Climate Crisis Has Tripled Length of Deadly Ocean Heatwaves, Study Finds
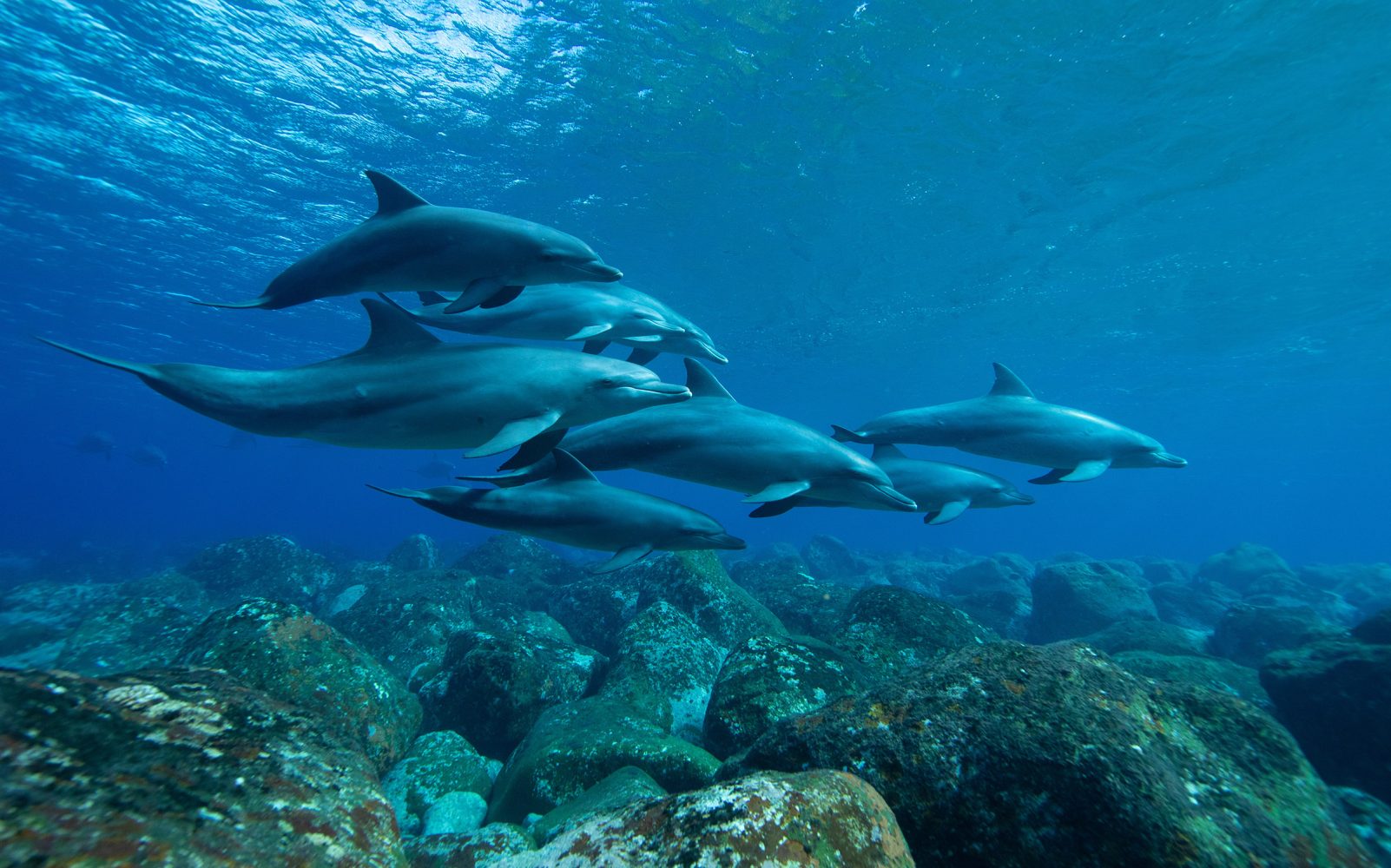
The climate crisis has tripled the length of ocean heatwaves, a study has found, supercharging deadly storms and destroying critical ecosystems such as kelp forests and coral reefs. From a report: Half of the marine heatwaves since 2000 would not have happened without global heating, which is caused by burning fossil fuels. The heatwaves have not only become more frequent but also more intense: 1C warmer on average, but much hotter in some places, the scientists said. The research is the first comprehensive assessment of the impact of the climate crisis on heatwaves in the world's oceans, and it reveals profound changes. Hotter oceans also soak up fewer of the carbon dioxide emissions that are driving temperatures up. "Here in the Mediterranean, we have some marine heatwaves that are 5C hotter," said Dr Marta Marcos at the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Studies in Mallorca, Spain, who led the study. "It's horrible when you go swimming. It looks like soup." As well as devastating underwater ecosystems such as sea grass meadows, Marcos said: "Warmer oceans provide more energy to the strong storms that affect people at the coast and inland." Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.


















































