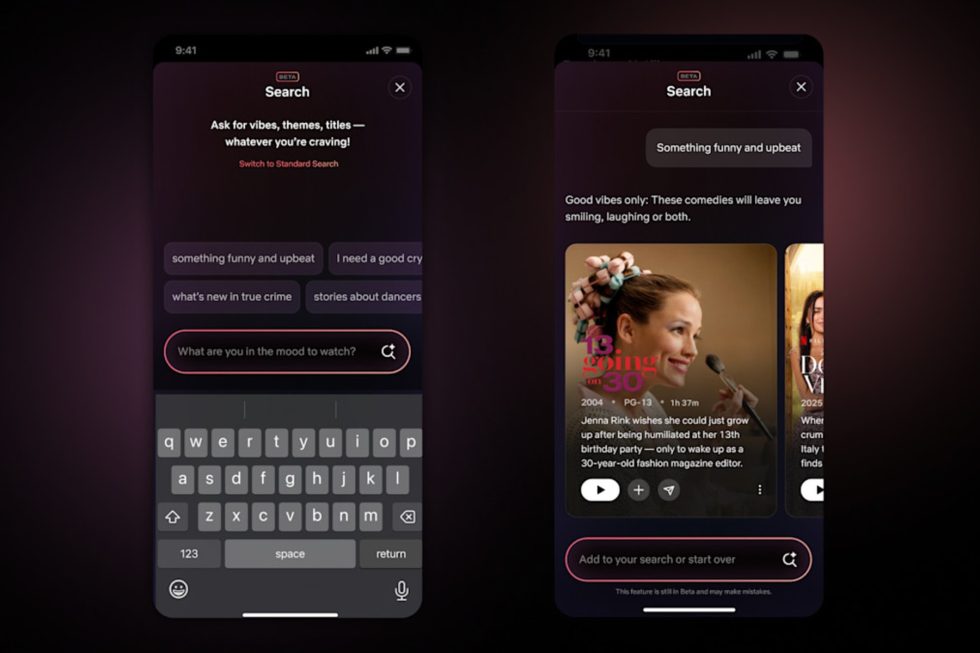
Blockchain for Charity and Non-Profits: Revolutionizing Social Impact through Transparency and Open Source Innovation
Abstract Blockchain technology, combined with NFTs and open source funding, is transforming how charitable organizations operate. This post explores how transparency, efficiency, decentralization, and community-driven models empower non-profits to drive genuine social change. We review definitions, key concepts such as smart contracts and tokenization, present real-world use cases—from transparent aid distribution to NFT-based donor rewards—analyze challenges such as scalability and regulatory uncertainties, and predict future trends. By integrating technical insights, practical examples, and authoritative links, this post offers a comprehensive overview for innovators, donors, and technical experts alike. Introduction Blockchain, once solely associated with cryptocurrencies, is now paving new avenues in the charitable sector. Non-profit organizations and social enterprises are embracing blockchain for its transparency, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced donor engagement. This technology enables secure, immutable ledgers where every transaction—from a donation to fund disbursement—is recorded for public verification. Alongside blockchain, NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) and open source funding models are generating fresh possibilities for incentivizing donations and tracking spending accurately. Philanthropy today demands accountability, and blockchain meets this need by ensuring data integrity, real-time tracking, and decentralized governance. In this post, we dive into the evolution of blockchain applications in charity, provide a background and core concepts, offer practical use cases and examples, discuss known challenges, and explore future prospects. Whether you are a non-profit leader, a blockchain developer, or an informed donor, read on to discover how these technologies are revolutionizing social impact initiatives. Background and Context Blockchain technology entered mainstream attention with Bitcoin’s launch; however, its decentralized ledger system has far-reaching applications beyond cryptocurrencies. At its essence, blockchain is a distributed database maintained by numerous nodes, where each transaction is recorded with cryptographic security. This system: Eliminates intermediaries: Ideal for reducing overhead in charity funding. Ensures data integrity: Immutable records help prevent fraud and mismanagement. Fosters transparency: Donors can trace contributions, building trust. Parallel to the blockchain evolution, the open source paradigm has encouraged community collaboration and rapid innovation. Open source funding models—often supported by platforms such as the Copyleft Licenses Ultimate Guide—allow developers, non-profits, and investors to co-create ethical and sustainable projects. The fusion of blockchain and open source funding is especially significant for the charity and non-profit sector. With global challenges and increased public demand for accountability, several organizations are now testing blockchain-based solutions. Such integrations support: Decentralized governance: Allowing stakeholders to participate in decision-making. Reduced bureaucratic overhead: Smart contracts automatically release funds when conditions are met. Global access and inclusion: Digital wallets and tokenized systems make it easier for underbanked populations to participate. Historically, inefficiencies in traditional charity funding models—stemming from reliance on intermediaries and opaque financial practices—have reduced the impact of donations. Blockchain-based systems address these issues and set the stage for a new era of philanthropic innovation. Core Concepts and Features Blockchain, NFTs, and open source funding models interconnect to create a robust, transparent ecosystem for charities. Let’s explore their core features: 1. Decentralization and Transparency Blockchain uses a distributed ledger that is collectively maintained by its network. Every transaction is verified and recorded simultaneously across all nodes, ensuring: Unalterable Transaction Records: Once a donation is made, it cannot be changed or falsified. Enhanced Accountability: Donors can follow each dollar, minimizing worries about mismanagement. Robust Security: Crypto-based techniques reduce the risk of data breaches. 