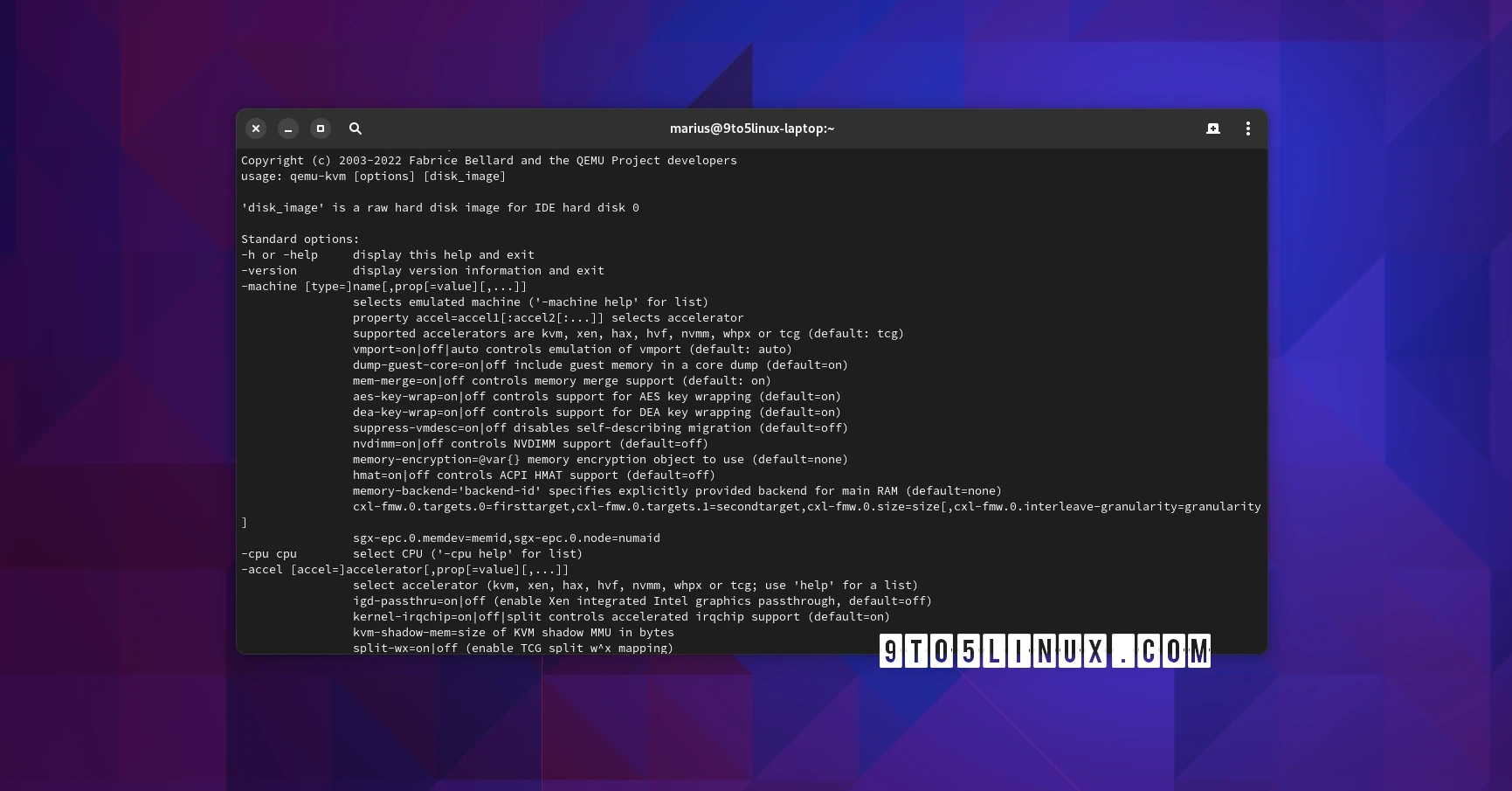
Stacking Elements with Z-index in CSS
This post was originally published at thedevspace.io. Everything you need to master web development, all in one place. z-index is used to control the order of elements when they are stacked on top of each other. The property accepts integer values, the higher the integer, the higher the order. For example, z-index: 1 z-index: 2 z-index: 3 z-index: 2 z-index: 1 Try to change the z-index of this box div { font-family: Georgia, "Times New Roman", Times, serif; font-size: x-large; text-align: center; padding: 20px; border: 1px solid orange; background-color: bisque; position: absolute; } .item { top: 0px; left: 0px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid skyblue; background-color: lightblue; } .item1 { top: 0px; left: 0px; z-index: 1; } .item2 { top: 50px; left: 50px; z-index: 2; } .item3 { top: 100px; left: 100px; z-index: 3; } .item4 { top: 150px; left: 50px; z-index: 2; } .item5 { top: 200px; left: 0px; z-index: 1; } Visit Code Demo