.jpg)





















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)






































































































































































































![Blue Archive tier list [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33404-1636469504/blue-archive-screenshot-2.jpg?#)






























.png?#)








































.webp?#)







































































































![Apple to Split Enterprise and Western Europe Roles as VP Exits [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97032/97032/97032-640.jpg)
![Nanoleaf Announces New Pegboard Desk Dock With Dual-Sided Lighting [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97030/97030/97030-640.jpg)

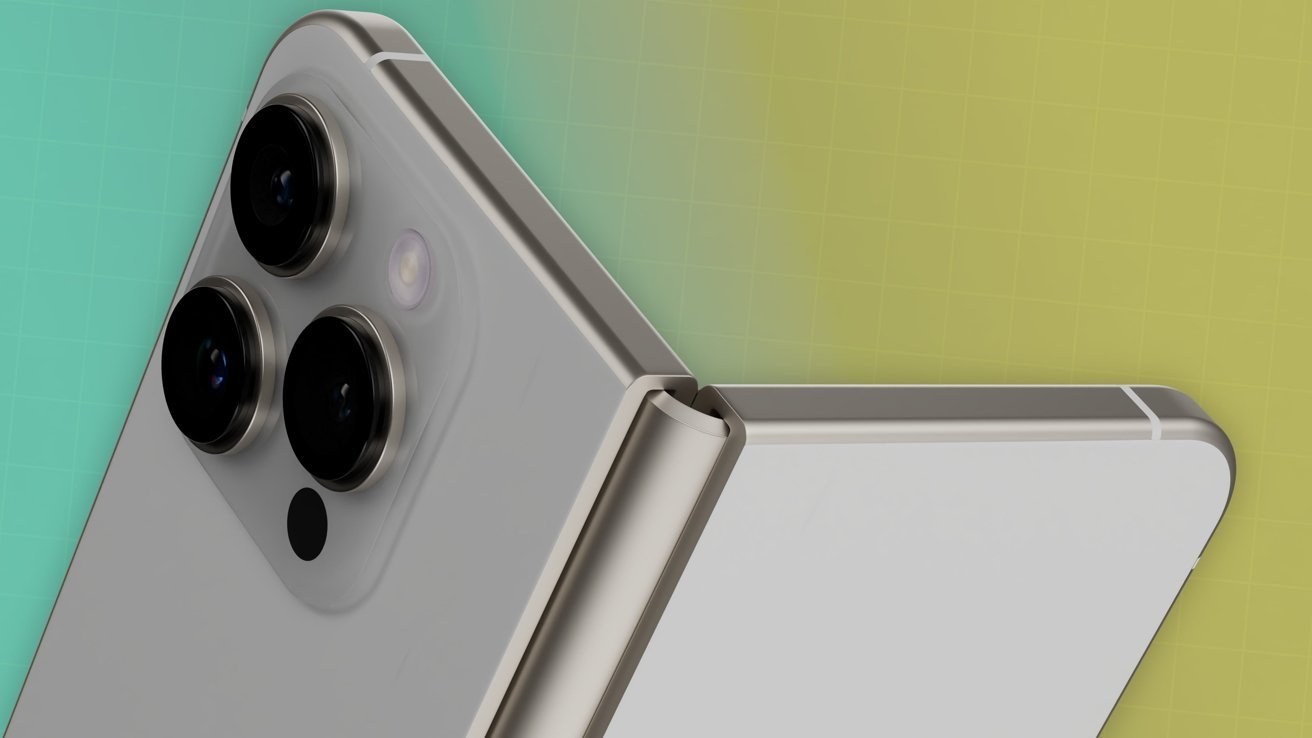
![Apple's Foldable iPhone May Cost Between $2100 and $2300 [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97028/97028/97028-640.jpg)
















![Daredevil Born Again season 1 ending explained: does [spoiler] show up, when does season 2 come out, and more Marvel questions answered](https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/i8Lf25QWuSoxWKGxWMLaaA.jpg?#)