Managing business data in a digital world: Best practices for protecting your company’s online identity (Sponsored)
For businesses, data is one of the most valuable assets they possess. From customer information to internal records, businesses rely heavily on data to operate efficiently, make informed decisions, and stay competitive. However, this reliance also brings significant risks, including data breaches, cyber threats, and reputational damage. Building trust with partners and customers, protecting company […] The post Managing business data in a digital world: Best practices for protecting your company’s online identity (Sponsored) appeared first on EU-Startups.

For businesses, data is one of the most valuable assets they possess. From customer information to internal records, businesses rely heavily on data to operate efficiently, make informed decisions, and stay competitive. However, this reliance also brings significant risks, including data breaches, cyber threats, and reputational damage.
Building trust with partners and customers, protecting company data, and maintaining regulatory compliance are all essential aspects of managing an online presence. In some cases, businesses might also consider opting out of data brokers and people-search sites that could expose sensitive information. With that in mind, let’s explore some of the best practices for protecting your company’s online identity.
How businesses handle and store data
Let’s begin by understanding how businesses handle and store data. Every business collects and retains various types of data, including employee records and customer information. Understanding this process is essential for minimising security risks and gaining greater control over your data.
Data collection and storage
Businesses collect data through several channels, including:
- Customer interactions: website visits, email sign-ups, online purchases, and feedback forms
- Employee records: personal details, contracts, and payroll information
- Partner agreements: contracts, invoices, and confidential deals
- Marketing: analytic tools, cookies, and CRM systems
All collected data must be stored securely to prevent unauthorised access, which can lead to misuse of sensitive information.
Data access and permissions
Securing data also means managing who can access it within the organisation.
- Role-based access control: grant access only to the information needed for an employee’s role
- Multi-factor authentication: add extra layers of protection for users with access to sensitive data
- Regular access reviews: continuously review and update access rights to ensure former employees cannot misuse company data
Compliance with data protection regulations
Businesses must comply with various data protection regulations, such as:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA)
Failure to comply with these laws can result in hefty fines, legal action, and a loss of customer trust. To prevent this, businesses must stay informed about regulatory requirements and regularly update their systems and practices.
Developing a business data protection policy
Every company should implement a clear data protection policy (DPP) outlining how data is collected, stored, used, and eventually deleted. Key components include:
Clear data handling guidelines
Define the types of data your business collects and establish rules for:
- Collecting and storing employee and customer information
- Deleting outdated or unnecessary data
- Protecting sensitive company information
Employee training and awareness
Data protection is a company-wide responsibility. Employees should be trained to:
- Recognise phishing scams and cybersecurity threats
- Follow secure password practices
- Understand data compliance requirements and the consequences of breaches
Response plan
Even with strong security protocols, breaches can occur. A response plan ensures your business can respond quickly and effectively. Key steps include:
- Identifying the breach and affected data
- Notifying regulatory authorities if required
- Taking action to prevent future incidents

Building customer trust through data transparency
Customers expect businesses to handle their data responsibly. Companies that prioritise data security gain a competitive advantage. Here’s how to build trust:
- Be transparent about data usage: clearly communicate how customer data is collected, stored, and used. A well-written privacy policy is key.
- Offer data control options: allow customers to update or delete their information and access data collected about them
- Ensure secure transactions and communications: use SSL encryption for websites that process payments and keep all customer support interactions confidential
By taking these steps, businesses can build stronger customer relationships, leading to increased loyalty and growth.
Long-term data protection habits for business owners
Managing data is an ongoing responsibility. Business owners should adopt long-term habits to keep data secure, including:
- Performing regular security checks
- Updating privacy policies and ensuring continued compliance
- Investing in cybersecurity tools
By making data security a central part of your business strategy, you can prevent data breaches, avoid legal complications, and protect your brand’s reputation. Data security is not just an IT issue – it’s a fundamental component of successfully operating in today’s digital world.
The post Managing business data in a digital world: Best practices for protecting your company’s online identity (Sponsored) appeared first on EU-Startups.


















































