Balanced vs Extreme vs SSD vs Standard: Choosing the Right Persistent Disk in GCP
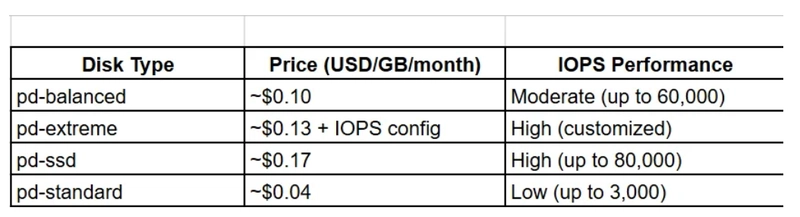
GCP Persistent Disks Compared: Balanced, Extreme, SSD, and Standard Explained Overview: Google Cloud offers 4 types of Persistent Disks for VM storage: Balanced Persistent Disk (pd-balanced) Extreme Persistent Disk (pd-extreme) SSD Persistent Disk (pd-ssd) Standard Persistent Disk (pd-standard) All types provide block storage with automatic encryption and snapshots. They are zonal or regional, ensuring high availability and durability. Key Features Balanced Persistent Disk (pd-balanced) SSD-backed general-purpose storage. Good balance between performance and cost. Up to 60,000 IOPS and 1,200 MB/s throughput. Extreme Persistent Disk (pd-extreme) SSD-backed and configurable IOPS. Designed for high-performance, I/O-intensive workloads. Supports over 100,000 IOPS with ultra-low latency. SSD Persistent Disk (pd-ssd) High-performance SSD. Best for latency-sensitive workloads. Up to 80,000 IOPS and 1,200 MB/s throughput. Standard Persistent Disk (pd-standard) Economical option for infrequent access. HDD-backed storage. Up to 3,000 IOPS and 180 MB/s throughput. Real-Time Use Cases Balanced Disk: Medium-size SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL). Web app backends and microservices. Dev/test environments. Extreme Disk: Enterprise workloads like SAP HANA, Oracle DB. Financial trading systems or analytics platforms. Scalable database clusters (e.g., Spanner, Cassandra). SSD Disk: OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) systems. Game servers and real-time data processing. NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Redis. Standard Disk: Backup and disaster recovery. Archival and logging data. Large batch processing with minimal read/write. Cost Comparision: When to Use Each Balanced Disk → For general-purpose workloads where performance and cost must be balanced. Extreme Disk → When you need ultra-high IOPS, such as for enterprise DBs. SSD Disk → When latency and fast performance are top priorities. Standard Disk → For cost-sensitive workloads with low I/O requirements. Final Summary Google Cloud provides flexible disk options for performance, cost, and scalability. Balanced is ideal for everyday apps. Extreme is built for performance-intensive enterprise systems. SSD excels in fast-response and low-latency apps. Standard is best for cold storage and cost efficiency. Choosing the right disk ensures better performance, lower cost, and higher reliability. Venkat C S
GCP Persistent Disks Compared: Balanced, Extreme, SSD, and Standard Explained
Overview:
Google Cloud offers 4 types of Persistent Disks for VM storage:
Balanced Persistent Disk (pd-balanced)
Extreme Persistent Disk (pd-extreme)
SSD Persistent Disk (pd-ssd)
Standard Persistent Disk (pd-standard)
All types provide block storage with automatic encryption and snapshots.
They are zonal or regional, ensuring high availability and durability.
Key Features
Balanced Persistent Disk (pd-balanced)
SSD-backed general-purpose storage.
Good balance between performance and cost.
Up to 60,000 IOPS and 1,200 MB/s throughput.
Extreme Persistent Disk (pd-extreme)
SSD-backed and configurable IOPS.
Designed for high-performance, I/O-intensive workloads.
Supports over 100,000 IOPS with ultra-low latency.
SSD Persistent Disk (pd-ssd)
High-performance SSD.
Best for latency-sensitive workloads.
Up to 80,000 IOPS and 1,200 MB/s throughput.
Standard Persistent Disk (pd-standard)
Economical option for infrequent access.
HDD-backed storage.
Up to 3,000 IOPS and 180 MB/s throughput.
Real-Time Use Cases
Balanced Disk:
Medium-size SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL).
Web app backends and microservices.
Dev/test environments.
Extreme Disk:
Enterprise workloads like SAP HANA, Oracle DB.
Financial trading systems or analytics platforms.
Scalable database clusters (e.g., Spanner, Cassandra).
SSD Disk:
OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) systems.
Game servers and real-time data processing.
NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Redis.
Standard Disk:
Backup and disaster recovery.
Archival and logging data.
Large batch processing with minimal read/write.
Cost Comparision:
When to Use Each
Balanced Disk → For general-purpose workloads where performance and cost must be balanced.
Extreme Disk → When you need ultra-high IOPS, such as for enterprise DBs.
SSD Disk → When latency and fast performance are top priorities.
Standard Disk → For cost-sensitive workloads with low I/O requirements.
Final Summary
Google Cloud provides flexible disk options for performance, cost, and scalability.
Balanced is ideal for everyday apps.
Extreme is built for performance-intensive enterprise systems.
SSD excels in fast-response and low-latency apps.
Standard is best for cold storage and cost efficiency.
Choosing the right disk ensures better performance, lower cost, and higher reliability.
Venkat C S





































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)















































































































































































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)




















































.jpg?#)






























_Alexey_Kotelnikov_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Brian_Jackson_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

_Steven_Jones_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)


 Stolen 884,000 Credit Card Details on 13 Million Clicks from Users Worldwide.webp?#)



















































































![Roku clarifies how ‘Pause Ads’ work amid issues with some HDR content [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/05/roku-pause-ad-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

![Look at this Chrome Dino figure and its adorable tiny boombox [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/05/chrome-dino-youtube-boombox-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)










![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 RC to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97240/97240/97240-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 RC to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97243/97243/97243-640.jpg)

![Apple Releases macOS Sequoia 15.5 RC to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97245/97245/97245-640.jpg)