2. Smart Contracts Smart contracts are programmed agreements that execute automatically when conditions are satisfied. In philanthropy, they play a pivotal role by: Automating Fund Disbursement: Funds are released only when specific milestones and verification conditions are met. Minimizing Administrative Costs: By reducing the need for manual intervention. Increasing Trust: Real-time monitoring of donations reassures contributors. 3. Tokenization and NFTs Tokenization transforms physical or digital assets into blockchain-based tokens. NFTs, being unique digital assets, enhance donor engagement: Uniqu

Abstract
Blockchain technology, combined with NFTs and open source funding, is transforming how charitable organizations operate. This post explores how transparency, efficiency, decentralization, and community-driven models empower non-profits to drive genuine social change. We review definitions, key concepts such as smart contracts and tokenization, present real-world use cases—from transparent aid distribution to NFT-based donor rewards—analyze challenges such as scalability and regulatory uncertainties, and predict future trends. By integrating technical insights, practical examples, and authoritative links, this post offers a comprehensive overview for innovators, donors, and technical experts alike.
Introduction
Blockchain, once solely associated with cryptocurrencies, is now paving new avenues in the charitable sector. Non-profit organizations and social enterprises are embracing blockchain for its transparency, reduced administrative costs, and enhanced donor engagement. This technology enables secure, immutable ledgers where every transaction—from a donation to fund disbursement—is recorded for public verification. Alongside blockchain, NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) and open source funding models are generating fresh possibilities for incentivizing donations and tracking spending accurately.
Philanthropy today demands accountability, and blockchain meets this need by ensuring data integrity, real-time tracking, and decentralized governance. In this post, we dive into the evolution of blockchain applications in charity, provide a background and core concepts, offer practical use cases and examples, discuss known challenges, and explore future prospects. Whether you are a non-profit leader, a blockchain developer, or an informed donor, read on to discover how these technologies are revolutionizing social impact initiatives.
Background and Context
Blockchain technology entered mainstream attention with Bitcoin’s launch; however, its decentralized ledger system has far-reaching applications beyond cryptocurrencies. At its essence, blockchain is a distributed database maintained by numerous nodes, where each transaction is recorded with cryptographic security. This system:
- Eliminates intermediaries: Ideal for reducing overhead in charity funding.
- Ensures data integrity: Immutable records help prevent fraud and mismanagement.
- Fosters transparency: Donors can trace contributions, building trust.
Parallel to the blockchain evolution, the open source paradigm has encouraged community collaboration and rapid innovation. Open source funding models—often supported by platforms such as the Copyleft Licenses Ultimate Guide—allow developers, non-profits, and investors to co-create ethical and sustainable projects.
The fusion of blockchain and open source funding is especially significant for the charity and non-profit sector. With global challenges and increased public demand for accountability, several organizations are now testing blockchain-based solutions. Such integrations support:
- Decentralized governance: Allowing stakeholders to participate in decision-making.
