HIPAA Compliance in WPF Apps: Auto-Delete PHI on Jailbreak
Why HIPAA Compliance Matters in WPF Medical Apps HIPAA Compliance in WPF Apps is crucial, as WPF (.NET) medical applications have a critical responsibility to protect Protected Health Information (PHI) from unauthorized access. Any security failure can expose sensitive medical data, leading to privacy violations and severe penalties for non-compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). The Importance of Protecting PHI in .NET Applications Medical applications store and process highly sensitive information, including electronic health records (EHRs), diagnoses, prescriptions, and medical images. If compromised, this data can be exploited for fraud, medical identity theft, or even the malicious alteration of patient records. Why Do WPF Apps Handling PHI Need HIPAA Compliance? Legal and financial risks: HIPAA regulations impose strict security requirements on any application handling PHI. Non-compliance can lead to heavy fines and legal consequences. Patient trust and reputation: A data breach can damage a healthcare provider’s reputation and result in loss of patient confidence. Cybersecurity threats: Without proper safeguards, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the application to steal or manipulate medical records. How Jailbroken Devices Compromise Medical App Security What Is a Jailbroken or Rooted Device, and Why Is It a Threat? A jailbroken (iOS) or rooted (Android) device is a smartphone, tablet, or computer that has been modified to bypass manufacturer security restrictions. While some users jailbreak their devices for customization, this process also disables key security mechanisms, exposing the system to threats. How Attackers Can Extract PHI from Unprotected Applications When a WPF medical application runs on a jailbroken or rooted device, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to: Intercept and decrypt stored medical records if encryption is weak or improperly implemented. Extract login credentials and session tokens to access patient data. Bypass security features such as biometric authentication or PIN verification. Attach debugging tools to analyze and manipulate the application’s behavior. Preventing Compliance Risks: Detecting and Auto-Deleting PHI on Jailbroken Devices Since HIPAA mandates strict data protection, allowing a medical application to run on a compromised device creates a major compliance risk. To prevent this, WPF developers need mechanisms to detect jailbroken devices and automatically delete PHI before it can be accessed. Understanding Runtime Threat Detection in WPF Apps Ensuring HIPAA compliance in WPF medical applications goes beyond encryption and access control. A critical aspect is real-time threat detection to prevent unauthorized access to Protected Health Information (PHI). Attackers often use debuggers, emulators, or jailbroken devices to extract sensitive data, bypass security controls, and manipulate application behavior. The Role of RASP (Runtime Application Self-Protection) in HIPAA Compliance How RASP Helps Secure WPF Medical Applications Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) is a security mechanism that monitors an application in real-time to detect and block potential threats. Unlike traditional security tools that focus on network traffic or system monitoring, RASP works inside the application to ensure immediate response to security breaches. Detects unauthorized modifications: Identifies debuggers, memory tampering, and jailbroken devices attempting to manipulate app behavior. Prevents data leaks: Automatically erases PHI or disables sensitive functionality when a security risk is detected. Ensures HIPAA compliance: Proactively protects patient data from real-world security threats, reducing the risk of violations. Example: Real-World Application of RASP in WPF Medical Apps Protecting PHI in WPF Medical Apps with RASP A WPF medical app used by hospitals for managing patient prescriptions is running on a compromised device where an attacker is using a debugger to extract PHI. With RASP protection, the application can: ✔ Detect the unauthorized debugger. ✔ Automatically wipe stored PHI from the device. ✔ Log the security event for compliance audits. ✔ Notify system administrators of the breach. This prevents unauthorized data access while maintaining HIPAA compliance. Detecting Debuggers and Jailbreaks in .NET Medical Apps Attackers rely on debugging tools, reverse engineering techniques, and jailbroken/rooted environments to bypass application security and extract medical data. Detecting these threats in real-time is essential to prevent data breaches. Common Techniques for Identifying Debuggers and Modified Environments Detecting Debugging Tools Using Debugger.IsAttached to check if a debugger is connected. Monitori
Why HIPAA Compliance Matters in WPF Medical Apps
HIPAA Compliance in WPF Apps is crucial, as WPF (.NET) medical applications have a critical responsibility to protect Protected Health Information (PHI) from unauthorized access. Any security failure can expose sensitive medical data, leading to privacy violations and severe penalties for non-compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
The Importance of Protecting PHI in .NET Applications
Medical applications store and process highly sensitive information, including electronic health records (EHRs), diagnoses, prescriptions, and medical images. If compromised, this data can be exploited for fraud, medical identity theft, or even the malicious alteration of patient records.
