The real win of AI PCs? Battery life
In 2022-2023, AI-powered PCs made quite a splash with their automatic generation and built-in virtual assistants. Those features are cool, sure, but they’re a little gimmicky at first blush. That said, amid the hype, the real standout feature emerged: battery life. Thanks to smarter resource management and power-efficient chip architecture, AI PCs became long-lasting devices that didn’t need to be plugged in all the time. Let’s take flying cross-country with a traditional laptop, for instance. You’d probably be anxiously keeping an eye on your battery icon throughout the flight, but with an AI PC you wouldn’t have to think twice about it. The longest-lasting laptop we’ve tested, Lenovo’s ThinkPad T14s Gen 6, delivers nearly 24 hours on a single charge in our testing — and it’s no longer an outlier. Let’s dig into why. Further reading: The best laptops we’ve tested The heart of efficiency: A smarter, specialized chip The new Neural Processing Units (aka the NPU) inside of Copilot+ PCs is where some of the magic happens, as it’s more energy-efficient than a traditional processor with the x86 architecture. CPUs and GPUs can be a massive drain on a laptop’s battery, especially if both are active at the same time. They also aren’t optimized for AI tasks. The NPU is different from a traditional processor in that it’s a specialized hardware chip that runs AI workloads like image recognition and real-time language translation. Offloading these intensive jobs allows the CPU and GPU to idle more often, effectively cutting down on power consumption. The NPU also gets a nice boost from its architecture, which uses parallel processing and lower clock speeds. Parallel processing allows the NPU handle multiple tasks simultaneously instead of completing them one at a time. By breaking these tasks into smaller chunks and then executing them at the same time, the laptop can return to idle mode more quickly, thus conserving energy. As for the clock speed, a lower one consumes less power than a higher one. The less power the NPU uses, the longer the battery lasts. Snapdragon X and the rise of CPU efficiency Another game-changer is Arm-based Snapdragon processor, which uses a mix of specialized cores–this is what makes them so efficient and consume less power. In fact, they’re so efficient we’ve seen one AI PC last up to 24 hours on a single charge. That sort of longevity means that the laptop should last an entire work or school day, with extra juice to spare. this snapdragon laptop can last 24 hours Lenovo ThinkPad T14s Gen 6 Read our review The key here is how the chip uses its “Performance” cores for demanding jobs (3D design or video rendering) and “Efficient” cores for lighter tasks (checking e-mail or playing music). The switching between these cores depends on the type of workload. This allows the system to deliver just the right amount of processing power when needed, so it shouldn’t waste power on simpler tasks, resulting in a smooth multitasking experience as well as improved energy conservation. These processors know how to handle idle time, too. So, when a laptop isn’t being used, the processor enters an ultra-low power mode, so it shouldn’t waste much, if any, energy. Intel’s rival “Lunar Lake” laptops, which arrived hot on the heels of Snapdragon X with its own NPU in tow, also deliver delightfully long battery life. Meanwhile, while AMD’s latest chips focus more on driving performance, Ryzen laptops have increased their endurance significantly over the last year. Sure, the parallel-processing NPU might pick up slack, but a large part of this exciting leap-forward in laptop battery life is being driven by improvements to overall CPU efficiency. AI-driven software optimization It’s not just the hardware that’s impressive–AI-driven software optimization plays a big part as well. At the crux, it intelligently manages how the system uses resources. For example, instead of constantly syncing files to the cloud like with OneDrive or Google Drive, an AI PC can reduce the syncing frequency when it’s on battery power or schedules it for moments when the laptop isn’t in use. The software also suppresses unnecessary notifications from social apps and shuts down background processes that haven’t been used in a while. It’s basically designed to adapt to your unique usage patterns and learning your daily habits. AI can even protect your battery’s health with something called “Intelligent Charging.” It does this by learning your routine; it’ll slow down charging overnight or stop the battery from charging at the 80-85 mark (if you keep your laptop plugged in overnight). The