- Reduced bureaucratic overhead: Smart contracts automatically release funds when conditions are met.
- Global access and inclusion: Digital wallets and tokenized systems make it easier for underbanked populations to participate.
Historically, inefficiencies in traditional charity funding models—stemming from reliance on intermediaries and opaque financial practices—have reduced the impact of donations. Blockchain-based systems address these issues and set the stage for a new era of philanthropic innovation.
Core Concepts and Features
Blockchain, NFTs, and open source funding models interconnect to create a robust, transparent ecosystem for charities. Let’s explore their core features:
1. Decentralization and Transparency
Blockchain uses a distributed ledger that is collectively maintained by its network. Every transaction is verified and recorded simultaneously across all nodes, ensuring:
- Unalterable Transaction Records: Once a donation is made, it cannot be changed or falsified.
- Enhanced Accountability: Donors can follow each dollar, minimizing worries about mismanagement.
- Robust Security: Crypto-based techniques reduce the risk of data breaches.
2. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are programmed agreements that execute automatically when conditions are satisfied. In philanthropy, they play a pivotal role by:
- Automating Fund Disbursement: Funds are released only when specific milestones and verification conditions are met.
- Minimizing Administrative Costs: By reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Increasing Trust: Real-time monitoring of donations reassures contributors.
3. Tokenization and NFTs
Tokenization transforms physical or digital assets into blockchain-based tokens. NFTs, being unique digital assets, enhance donor engagement:
- Unique Donor Rewards: Exclusive NFTs serve as tokens of appreciation and proof of contribution.
- Innovative Fundraising Models: Limited-edition NFTs can be sold or auctioned, creating an engaging donation experience.
- Increased Donor Loyalty: Tokenized assets help donors feel part of the project’s success.
For example, organizations may use NFT campaigns—similar to initiatives found in The Nemesis NFT Collection and The Sandbox Assets NFT Collection—to generate enthusiasm and boost fundraising.
4. Open Source Funding Models
Open source funding is built on community collaboration and transparency. Key benefits include:
- Collaborative Development: Developers around the world contribute improvements and updates.
- Community-Driven Projects: Decisions and fund allocations are made collectively, ensuring fairness.
- Innovative Micro-Funding Solutions: Crowdsourcing and small grants can be managed transparently.
5. Interoperability and Integration
Modern blockchain designs focus on interoperability. This means:
- Seamless Data Exchange: Different blockchain networks can work together securely.
- Unified Platforms: Integrated dashboards offer simultaneous insights into donation flows, project progress, and financial sustainability.
- Enhanced User Experience: Donors, administrators, and beneficiaries enjoy a cohesive experience.
Below is a table comparing traditional charity funding with blockchain-based funding methods:
| Feature | Traditional Charity Funding | Blockchain-Based Funding |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Opaque, limited donor insight | Immutable ledger; real-time tracking |
| Security | Centralized systems vulnerable to breaches | Decentralized with robust cryptographic security |
| Efficiency | High administrative overhead | Smart contracts automate fund disbursement |
| Global Access | Limited, often excluding underbanked regions | Digital wallets bring financial inclusion globally |
| Donor Engagement | Minimal interaction and feedback | Unique NFT rewards and transparent dashboards |
6. Community Governance and Open Source Advantages
Blockchain empowers non-profits by enabling decentralized governance. In these systems, stakeholders can vote on proposals and funding allocations, ensuring that:
- Decisions are transparent: Reducing risks of fraud or mismanagement.
- All voices are heard: Engaging a broader community of donors, developers, and experts.
- Innovation Flourishes: Open source code allows continuous improvements, advantages detailed in articles like Unveiling CECILL C: A Deep Dive into Fair Open Source Licensing.
Applications and Use Cases
Blockchain and open source funding models have already found practical applications in charity. Below are a few examples:
Case Study 1: Transparent Aid Distribution
One pioneering example is the United Nations World Food Programme (WFP) and its "Building Blocks" initiative. By leveraging blockchain, the WFP can track food and supply deliveries in refugee camps. This model ensures:
- Real-Time Verification: Donors can check exactly how and where their contributions are spent.
- Fraud Prevention: Immutable ledger guarantees that funds are used as intended.
