has configured the direct link to the app market, clicking the link will directly redirect to the app market's app detail page. After installation, the app will automatically navigate to the original shared content via deferred link functionality without the user needing to search or take further actions.
Scenario 3: Target App Not Installed, No Direct Link to App Market Configured (Has Web Page)
When the user clicks the link, the system opens the web page in the browser, allowing the user to directly view the content. The web page may offer a “Download” button to guide the user to install the app for a better experience. After installation, the app can still use the deferred link to direct the user to the original content.
Overall Process
The process is divided into two types of content: one for what the social app needs to do, and another for the behavior of the intermediate or system app. For example, if user A shares an article link on their social account, typically an app link, it will first be processed by the share panel, which sends it to a sharing app.
In the case of user B, the shared link can be clicked within the sharing app. Depending on whether the social app is installed, if installed, it will directly jump to the article detail page. If not installed, the system will check for the API15 capability to offer a direct link to the app market. If configured, the app market detail page will open, and upon installation, the deferred link feature will bring the user to the original content.
If not API15, the browser will open, showing the web content, and the user may be guided to download the app. This method still ensures that the user can be directed to the target page with a one-click solution upon first use.
Social Sharing Redirection Overview
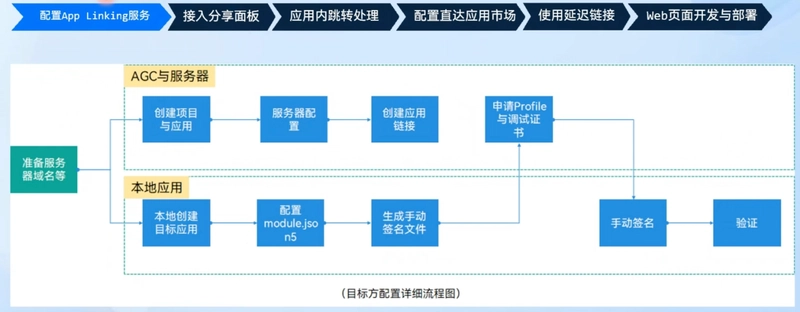
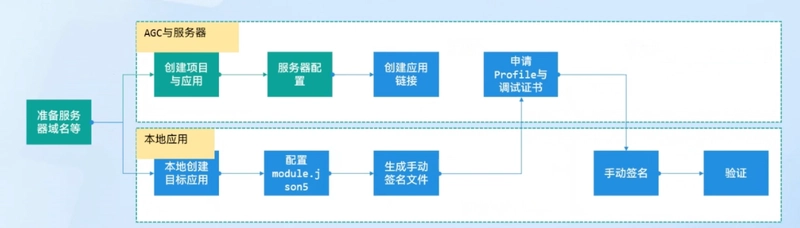
Configuring AppLinking Service -- Preparation
Prerequisites:
- A server
- Domain name (recommended to file for record)
- SSL certificate, as AppLinking links only support http links
- Huawei account
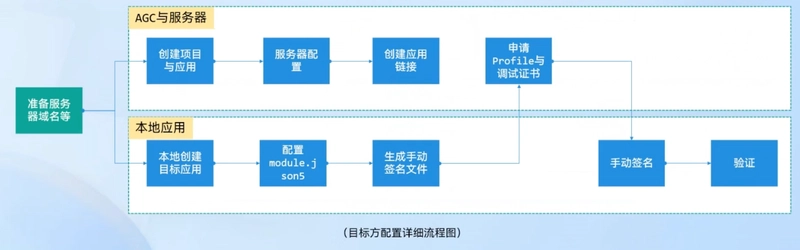
Configuring AppLinking Service -- Server Configuration
- Create a .well-known folder on your website
- In that folder, create an applinking.json file with the following content. The appIdentifier is the app’s APPID:
{
"applinking": {
"apps": [
{
"appIdentifier": "appId" // Generated App ID during app creation
}
]
}
}
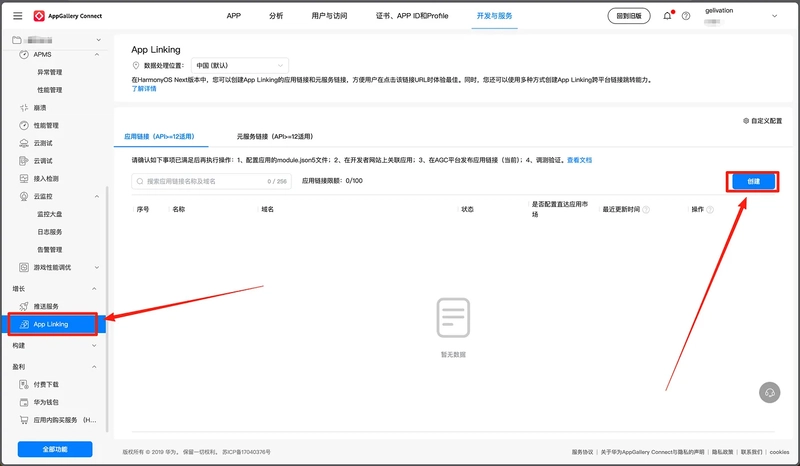
Creating an App Link
Configuring AppLinking Service -- Creating the App
Configuring AppLinking Service -- Configuring module.json5
If it’s a single HAP, the following must be configured under entry in module.json5:
"skills": [
{
"entities": [
"entity.system.home" // Required configuration
],
"actions": [
"action.system.home" // Required configuration
],
"uris": [
{
"scheme": "https",
"host": "",
"path":"path1"
}
],
"domainVerify": true
}
]
Once configured, sometimes links don’t work because the URL hasn’t matched, so check the matching rules, especially for path features.
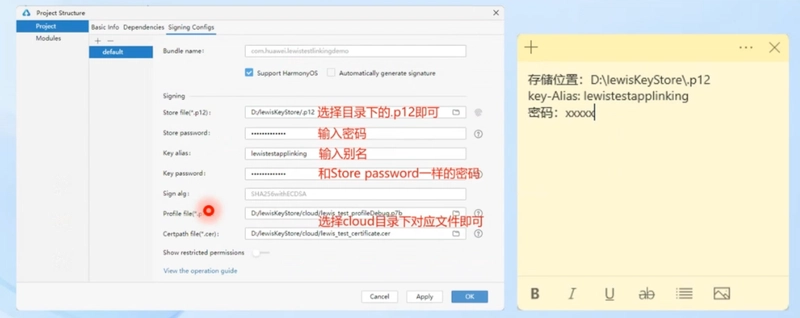
Configuring AppLinking Service -- Generating Manual Signing Files
Configuring AppLinking Service -- Verification
- Simply write the AppLinking URL in a memo and click to see if it launches. This is a quicker method than writing code.
- There are two more methods through code or commands, but these are easier to look up.
Integrating the Share Panel
By integrating Share Kit (sharing service), the share panel is used to share the AppLinking link to article details.

