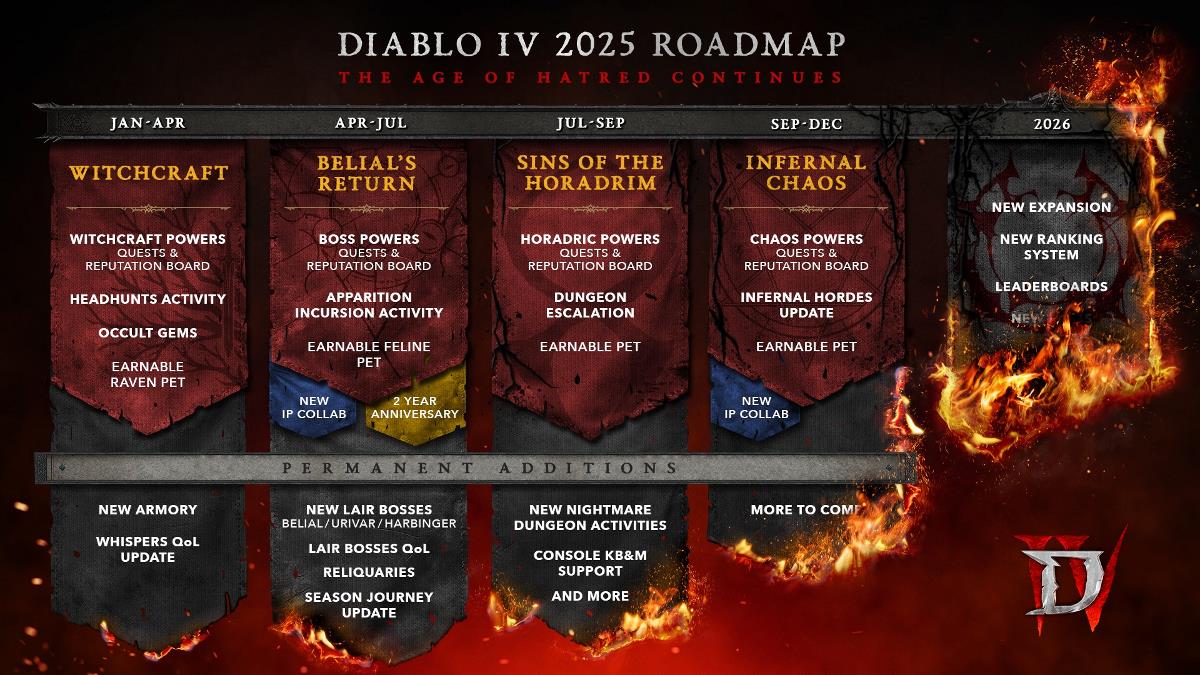
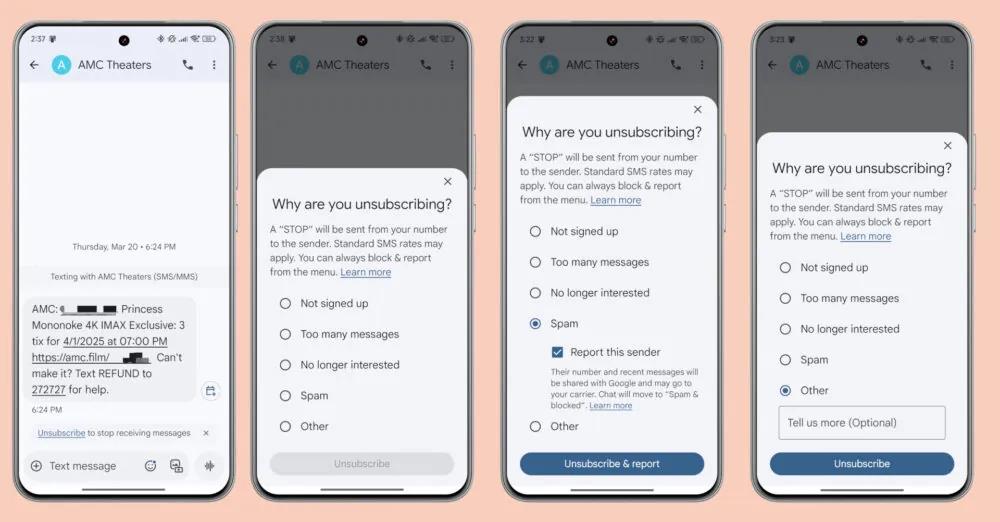
# Job Scheduling - Greedy Approach
# Description: Schedules jobs on a fixed number of machines to minimize total completion time by assigning each job to the machine with the least current load.
# Job Scheduling - Greedy Load Balancing Algorithm
def schedule_jobs(jobs, num_machines):
"""
Distribute jobs across machines to minimize total completion time.
The algorithm uses a greedy approach to balance workload:
1. Sort jobs in descending order to prioritize larger jobs
2. Assign each job to the least loaded machine
Args:
jobs (list of int): Duration of each job to be scheduled
num_machines (int): Number of available machines to distribute jobs
Returns:
list of int: Total load on each machine after job assignment
Time Complexity: O(n log n + n * m)
Space Complexity: O(m), where n is number of jobs, m is number of machines
Example:
# Distribute 5 jobs across 3 machines
>>> schedule_jobs([10, 15, 20, 25, 30], 3)
[40, 40, 40]
"""
# Validate input
if not jobs or num_machines <= 0:
return []
# Sort jobs in descending order to optimize load balancing
sorted_jobs = sorted(jobs, reverse=True)
# Initialize machine loads
machine_loads = [0] * num_machines
# Assign each job to the least loaded machine
for job in sorted_jobs:
# Find the machine with minimum current load
min_load_index = machine_loads.index(min(machine_loads))
# Add job to the least loaded machine
machine_loads[min_load_index] += job
return machine_loads
# Demonstration of job scheduling
def demonstrate_job_scheduling():
"""
Demonstrate the job scheduling algorithm with sample inputs.
"""
# Test case 1: Even distribution
jobs1 = [10, 15, 20, 25, 30]
machines1 = 3
print(f"Jobs {jobs1} on {machines1} machines:")
print(schedule_jobs(jobs1, machines1))
# Test case 2: Uneven job distribution
jobs2 = [5, 8, 12, 13, 16, 20, 25, 30]
machines2 = 4
print(f"\nJobs {jobs2} on {machines2} machines:")
print(schedule_jobs(jobs2, machines2))








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)
































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)















































































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)

































































































































![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)



















![3 big talking points after Daredevil Born Again episode 8: why did Daredevil save [spoiler], who really killed Foggy in the Marvel TV show, and more](https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/FpR4EjKc9Pgn4VSqYqqoc3.jpg?#)