Biometric Security: MFA & SSO Explained for Secure Access
In today’s digital age, protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure access to systems is more important than ever. One of the most advanced and reliable methods of securing access is biometric security. This article will explore what biometric security is, how it integrates with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and the role of Single Sign-On (SSO) login systems in streamlining secure access. What is Biometric Security? Biometric security refers to the use of unique physical or behavioral characteristics to verify an individual's identity. Instead of relying on traditional passwords or PINs, biometric systems use traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, voice patterns, or even gait (the way a person walks) to grant access. Read what is biometric security Biometric security offers several advantages: Uniqueness: Biometric features are unique to each person, making it difficult for someone else to replicate or fake. Convenience: Users don’t need to remember complex passwords. Speed: Authentication is often quick, requiring just a scan or a glance. Common applications of biometric security include unlocking smartphones, accessing secured buildings, and verifying identities for financial transactions. However, biometric data must be handled with care, as it is sensitive and permanent — unlike passwords, you cannot change your fingerprint if it’s compromised. What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more independent credentials to verify their identity. These credentials fall into three categories: Something you know: A password or PIN. Something you have: A security token or mobile phone. Something you are: A biometric feature, like a fingerprint or facial recognition. Read what is mfa authentication By requiring multiple factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Even if one factor (like a password) is stolen, an attacker would still need the other factors to break in. Biometric security often serves as the “something you are” factor in MFA setups. For example, after entering a password (something you know), a user might be prompted to scan their fingerprint or use facial recognition (something you are) to complete the login process. This layered approach boosts security, especially for sensitive systems such as online banking or corporate networks. What is Single Sign-On (SSO) Login? Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication process that allows users to access multiple applications or systems with one set of login credentials. Instead of logging in separately to each service, users authenticate once through a central identity provider, which then grants access to connected applications.Read what is sso login SSO offers several benefits: Convenience: Users only need to remember one password or use one biometric login. Efficiency: Reduces the time spent on repeated logins. Security: Limits password fatigue, which reduces the risk of weak or reused passwords. SSO can also be combined with MFA to enhance security. For instance, when a user logs in via SSO, they may be required to complete MFA, such as entering a password and then providing a fingerprint scan. Once authenticated, they gain seamless access to multiple applications without re-entering credentials. The Future of Secure Access Biometric security, MFA, and SSO are increasingly becoming foundational elements of modern cybersecurity frameworks. Biometric data, integrated into MFA, adds a robust layer of protection by verifying identities based on inherent physical characteristics. Meanwhile, SSO simplifies user experiences by reducing login friction while maintaining strong security, especially when paired with MFA. Organizations adopting these technologies are better equipped to protect sensitive data and provide smooth, secure access to their users. As threats continue to evolve, combining biometric security with MFA and SSO represents a powerful strategy to stay ahead of cybercriminals and ensure trustworthy authentication.
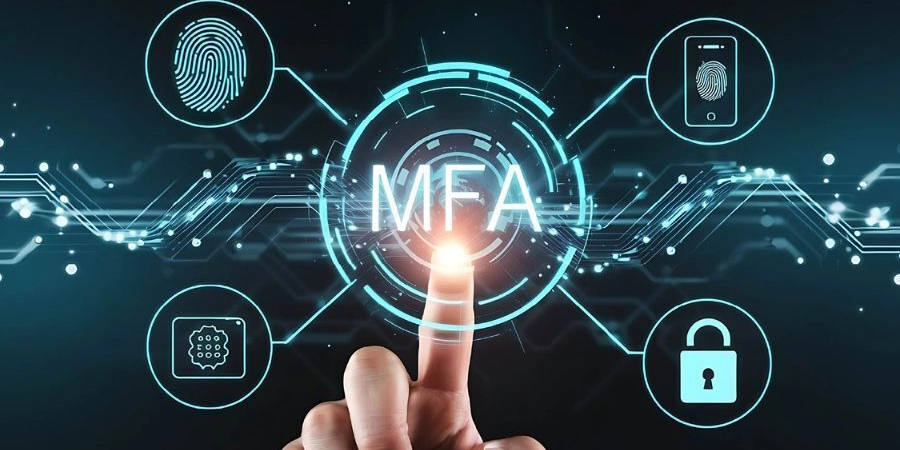