- Global Accountability: Every stakeholder, from the donor to the regulatory agency, can monitor progress.
Case Study 2: Cryptocurrency-Driven Charity Platforms
Platforms like BitGive have incorporated blockchain for transparent and accountable donations. Their platform, GiveTrack, uses smart contracts to map donations and expenditures. Benefits include:
- Verified Transactions: Donors observe when funds are released after meeting milestones.
- Cost Reduction: Automation dramatically reduces administrative costs.
- Enhanced Engagement: Additional NFT rewards, as seen in initiatives similar to The Nemesis NFT Collection, motivate contributor participation.
Case Study 3: NFT-Based Fundraising Initiatives
NFT-driven campaigns are emerging as innovative fundraising tools. By issuing limited-edition NFTs as donor badges, charities can:
- Create a Digital Connection: Donors receive a unique collectible that represents their contribution.
- Facilitate New Revenue Streams: NFTs can be resold or traded, adding an investment dimension to charitable giving.
- Boost Donor Loyalty: Exclusive offers and continuous engagement help build long-term support.
Practical Use Cases in a Table
| Use Case | Core Feature | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Aid Delivery Tracking | Immutable ledger | WFP’s Building Blocks initiative |
| Donor Engagement Platform | Smart contracts | BitGive’s GiveTrack with automated fund release |
| NFT-Driven Campaigns | Tokenization & Rewards | Limited-edition NFTs for donor recognition and fundraising |
Key Benefits (Bullet List)
- Global Financial Inclusion: Secure, digital wallets allow even underbanked communities to participate.
- Lower Overhead Costs: Automation and decentralization reduce the need for intermediaries.
- Community Collaboration: Open source models invite collective improvements to funding platforms.
- Enhanced Donor Trust: Real-time tracking of contributions builds accountability and transparency.
For further details on innovative funding in open source projects, check out Exploring the Drip Network Referral System: A New Wave in DeFi Innovation.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its transformative potential, blockchain in charity is not without obstacles. Some challenges include:
Technical Barriers
- Scalability: Blockchain networks can slow down during high transaction volumes. Although Layer 2 solutions and sidechains are on the horizon, scalability remains a challenge.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain projects may not seamlessly connect. Standardized protocols are still in development for smooth data exchange.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Though blockchain is inherently secure, bugs in smart contracts or NFT platforms can become targets for cyberattacks.
Adoption and Operational Challenges
- Technological Literacy: Many non-profits are not yet familiar with blockchain technologies. Educational initiatives and training programs are essential.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Varying global regulations around cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications create a complex legal landscape for non-profits.
- High Initial Investment: Implementing blockchain systems often requires upfront expenditures in technology and talent, which can deter smaller organizations.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many established charities depend on legacy systems that are not easily integrated with modern blockchain solutions.
Additional Challenges (Bullet List)
- Donor Skepticism: Some donors may be hesitant due to unfamiliarity with digital assets.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: Increasing reliance on digital platforms heightens the risk of cyberattacks.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Ongoing development is necessary to keep blockchain protocols updated.
- Cost of Implementation: Initial investments can be prohibitive for smaller organizations.
For a deeper analysis on overcoming challenges in blockchain projects, see Arbitrum Sequencer: Transforming Ethereum’s Capabilities.
Future Outlook and Innovations
The future holds immense promise for blockchain applications in charity and non-profits. Here are a few emerging trends:
1. Broader Adoption and Integration
As non-profits recognize the benefits of decentralized systems, blockchain adoption will likely increase. Future trends include:
- Interoperable Ecosystems: More projects will integrate seamlessly across different blockchain networks.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Digital wallets and blockchain-powered platforms will become standard tools for global donations.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Continued improvements in scalability and consensus mechanisms will further lower fees.
2. Evolution of Smart Contracts
The next generation of smart contracts will feature dynamic conditions and more robust bug resilience. This will enhance:
- Automated Governance: Allowing schemes where funds are dispensed as projects meet evolving metrics.
- Real-Time Adaptations: Smart contracts that automatically adjust conditions based on data feeds and project performance.
3. NFT-Driven Campaign Innovations
NFTs will continue to redefine donor rewards. Future campaigns could include:
- Interactive Donor Experiences: Gamification through collectible NFTs that change according to project milestones.
