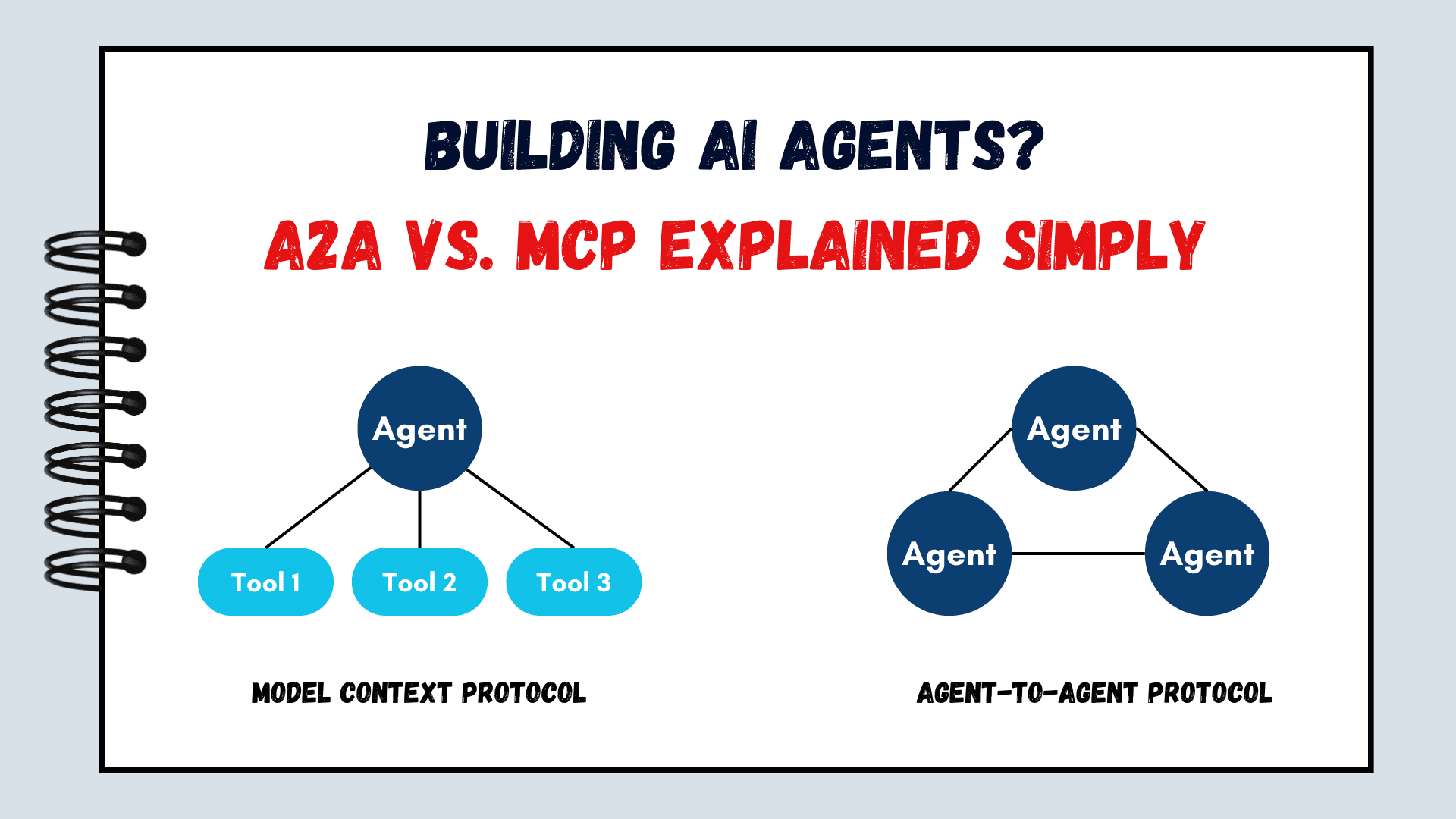
Microsoft’s Windows Subsystem for Linux is now open-source
Microsoft is making its Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) open-source today, opening up the code for community members to contribute to. After launching WSL for Windows 10 nearly nine years ago, it has been a multiyear effort at Microsoft to open-source the feature that enables a Linux environment within Windows. “It has been a consistent […]


Microsoft is making its Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) open-source today, opening up the code for community members to contribute to. After launching WSL for Windows 10 nearly nine years ago, it has been a multiyear effort at Microsoft to open-source the feature that enables a Linux environment within Windows.
“It has been a consistent request from the developer community for some time now,” says Windows chief Pavan Davuluri in an interview with The Verge. “It took us a little bit of time, because we needed to refactor the operating system to allow WSL to live in a standalone capacity that then allowed us to open-source the project and be able to have developers go and make contributions and for us to ingest those into the Windows pipeline and ship it at scale.”
The WSL code is now available on GitHub, allowing developers to download it and build it from source, participate in fixes, or even add new features. The WSL community hasn’t had access to Microsoft’s source code in the past, but that hasn’t stopped them from making contributions that have helped improve WSL over the years. Davuluri says he’s now expecting that developers will use the open-source project to help improve WSL performance, or for more integration into Linux services.

It’s a major milestone for WSL, which started off life in 2016 as part of the Windows 10 Anniversary update. “At that time WSL was based on a pico process provider, lxcore.sys, which enabled Windows to natively run ELF executables, and implement Linux syscalls inside the Windows kernel,” explains Pierre Boulay, senior software engineer at Microsoft. “Over time it became clear that the best way to provide optimal compatibility with native Linux was to rely on the Linux kernel itself.”
Microsoft announced its second major version of WSL in 2019, eventually adding GPU support and then moving to ship the project separate to Windows. “It eventually became clear that to keep up the growing community and feature requests, WSL had to move faster, and ship separately from Windows,” says Boulay. “That’s why in 2021 we separated WSL from the Windows codebase, and moved it to its own codebase.” In the latest 24H2 update for Windows 11, Microsoft has fully transitioned WSL users to a package that’s separate from Windows, instead of the WSL component that was baked into the OS.
All of these changes to WSL in recent years have led Microsoft to close off the first ever issue raised on its WSL repo on GitHub, asking “Will this be open-source?” That answer is very much yes now, and it’s a part of making Windows more developer-friendly. “Our goal is quite simple: we want Windows to be a great dev box for developers,” says Davuluri. “That’s really the ambition.”








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The ChatGPT & AI Super Bundle (91% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)

![How to make Developer Friends When You Don't Live in Silicon Valley, with Iraqi Engineer Code;Life [Podcast #172]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1747360508340/f07040cd-3eeb-443c-b4fb-370f6a4a14da.png?#)






































































































































































































































![A rare look inside the TSMC Arizona plant making chips for Apple [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/05/A-look-inside-the-TSMC-Arizona-plant-making-chips-for-Apple.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

















![Why Apple Still Can't Catch Up in AI and What It's Doing About It [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97352/97352/97352-640.jpg)
![Sonos Move 2 On Sale for 25% Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97355/97355/97355-640.jpg)
![Apple May Not Update AirPods Until 2026, Lighter AirPods Max Coming in 2027 [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97350/97350/97350-640.jpg)