Hackers Actively Exploit Patched Fortinet FortiGate Devices to Gain Root Access Using Symbolic Link
Fortinet has uncovered a sophisticated post-exploitation technique used by a threat actor to maintain unauthorized access to FortiGate devices, even after initial vulnerabilities were patched. The discovery, detailed in a recent Fortinet investigation, highlights the persistent risks of unpatched systems and underscores the company’s commitment to responsible transparency and rapid response. According to Fortinet’s findings, […] The post Hackers Actively Exploit Patched Fortinet FortiGate Devices to Gain Root Access Using Symbolic Link appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Fortinet has uncovered a sophisticated post-exploitation technique used by a threat actor to maintain unauthorized access to FortiGate devices, even after initial vulnerabilities were patched.
The discovery, detailed in a recent Fortinet investigation, highlights the persistent risks of unpatched systems and underscores the company’s commitment to responsible transparency and rapid response.
According to Fortinet’s findings, the threat actor exploited known vulnerabilities previously identified as FG-IR-22-398, FG-IR-23-097, and FG-IR-24-015—to gain access to FortiGate devices.
- CVE-2022-42475: Tied to FG-IR-22-398, used in the attack.
- CVE-2023-27997: Tied to FG-IR-23-097, used in the attack.
- CVE-2024-21762: Not explicitly confirmed, possible link to FG-IR-24-015 but uncertain.
How Does this Attack Initiated
In a novel approach, the actor created a symbolic link between the user and root filesystems in a folder serving language files for SSL-VPN. This allowed read-only access to device files, including configurations, without triggering detection.
Alarmingly, the link could persist even after devices were updated to address the original vulnerabilities, leaving systems exposed.
Fortinet’s investigation, supported by internal telemetry and third-party collaboration, confirmed that the activity was not limited to a specific region or industry. Customers who never enabled SSL-VPN on their devices are unaffected by this issue.
Upon identifying the technique, Fortinet activated its Product Security Incident Response Team (PSIRT) and implemented immediate mitigations. These include:
- Releasing an AV/IPS signature to detect and remove the malicious symbolic link.
- Modifying FortiOS versions 7.6.2, 7.4.7, 7.2.11, 7.0.17, and 6.4.16 to eliminate the link and secure SSL-VPN functionality.
- Directly notifying affected customers and urging them to upgrade to the latest releases, review configurations, and treat existing setups as potentially compromised.
Fortinet recommends that all customers impacted or not upgrade to the patched versions and follow recovery steps outlined in its community resources.
The company emphasized the urgency of timely updates, citing its 2H 2023 Global Threat Landscape Report, which found that threat actors exploit known vulnerabilities within an average of 4.76 days of public disclosure.
“This incident reflects the evolving tactics of threat actors and the critical need for robust cyber hygiene,” said Carl Windsor, a Fortinet spokesperson to Cyber Security News “We’re committed to supporting our customers with proactive solutions and transparent communication to stay ahead of these threats.”
To bolster defenses, Fortinet has introduced enhanced security features in recent updates, including compile-time hardening, virtual patching, firmware integrity validation, and automated upgrade tools like Uninterrupted Cluster Upgrade and Automatic Patch Upgrades.
The company continues to advocate for industry-wide collaboration to strengthen cybersecurity standards.
Customers seeking guidance can access Fortinet’s best practice resources or contact the company directly for support. With over 40,000 vulnerabilities recorded in 2024, according to NIST data, Fortinet’s message is clear: staying vigilant and up to date is the best defense against today’s cyber threats.
The founder of WatchTowr reported that backdoor deployments linked to the Fortinet exploit are being identified across their client base—including organizations deemed critical infrastructure. He urged the community to take Fortinet’s alert seriously, while questioning the industry’s current response process to high-profile vulnerabilities in critical systems.
CISA’s Recommendations
CISA’s April 11 advisory reinforces Fortinet’s guidance, urging administrators to:
- Upgrade to FortiOS 7.6.2, 7.4.7, 7.2.11, 7.0.17, or 6.4.16 to remove the malicious file and prevent re-compromise.
- Review device configurations and reset potentially exposed credentials.
- Consider disabling SSL-VPN functionality as a temporary workaround until patches are applied.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Security News Updates!
The post Hackers Actively Exploit Patched Fortinet FortiGate Devices to Gain Root Access Using Symbolic Link appeared first on Cyber Security News.







































































