Optimizing API Performance – Part 2: Load Balancing
APIs are the backbone of modern applications, handling thousands (or even millions) of requests daily. But as traffic grows, a single server can quickly become overwhelmed, leading to slow responses, timeouts, crashes and ultimately loss in business revenue. This is where load balancing comes in. Load balancers are capable of distributing traffic across multiple servers, ensuring your API remains fast, scalable, and highly available. This tutorial is part of a series on Optimising api performance. You can read part 1 of this series on Caching here In this guide, we’ll explore: When you should consider load balancing in your application How load balancing works Load balancing strategies Real-World Case Study: PayU Common load balancing issues and fixes Best practices Conclusion & Resources 1. When Should I consider Load Balancing? Not every API needs load balancing from day one. But you should strongly consider it if: ✅ Your API receives 1,000+ requests per second. ✅ Your server CPU usage consistently exceeds 70%. ✅ You need high availability (e.g., financial transactions, streaming) ✅ You’ve experienced downtime due to traffic spikes - Does graphs are telling you something ✅ Reliability - Robust Load balancer like Elastic load balancer are capable of performing health checks on upstreams servers before distributing requests - helping maximise performance and resiliency. ✅ You need an added layer of Security - Load balancers are capable of playing crucial role in security. They are capable of acting as a buffer against DDoS attacks, and enabling features like SSL encryption and WAF integration. Likewise, Load balancers can be instructed to drop requests from suspicious source. Ensuring these malicious requests do not reach your core application resources. If any of these apply to your system, it’s time to implement a load balancer. 2. How Load Balancing Works A load balancer acts as a middle layer between clients and backend servers. It distributes incoming networks and or application requests across multiple servers or "targets" based on predefined rules. Load balancer prevents overload and improve performance, availability, and scalability of an application. Load balancer acts as a single point of contact for clients, routing requests to healthy servers and monitoring their health.
APIs are the backbone of modern applications, handling thousands (or even millions) of requests daily. But as traffic grows, a single server can quickly become overwhelmed, leading to slow responses, timeouts, crashes and ultimately loss in business revenue.
This is where load balancing comes in. Load balancers are capable of distributing traffic across multiple servers, ensuring your API remains fast, scalable, and highly available. This tutorial is part of a series on Optimising api performance. You can read part 1 of this series on Caching here
In this guide, we’ll explore:
- When you should consider load balancing in your application
- How load balancing works
- Load balancing strategies
- Real-World Case Study: PayU
- Common load balancing issues and fixes
- Best practices
- Conclusion & Resources
1. When Should I consider Load Balancing?
Not every API needs load balancing from day one. But you should strongly consider it if:
✅ Your API receives 1,000+ requests per second.
✅ Your server CPU usage consistently exceeds 70%.
✅ You need high availability (e.g., financial transactions, streaming)
✅ You’ve experienced downtime due to traffic spikes - Does graphs are telling you something
✅ Reliability - Robust Load balancer like Elastic load balancer are capable of performing health checks on upstreams servers before distributing requests - helping maximise performance and resiliency.
✅ You need an added layer of Security - Load balancers are capable of playing crucial role in security. They are capable of acting as a buffer against DDoS attacks, and enabling features like SSL encryption and WAF integration.
Likewise, Load balancers can be instructed to drop requests from suspicious source. Ensuring these malicious requests do not reach your core application resources.
If any of these apply to your system, it’s time to implement a load balancer.
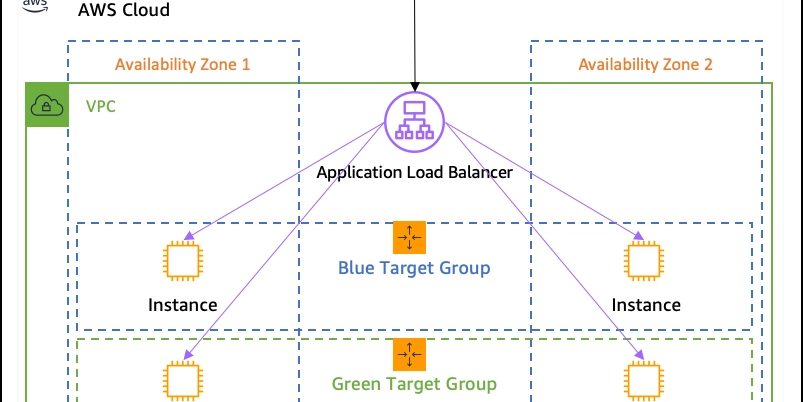
2. How Load Balancing Works
A load balancer acts as a middle layer between clients and backend servers. It distributes incoming networks and or application requests across multiple servers or "targets" based on predefined rules.
Load balancer prevents overload and improve performance, availability, and scalability of an application. Load balancer acts as a single point of contact for clients, routing requests to healthy servers and monitoring their health.






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)


































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)











































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)




























































.jpg?#)







.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)























_ArtemisDiana_Alamy.jpg?#)










































































-xl.jpg)











![Yes, the Gemini icon is now bigger and brighter on Android [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/02/Gemini-on-Galaxy-S25.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)