Why Do WPF Apps Handling PHI Need HIPAA Compliance?
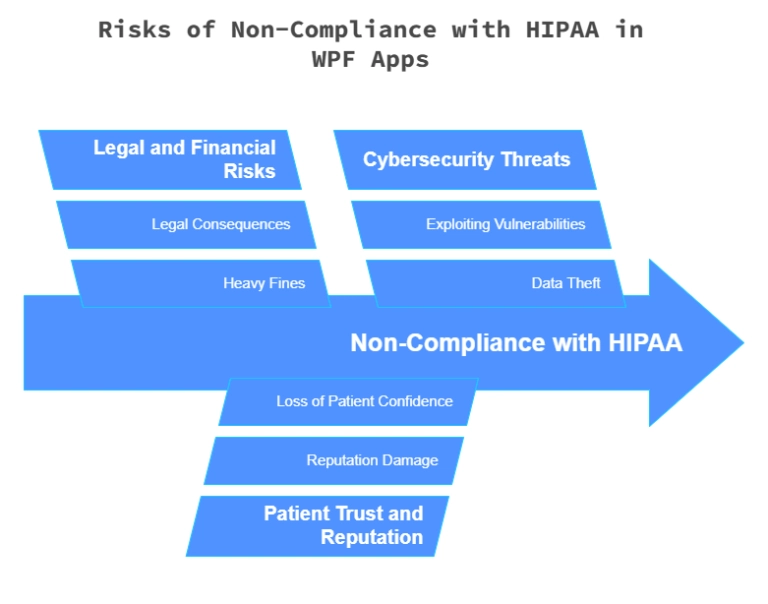
- Legal and financial risks: HIPAA regulations impose strict security requirements on any application handling PHI. Non-compliance can lead to heavy fines and legal consequences.
- Patient trust and reputation: A data breach can damage a healthcare provider’s reputation and result in loss of patient confidence.
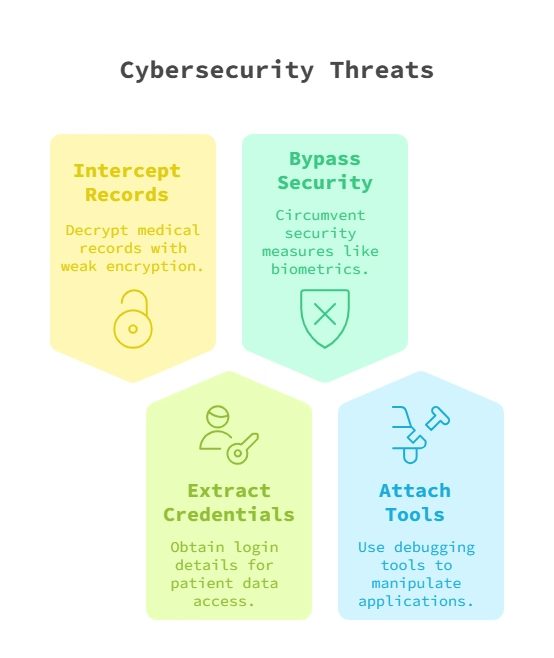
- Cybersecurity threats: Without proper safeguards, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the application to steal or manipulate medical records.
How Jailbroken Devices Compromise Medical App Security
What Is a Jailbroken or Rooted Device, and Why Is It a Threat?
A jailbroken (iOS) or rooted (Android) device is a smartphone, tablet, or computer that has been modified to bypass manufacturer security restrictions. While some users jailbreak their devices for customization, this process also disables key security mechanisms, exposing the system to threats.
How Attackers Can Extract PHI from Unprotected Applications
When a WPF medical application runs on a jailbroken or rooted device, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to:
- Intercept and decrypt stored medical records if encryption is weak or improperly implemented.
- Extract login credentials and session tokens to access patient data.
- Bypass security features such as biometric authentication or PIN verification.
- Attach debugging tools to analyze and manipulate the application’s behavior.
Preventing Compliance Risks: Detecting and Auto-Deleting PHI on Jailbroken Devices
Since HIPAA mandates strict data protection, allowing a medical application to run on a compromised device creates a major compliance risk. To prevent this, WPF developers need mechanisms to detect jailbroken devices and automatically delete PHI before it can be accessed.
Understanding Runtime Threat Detection in WPF Apps
Ensuring HIPAA compliance in WPF medical applications goes beyond encryption and access control. A critical aspect is real-time threat detection to prevent unauthorized access to Protected Health Information (PHI). Attackers often use debuggers, emulators, or jailbroken devices to extract sensitive data, bypass security controls, and manipulate application behavior.
The Role of RASP (Runtime Application Self-Protection) in HIPAA Compliance
How RASP Helps Secure WPF Medical Applications
Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) is a security mechanism that monitors an application in real-time to detect and block potential threats. Unlike traditional security tools that focus on network traffic or system monitoring, RASP works inside the application to ensure immediate response to security breaches.
- Detects unauthorized modifications: Identifies debuggers, memory tampering, and jailbroken devices attempting to manipulate app behavior.
- Prevents data leaks: Automatically erases PHI or disables sensitive functionality when a security risk is detected.
- Ensures HIPAA compliance: Proactively protects patient data from real-world security threats, reducing the risk of violations.
Example: Real-World Application of RASP in WPF Medical Apps
Protecting PHI in WPF Medical Apps with RASP
A WPF medical app used by hospitals for managing patient prescriptions is running on a compromised device where an attacker is using a debugger to extract PHI. With RASP protection, the application can:
✔ Detect the unauthorized debugger.
✔ Automatically wipe stored PHI from the device.
✔ Log the security event for compliance audits.
✔ Notify system administrators of the breach.
This prevents unauthorized data access while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
Detecting Debuggers and Jailbreaks in .NET Medical Apps
Attackers rely on debugging tools, reverse engineering techniques, and jailbroken/rooted environments to bypass application security and extract medical data. Detecting these threats in real-time is essential to prevent data breaches.
Common Techniques for Identifying Debuggers and Modified Environments
Detecting Debugging Tools
- Using
Debugger.IsAttachedto check if a debugger is connected. - Monitoring system APIs for debugging-related behavior.
Identifying Jailbroken or Rooted Devices
- Checking for modified system files indicating an altered OS.
- Detecting jailbreak tools commonly used by attackers.
Preventing Memory Tampering
- Scanning memory regions for unauthorized modifications.
- Verifying the integrity of stored PHI.
Why Stopping Execution Is Not Enough – The Need for Automated PHI Deletion
Simply terminating the application when a security threat is detected is not sufficient for HIPAA compliance. If PHI remains stored on the device, attackers can still access it later. To fully protect patient data, the app must automatically delete PHI as soon as a security breach is detected.






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)


































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)











































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)




























































.jpg?#)







.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)























_ArtemisDiana_Alamy.jpg?#)










































































-xl.jpg)











![Yes, the Gemini icon is now bigger and brighter on Android [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/02/Gemini-on-Galaxy-S25.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)