This post was originally published at thedevspace.io. Everything you need to master web development, all in one place.
z-index is used to control the order of elements when they are stacked on top of each other. The property accepts integer values, the higher the integer, the higher the order. For example,
class="item1">z-index: 1 









































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)
























































































































































![Is This Programming Paradigm New? [closed]](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:1200/format:webp/1*nKR2930riHA4VC7dLwIuxA.gif)

























































































-Classic-Nintendo-GameCube-games-are-coming-to-Nintendo-Switch-2!-00-00-13.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
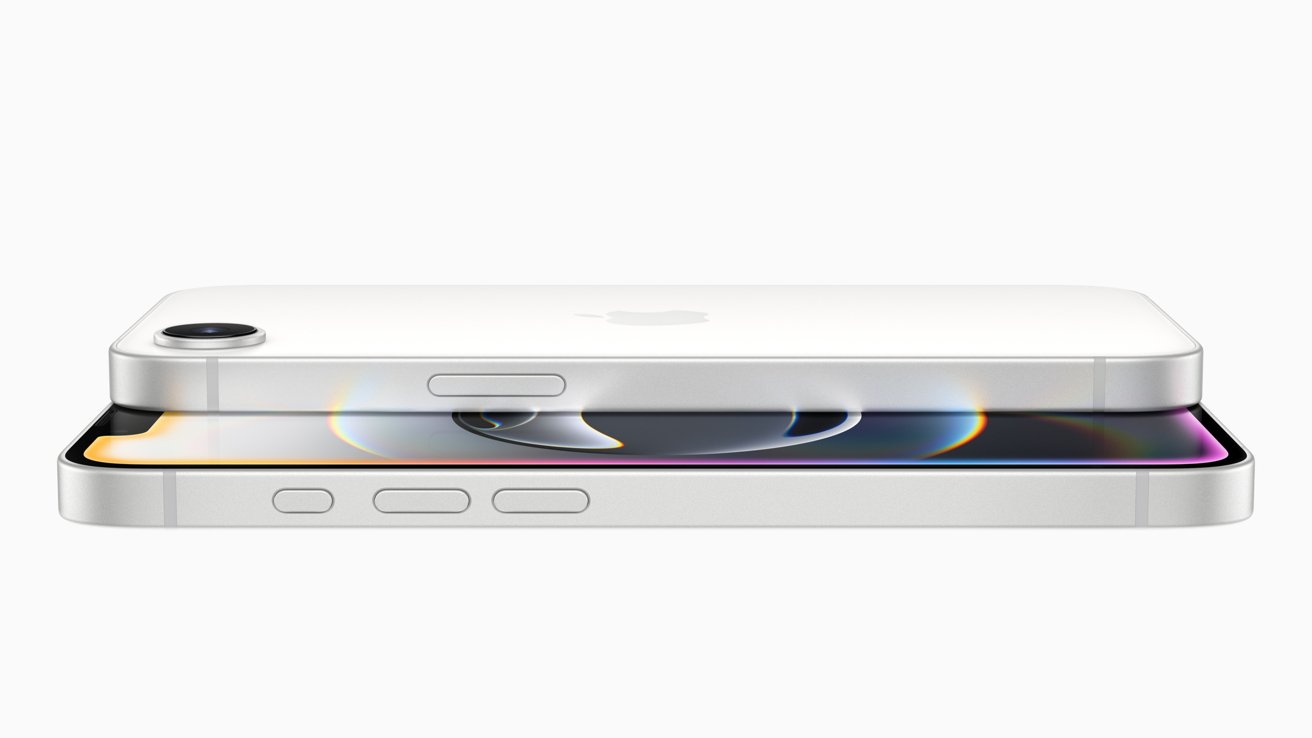











































































































































![New iPhone 17 Dummy Models Surface in Black and White [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97106/97106/97106-640.jpg)


![Hands-On With 'iPhone 17 Air' Dummy Reveals 'Scary Thin' Design [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97100/97100/97100-640.jpg)