In 2022-2023, AI-powered PCs made quite a splash with their automatic generation and built-in virtual assistants. Those features are cool, sure, but they’re a little gimmicky at first blush. That said, amid the hype, the real standout feature emerged: battery life. Thanks to smarter resource management and power-efficient chip architecture, AI PCs became long-lasting devices that didn’t need to be plugged in all the time.
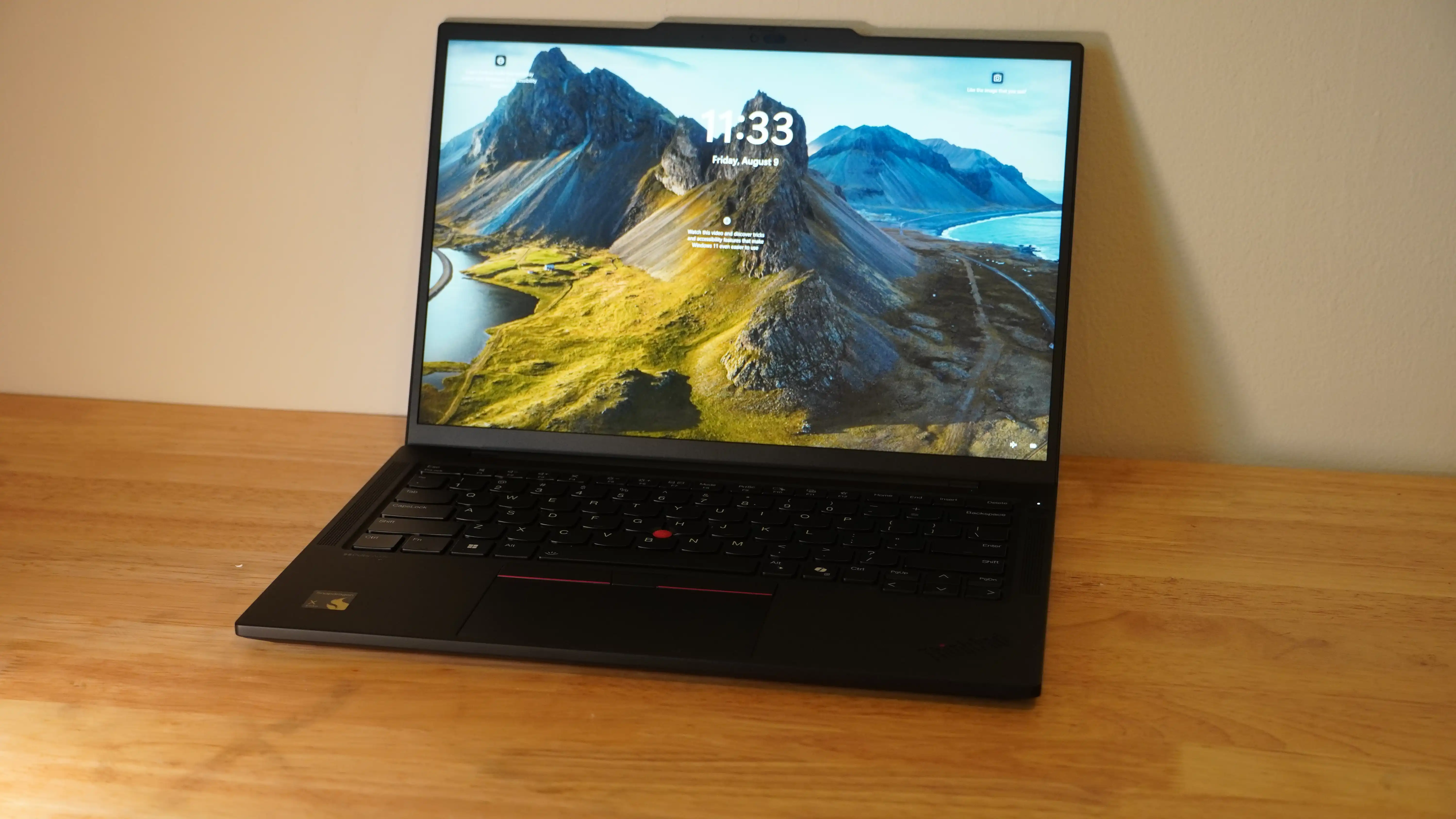
Let’s take flying cross-country with a traditional laptop, for instance. You’d probably be anxiously keeping an eye on your battery icon throughout the flight, but with an AI PC you wouldn’t have to think twice about it. The longest-lasting laptop we’ve tested, Lenovo’s ThinkPad T14s Gen 6, delivers nearly 24 hours on a single charge in our testing — and it’s no longer an outlier. Let’s dig into why.
Further reading: The best laptops we’ve tested
The heart of efficiency: A smarter, specialized chip
The new Neural Processing Units (aka the NPU) inside of Copilot+ PCs is where some of the magic happens, as it’s more energy-efficient than a traditional processor with the x86 architecture. CPUs and GPUs can be a massive drain on a laptop’s battery, especially if both are active at the same time. They also aren’t optimized for AI tasks.
The NPU is different from a traditional processor in that it’s a specialized hardware chip that runs AI workloads like image recognition and real-time language translation. Offloading these intensive jobs allows the CPU and GPU to idle more often, effectively cutting down on power consumption.
The NPU also gets a nice boost from its architecture, which uses parallel processing and lower clock speeds. Parallel processing allows the NPU handle multiple tasks simultaneously instead of completing them one at a time. By breaking these tasks into smaller chunks and then executing them at the same time, the laptop can return to idle mode more quickly, thus conserving energy. As for the clock speed, a lower one consumes less power than a higher one. The less power the NPU uses, the longer the battery lasts.
Snapdragon X and the rise of CPU efficiency
Another game-changer is Arm-based Snapdragon processor, which uses a mix of specialized cores–this is what makes them so efficient and consume less power. In fact, they’re so efficient we’ve seen one AI PC last up to 24 hours on a single charge. That sort of longevity means that the laptop should last an entire work or school day, with extra juice to spare.
The key here is how the chip uses its “Performance” cores for demanding jobs (3D design or video rendering) and “Efficient” cores for lighter tasks (checking e-mail or playing music). The switching between these cores depends on the type of workload. This allows the system to deliver just the right amount of processing power when needed, so it shouldn’t waste power on simpler tasks, resulting in a smooth multitasking experience as well as improved energy conservation.
These processors know how to handle idle time, too. So, when a laptop isn’t being used, the processor enters an ultra-low power mode, so it shouldn’t waste much, if any, energy.