- Secondary Markets: Resale and trading of NFT tokens, providing ongoing engagement and potential revenue streams.
4. Advanced Data Analytics with Blockchain Dashboards
Real-time analytics platforms will offer deeper insights into funding flows and impact assessments. These dashboards:
- Enhance Transparency: Providing detailed breakdowns of spending and impact.
- Boost Donor Confidence: With comprehensive visualizations of how contributions make a difference.
5. Collaborative Regulatory Frameworks
As blockchain becomes more integral to philanthropy, governments and industry bodies are expected to establish supportive regulatory guidelines that:
- Promote Innovation: Ensuring blockchain remains a trusted tool for social impact.
- Protect Stakeholders: Providing legal clarity and accountability.
- Facilitate Integration: Streamlining the transition from legacy systems to decentralized platforms.
For further insights on these emerging trends, check out Blockchain and Digital Rights Management: A Revolutionary Synergy.
Summary
Blockchain is fundamentally changing how charitable organizations operate. By eliminating intermediaries, ensuring uncompromised transparency, and automating fund management through smart contracts, blockchain equips non-profits with the tools needed for global accountability and efficiency. The integration of NFTs and open source funding not only provides unique donor rewards but also strengthens community engagement, allowing every contribution to have a measurable impact.
In summary:
- Transparency and Security: Distributed ledgers document every transaction, building trust among donors.
- Efficient Fund Distribution: Smart contracts cut administrative costs and automatically validate project milestones.
- Innovative Donor Engagement: NFT rewards create a personal, interactive connection with the cause.
- Collaborative Approach: Open source models foster global community participation and continuous improvement.
While challenges such as scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and the need for technological literacy remain, the future is bright. Innovative trends like dynamic smart contracts, NFT-integrated campaigns, and advanced analytics dashboards are set to further revolutionize open source funding and blockchain philanthropy.
The call to action is clear—stakeholders, developers, and donors must collaborate to embrace these technologies. As blockchain continues to evolve, it will drive new efficiencies and foster a more equitable, sustainable global society. For further exploration into how open source incentives drive social change, see Exploring the MIT License Innovation, Impact, and Integrity.
Conclusion
Blockchain, NFTs, and open source funding models are not merely technological trends; they represent transformative tools for accelerating social impact. By enabling secure, transparent, and cost-effective donation management, these innovations empower non-profits to scale globally and operate with unprecedented accountability. As donor engagement becomes richer through tokenization and real-time tracking, traditional limitations of charity funding are overcome.
The synergy between decentralized technology and community governance is revolutionizing philanthropy. With sustained investments in education, regulatory improvements, and technological enhancements, the non-profit sector is poised to lead a new era of equitable and transparent funding.
For those interested in further technical insights and use cases, additional resources such as the Copyleft Licenses Ultimate Guide, The Sandbox Assets NFT Collection, and industry discussions like Exploring the Drip Network Referral System provide deeper dives into this exciting ecosystem.
By aligning technological innovation with philanthropic goals, blockchain paves the way to a future where every contribution is transparent, every donor is empowered, and every cause thrives on community-driven support.
Embrace the digital, decentralized future of charity, and together let’s create positive, lasting social impact.







































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Python Programming PCEP Certification Prep Bundle (67% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)













































































































































































































































![Honor 400 series officially launching on May 22 as design is revealed [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/05/honor-400-series-announcement-1.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)














![Beats Studio Pro Wireless Headphones Now Just $169.95 - Save 51%! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97258/97258/97258-640.jpg)