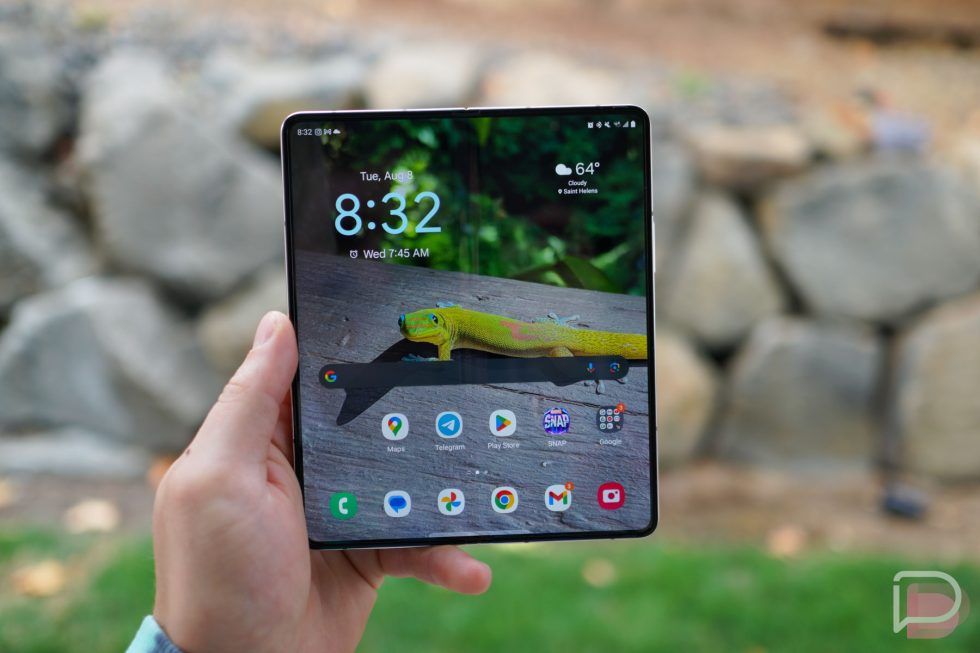
Mental Models for Vector Dimensions
Personalized insight for intuitively understanding vector dimensions 1. Ways to Conceptualize Dimensions A) Physical Dimensions (Degrees of Freedom) Definition: Independent directions along which an entity can move or shift. 4D Illustration: Four available paths: East/West (X-axis) North/South (Y-axis) Up/Down (Z-axis) Forward-only in time (Time axis) Analogy: Imagine controlling a toy car in a video game: Use left/right buttons to steer (east/west). Use forward/back buttons to accelerate or reverse (north/south). Press a jump button to lift off ramps (up/down). A race timer shows elapsed time, counting forward only. B) Characteristic Dimensions (Independent Traits) Definition: Distinct properties required to describe an entity fully. 4D Illustration: Four attributes defining a profile. Analogy: A game character defined by Strength, Agility, Intelligence, and Charisma. The vector (7,5,9,3) conveys the complete trait set instantly. 2. Time as the Fourth Dimension Adapting Each Model to Include Time: Physical View Analogy: A boat sailing on a lake: a) Move forward/backward and left/right (2 Dimensions). b) Transforms into a submarine, allowing it to dive below and surface back up on the lake (up/down axis, 3rd Dimension). c) The clock tracks how long you sail, time flows forward (4th Dimension) Characteristic View Analogy: A photo catalog uses tags such as location, subject, mood, and date to describe images. Date functions (representing time) as an additional tag alongside other attributes. It is easier to digest time as a dimension here. 3. What Does a 2D Vector Represent? When a statement reads "A 2d Vector ...", what could that translate to? Movement Interpretation: It can describe an object with two independent ways of movement (degrees of freedom). Characteristic Interpretation: It can also represent an object defined by two unique characteristics (traits).

Personalized insight for intuitively understanding vector dimensions
1. Ways to Conceptualize Dimensions
A) Physical Dimensions (Degrees of Freedom)
Definition: Independent directions along which an entity can move or shift.
-
4D Illustration: Four available paths:
- East/West (X-axis)
- North/South (Y-axis)
- Up/Down (Z-axis)
- Forward-only in time (Time axis)
-
Analogy: Imagine controlling a toy car in a video game:
- Use left/right buttons to steer (east/west).
- Use forward/back buttons to accelerate or reverse (north/south).
- Press a jump button to lift off ramps (up/down).
- A race timer shows elapsed time, counting forward only.
B) Characteristic Dimensions (Independent Traits)
Definition: Distinct properties required to describe an entity fully.
4D Illustration: Four attributes defining a profile.
Analogy: A game character defined by Strength, Agility, Intelligence, and Charisma. The vector (7,5,9,3) conveys the complete trait set instantly.
2. Time as the Fourth Dimension
Adapting Each Model to Include Time:
Physical View Analogy:
A boat sailing on a lake:
a) Move forward/backward and left/right (2 Dimensions).
b) Transforms into a submarine, allowing it to dive below
and surface back up on the lake (up/down axis, 3rd Dimension).
c) The clock tracks how long you sail, time flows forward (4th Dimension)Characteristic View Analogy:
A photo catalog uses tags such as location, subject, mood, and
date to describe images. Date functions (representing time) as an
additional tag alongside other attributes. It is easier to digest
time as a dimension here.
3. What Does a 2D Vector Represent?
When a statement reads "A 2d Vector ...", what could that translate to?
-
Movement Interpretation:
- It can describe an object with two independent ways of movement (degrees of freedom).
-
Characteristic Interpretation:
- It can also represent an object defined by two unique characteristics (traits).









































































![[The AI Show Episode 156]: AI Answers - Data Privacy, AI Roadmaps, Regulated Industries, Selling AI to the C-Suite & Change Management](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20156%20cover.png)






























































































![[The AI Show Episode 155]: The New Jobs AI Will Create, Amazon CEO: AI Will Cut Jobs, Your Brain on ChatGPT, Possible OpenAI-Microsoft Breakup & Veo 3 IP Issues](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20155%20cover.png)
















































































































































































































































































































































































![Mercedes, Audi, Volvo Reject Apple's New CarPlay Ultra [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97711/97711/97711-640.jpg)