.jpg)





















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)






































































































































































































![Blue Archive tier list [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33404-1636469504/blue-archive-screenshot-2.jpg?#)






























.png?#)








































.webp?#)







































































































![Apple to Split Enterprise and Western Europe Roles as VP Exits [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97032/97032/97032-640.jpg)
![Nanoleaf Announces New Pegboard Desk Dock With Dual-Sided Lighting [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97030/97030/97030-640.jpg)

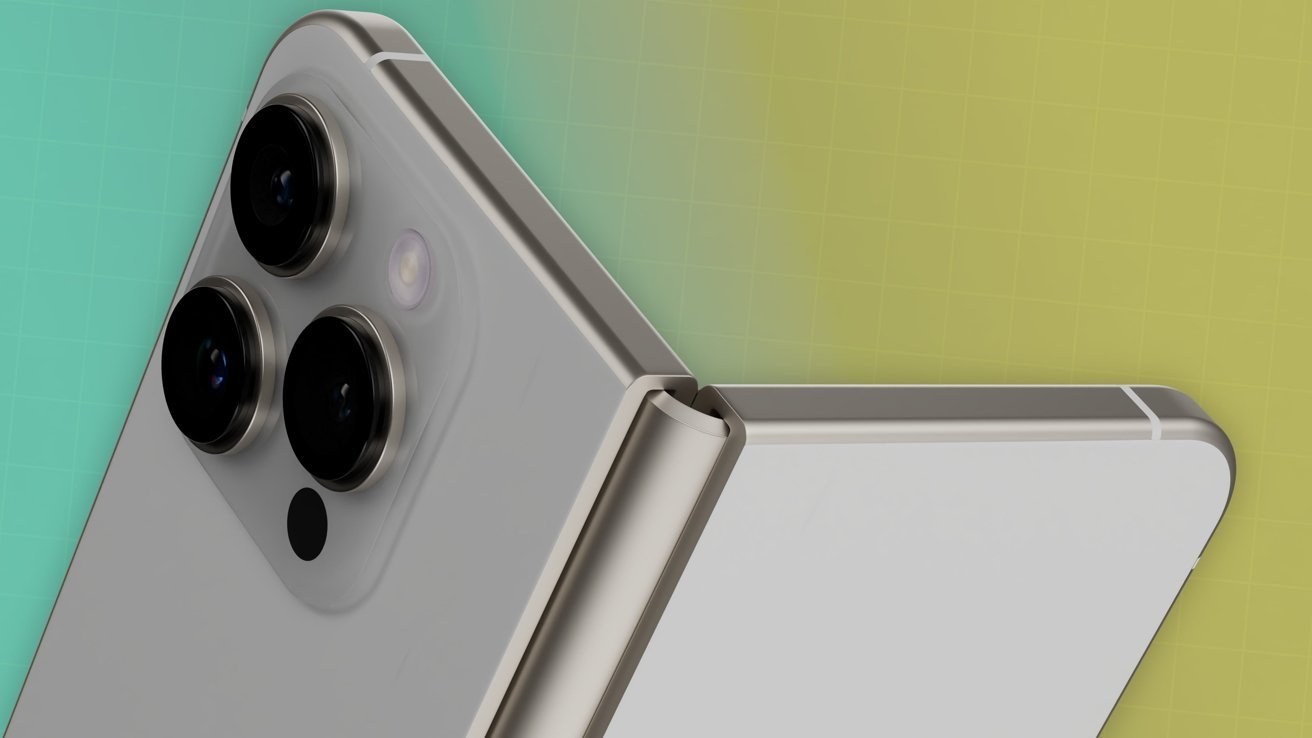
![Apple's Foldable iPhone May Cost Between $2100 and $2300 [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97028/97028/97028-640.jpg)
















![Daredevil Born Again season 1 ending explained: does [spoiler] show up, when does season 2 come out, and more Marvel questions answered](https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/i8Lf25QWuSoxWKGxWMLaaA.jpg?#)