Target App Configuration Process -- Integrating the Share Panel
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit'
import { systemShare } from '@kit.ShareKit'
import { uniformTypeDescriptor } from '@kit.ArkData'
@Component
struct Detail {
private async share() {
let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext
//...
let shareData: systemShare.SharedData = new systemShare.SharedData({
utd: uniformTypeDescriptor.UniformDataType.HYPERLINK, // Set share data type as hyperlink
content: `https//xxxxxxx?aid=aid`, // Share the AppLinking link
//...
})
let controller: systemShare.ShareController = new systemShare.ShareController(shareData)
controller.show(context, { // Show share panel
previewMode: systemShare.SharePreviewMode.DEFAULT,
selectionMode: systemShare.SelectionMode.SINGLE
})
//...
}
build() {
}
}
In-App Navigation Handling (Key Part)
export default class Go1Ability extends UIAbility {
private uiContext: UIContext | undefined = undefined
private mAid: string = ''
/**
* Parse parameters in the link
* @param want
* @returns
*/
getAid(want: Want): string {
let uri = want?.uri
let aid: string = ''
if (uri) {
let urlObject = url.URL.parseURL(want?.uri)
aid = urlObject.params.get('aid') as string
}
return aid
}
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
this.mAid = this.getAid(want)
}
onNewWant(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
let aid: string = this.getAid(want)
if (aid && aid !== '') {
// Redirect to the specified page
}
}
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void {
let pageUrl: string = 'pages/Index'
if (this.mAid && this.mAid !== '') {
pageUrl = 'pages/Detail'
AppStorage.setOrCreate('aid', this.mAid)
}
windowStage.loadContent(pageUrl) // Redirect to the target page
}
}
In our AppLinking sharing to user B, once the app is opened, how do we parse the link and navigate to the corresponding detail page? We use getAid() to parse the AppLinking link and the special identifier. With this identifier, we use the onCreate or onNewWant callback methods, and onWindowStageCreate to determine the appropriate page to load.
Page Parsing Inside the App
@Component
struct Detail {
@StorageProp('aid') aid: string = ''
private article: Article | undefined // Get article unique identifier aid
aboutToAppear(): void {
if (this.aid && this.aid !== '') {
this.article = getArticlebyId(this.aid)
} else {
}
}
build() {
}
}
Configuring Direct App Market Redirection
For API15 and above, the Direct to App Market feature can be configured.