In today’s digital age, protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure access to systems is more important than ever. One of the most advanced and reliable methods of securing access is biometric security. This article will explore what biometric security is, how it integrates with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and the role of Single Sign-On (SSO) login systems in streamlining secure access.
What is Biometric Security?
Biometric security refers to the use of unique physical or behavioral characteristics to verify an individual's identity. Instead of relying on traditional passwords or PINs, biometric systems use traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, voice patterns, or even gait (the way a person walks) to grant access. Read what is biometric security
Biometric security offers several advantages:
Uniqueness: Biometric features are unique to each person, making it difficult for someone else to replicate or fake.
Convenience: Users don’t need to remember complex passwords.
Speed: Authentication is often quick, requiring just a scan or a glance.
Common applications of biometric security include unlocking smartphones, accessing secured buildings, and verifying identities for financial transactions.
However, biometric data must be handled with care, as it is sensitive and permanent — unlike passwords, you cannot change your fingerprint if it’s compromised.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more independent credentials to verify their identity. These credentials fall into three categories:
Something you know: A password or PIN.
Something you have: A security token or mobile phone.
Something you are: A biometric feature, like a fingerprint or facial recognition. Read what is mfa authentication
By requiring multiple factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Even if one factor (like a password) is stolen, an attacker would still need the other factors to break in.
Biometric security often serves as the “something you are” factor in MFA setups. For example, after entering a password (something you know), a user might be prompted to scan their fingerprint or use facial recognition (something you are) to complete the login process. This layered approach boosts security, especially for sensitive systems such as online banking or corporate networks.
What is Single Sign-On (SSO) Login?
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication process that allows users to access multiple applications or systems with one set of login credentials. Instead of logging in separately to each service, users authenticate once through a central identity provider, which then grants access to connected applications.Read what is sso login
SSO offers several benefits:
Convenience: Users only need to remember one password or use one biometric login.
Efficiency: Reduces the time spent on repeated logins.
Security: Limits password fatigue, which reduces the risk of weak or reused passwords.
SSO can also be combined with MFA to enhance security. For instance, when a user logs in via SSO, they may be required to complete MFA, such as entering a password and then providing a fingerprint scan. Once authenticated, they gain seamless access to multiple applications without re-entering credentials.
The Future of Secure Access
Biometric security, MFA, and SSO are increasingly becoming foundational elements of modern cybersecurity frameworks. Biometric data, integrated into MFA, adds a robust layer of protection by verifying identities based on inherent physical characteristics. Meanwhile, SSO simplifies user experiences by reducing login friction while maintaining strong security, especially when paired with MFA.
Organizations adopting these technologies are better equipped to protect sensitive data and provide smooth, secure access to their users. As threats continue to evolve, combining biometric security with MFA and SSO represents a powerful strategy to stay ahead of cybercriminals and ensure trustworthy authentication.












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 152]: ChatGPT Connectors, AI-Human Relationships, New AI Job Data, OpenAI Court-Ordered to Keep ChatGPT Logs & WPP’s Large Marketing Model](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20152%20cover.png)


















































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] Natural Language Processing with Python, Microsoft 365 Copilot At Work & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



















































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


















































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

_designer491_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)





























































































![The new Google TV setup process is impressively fast and easy [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/Google-TV-logo.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

![Apple’s latest CarPlay update revives something Android Auto did right 10 years ago [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/06/carplay-live-activities-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)














![3DMark Launches Native Benchmark App for macOS [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97603/97603/97603-640.jpg)
![Craig Federighi: Putting macOS on iPad Would 'Lose What Makes iPad iPad' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97606/97606/97606-640.jpg)