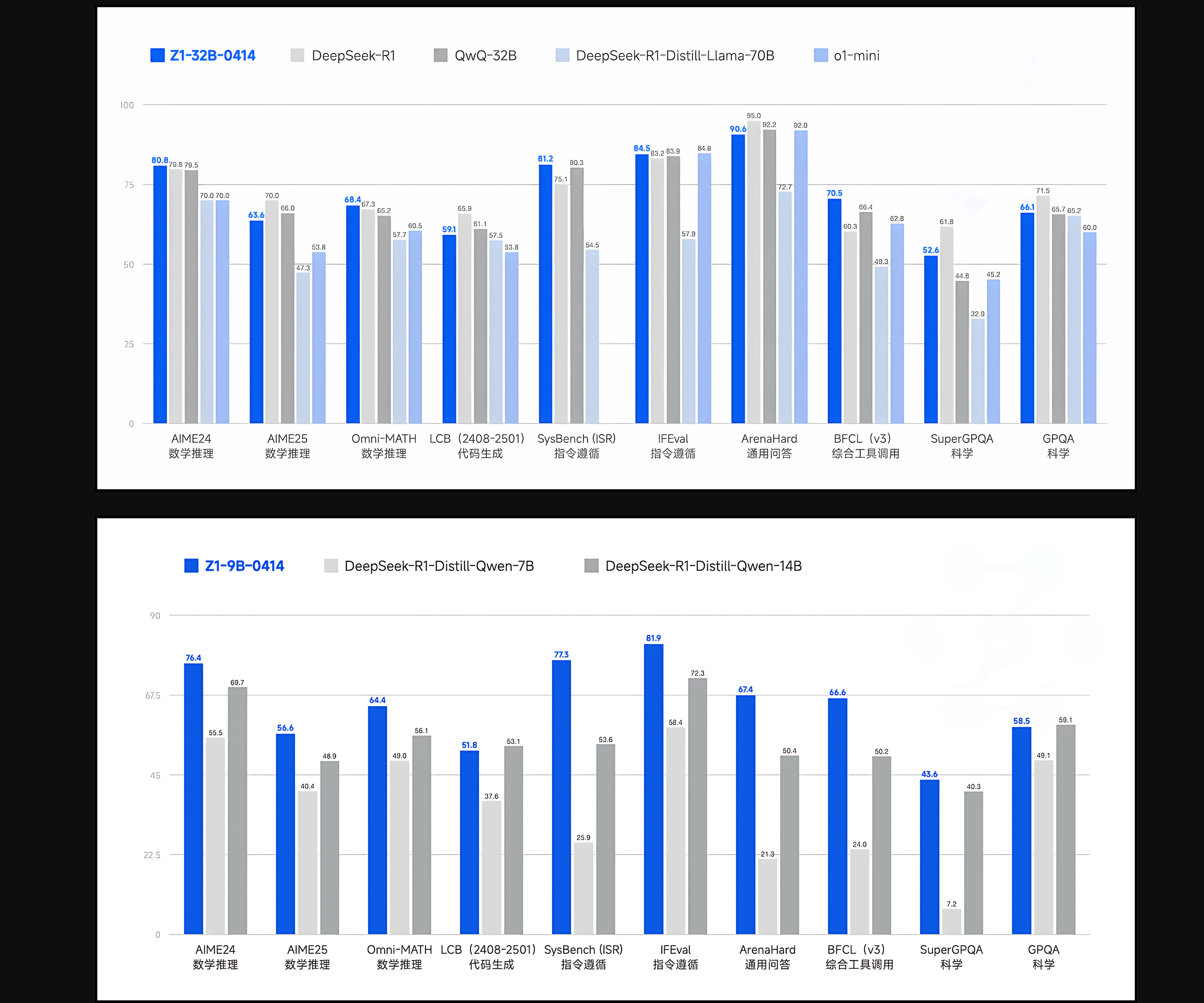



































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)



































































































































































































































.png?#)
































.webp?#)
.webp?#)

.webp?#)
























































































![[Fixed] Gemini app is failing to generate Audio Overviews](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/03/Gemini-Audio-Overview-cover.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

![What’s new in Android’s April 2025 Google System Updates [U: 4/14]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-3.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)












![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 Beta 2 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97011/97011/97011-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases macOS Sequoia 15.5 Beta 2 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97014/97014/97014-640.jpg)





























































































































.webp?#)