Using Deferred Links
Use the deferredLink.popDeferredLink() interface to fetch the original AppLinking link and redirect to the corresponding content detail page.
aboutToAppear(): void {
// Fetch the deferred link and navigate to the target page
deferredLink.popDeferredLink().then((link: string)=> {
if (link) {
// Parse the link parameters
let urlObject = url.URL.parseURL(link)
let aid = urlObject.params.get('aid') as string
// Redirect to the detail page
this.getUIContext().getRouter().pushUrl({
url: 'pages/Detail',
params: {
aid: aid
}
})
}
})
}
Web Page Development and Deployment
Ensuring consistency across multiple platforms

Ad Redirection
Splash Ads => Redirect to Detail Page
Similar to the sharing process
Redirection Process
Special Text Recognition Redirection
Activate the enableDataDetector attribute on the Text component to automatically recognize and mark special texts like links, dates, phone numbers, addresses, emails, etc.
Text('Phone 19988888888')
.enableDataDetector(true)
Common Issues
How to check if AppLinking is configured successfully on AGC?

What to do if configuration fails?
- First, if the AppLinking status shows failure, it doesn’t necessarily mean an error in configuration. It may be correctly configured but AGC has not updated in time. You can delete and re-add the link to verify. If the issue persists, it could be a server configuration issue.
- AppLinking links only support HTTPS, so if it is HTTP, SSL certificates need to be applied.
- Ensure the configuration file is in the correct directory with proper access rights for external access.
- If none of the above works, it’s recommended to seek help from website operation and maintenance staff for further troubleshooting.
AGC shows the link address is configured successfully, but when trying to use openLink() or other methods to launch the app, the app doesn’t open.
- AGC configures AppLinking links with a "/" at the end. Check if the link in AGC has an extra "/".
- Check if the link in module.json5 matches the one configured in AGC.
- If the app hasn’t manually applied for a certificate for signing, developers should follow the procedure to manually apply for certificates and profiles for signing.
- The developer's network may have restrictions. Try using a different network.
- Incorrect configuration in module.json5.
Summary
- Cross-app navigation scenarios
- Implementation plan for cross-app navigation
- Configuring App Linking
- How the caller passes parameters to the target app and how the target app receives them, and returns results to the caller
- Adapting link addresses in cases where the app is not installed while using App Linking
- Common issues
I am Gelivation, a knowledge conveyor.
Live replay: Application Navigation Technology and Best Practices - Zhao Yichun












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 152]: ChatGPT Connectors, AI-Human Relationships, New AI Job Data, OpenAI Court-Ordered to Keep ChatGPT Logs & WPP’s Large Marketing Model](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20152%20cover.png)


















































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] Natural Language Processing with Python, Microsoft 365 Copilot At Work & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



















































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


















































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

_designer491_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)





























































































![The new Google TV setup process is impressively fast and easy [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/Google-TV-logo.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

![Apple’s latest CarPlay update revives something Android Auto did right 10 years ago [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/carplay-live-activities-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)










![3DMark Launches Native Benchmark App for macOS [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97603/97603/97603-640.jpg)
![Craig Federighi: Putting macOS on iPad Would 'Lose What Makes iPad iPad' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97606/97606/97606-640.jpg)