Update your Chrome to fix serious actively exploited vulnerability
Make sure your Chrome is on the latest version, to patch against an actively exploited vulnerability that can be used to steal sensitive information from websites.

Google released an emergency update for the Chrome browser to patch an actively exploited vulnerability that could have serious ramifications.
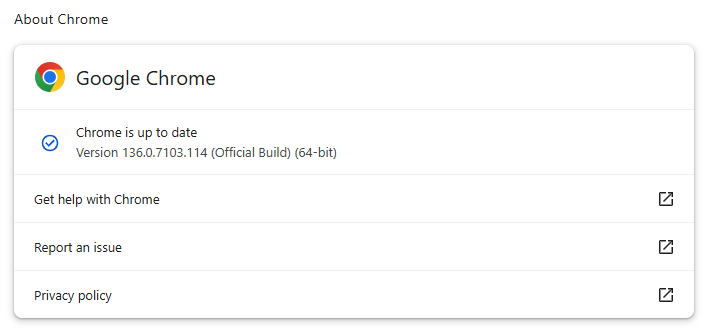
The update brings the Stable channel to versions 136.0.7103.113/.114 for Windows and Mac and 136.0.7103.113 for Linux.
The easiest way to update Chrome is to allow it to update automatically, but you can end up lagging behind if you never close your browser or if something goes wrong—such as an extension stopping you from updating the browser.
To manually get the update, click Settings > About Chrome. If there is an update available, Chrome will notify you and start downloading it. Then all you have to do is restart the browser in order for the update to complete, and for you to be safe from those vulnerabilities.
This update is crucial since it addresses an actively exploited vulnerability which could allow an attacker to steal information you share with other websites. Google says it’s aware that knowledge of CVE-2025-4664 exists in the wild. But while Google didn’t acknowledge that the vulnerability is actually being actively exploited, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added the vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog—a strong indication the vulnerability is being used out there.
Technical details
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025–4664, lies in the Chrome Loader component, which handles resource requests. When you visit a website, your browser often needs to load additional pieces of that site, such as images, scripts, or stylesheets, which may come from various sources. The Loader manages these requests to fetch and display those resources properly.
While it does that, it should enforce security policies that prevent one website from accessing data belonging to another website, a principle known as the “same-origin policy.”
The vulnerability lies in the fact that those security policies were not applied properly to Link headers. This allowed an attacker to set a referrer-policy in the Link header which tells Chrome to include full URLs, including sensitive query parameters.
This is undesirable since query parameters in full URLs often contain sensitive information such as OAuth tokens (used for authentication), session identifiers, and other private data.
Imagine you visit a website related to sensitive or financial information, and the URL includes a secret code in the address bar that proves it’s really you. Normally, when your browser loads images or other content from different websites, it keeps that secret code private. But because of this Chrome Loader flaw, a successful attacker can trick your browser into sending that secret code to a malicious website just by embedding an image or other resource there.
The attacker could, for example, embed a hidden image hosted at their own server, and harvest the full URLs. This means they can steal your private information without you realizing it, potentially letting them take over your account or other online services.
We don’t just report on threats – we help safeguard your entire digital identity
Cybersecurity risks should never spread beyond a headline. Protect your—and your family’s—personal information by using identity protection.









































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The ChatGPT & AI Super Bundle (91% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)

![How to make Developer Friends When You Don't Live in Silicon Valley, with Iraqi Engineer Code;Life [Podcast #172]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1747360508340/f07040cd-3eeb-443c-b4fb-370f6a4a14da.png?#)






































































































































































































































![A rare look inside the TSMC Arizona plant making chips for Apple [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/05/A-look-inside-the-TSMC-Arizona-plant-making-chips-for-Apple.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

















![Why Apple Still Can't Catch Up in AI and What It's Doing About It [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97352/97352/97352-640.jpg)
![Sonos Move 2 On Sale for 25% Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97355/97355/97355-640.jpg)
![Apple May Not Update AirPods Until 2026, Lighter AirPods Max Coming in 2027 [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97350/97350/97350-640.jpg)