Intel’s rival “Lunar Lake” laptops, which arrived hot on the heels of Snapdragon X with its own NPU in tow, also deliver delightfully long battery life. Meanwhile, while AMD’s latest chips focus more on driving performance, Ryzen laptops have increased their endurance significantly over the last year. Sure, the parallel-processing NPU might pick up slack, but a large part of this exciting leap-forward in laptop battery life is being driven by improvements to overall CPU efficiency.
AI-driven software optimization
It’s not just the hardware that’s impressive–AI-driven software optimization plays a big part as well. At the crux, it intelligently manages how the system uses resources.
For example, instead of constantly syncing files to the cloud like with OneDrive or Google Drive, an AI PC can reduce the syncing frequency when it’s on battery power or schedules it for moments when the laptop isn’t in use. The software also suppresses unnecessary notifications from social apps and shuts down background processes that haven’t been used in a while. It’s basically designed to adapt to your unique usage patterns and learning your daily habits.
AI can even protect your battery’s health with something called “Intelligent Charging.” It does this by learning your routine; it’ll slow down charging overnight or stop the battery from charging at the 80-85 mark (if you keep your laptop plugged in overnight). The reason for this cap is because lithium-ion batteries degrade faster when they’re constantly charged to 100 percent. Plus, AI can even monitor the internal temperature of your machine, slowing down the charge if things get too hot. Heat can increase energy consumption and shorten a battery’s lifespan.
Looking ahead: A more power-efficient future
With NPUs, CPUs, and machine learning constantly evolving, we’re heading towards a future where bad battery life is a thing of the past. The combination of smarter hardware and software will only improve with time–I’m confident in this. If you’re tired of constantly monitoring your battery, it might be time to welcome this new wave of AI-powered PCs with open arms.




































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)















































































































































































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


















































































_Brian_Jackson_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

_Steven_Jones_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)


 Stolen 884,000 Credit Card Details on 13 Million Clicks from Users Worldwide.webp?#)


























































































![Look at this Chrome Dino figure and its adorable tiny boombox [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/05/chrome-dino-youtube-boombox-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 RC to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97240/97240/97240-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 RC to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97243/97243/97243-640.jpg)

![Apple Releases macOS Sequoia 15.5 RC to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97245/97245/97245-640.jpg)