Microsoft just adopted Google’s AI Agent protocol here’s why it matters
Microsoft adopts Google’s A2A protocol to enhance AI agent interoperability across platforms, integrating it into Azure AI Studio and Copilot Studio.


Microsoft has announced its adoption of Google’s Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol, an open technical standard that allows artificial intelligence (AI) agents to communicate and work together across different systems.
The decision, made public on May 7, reflects a growing industry shift toward standardising how AI tools from different companies interact.
Google introduced the A2A protocol in April 2025. It’s designed to let AI agents—autonomous software programs capable of taking actions—exchange information and coordinate tasks even if they’re built on separate platforms.
By supporting the protocol, Microsoft aims to make its AI tools more collaborative, especially in enterprise environments where systems from multiple vendors are often used.
How does Agent2Agent work?
AI agents are increasingly being used to automate tasks like booking meetings, generating documents, summarising data, and sending messages. With A2A, these agents can communicate with one another, passing off tasks or requesting assistance, regardless of the underlying architecture or cloud platform.
For example, a Microsoft-built AI agent could manage a user’s calendar, while a Google-built agent handles email reminders, with both working in sync to complete a shared workflow. The protocol enables this by providing a standard set of rules for how agents describe their goals and capabilities.
Microsoft will integrate A2A into its platforms, including Azure AI Studio and Copilot Studio. The company also plans to participate in further development of the protocol through the A2A working group hosted on GitHub, contributing to its governance and technical evolution.
Aligning with other open standards
Microsoft’s adoption of A2A follows a similar move earlier this year when it implemented the Model Connector Protocol (MCP). MCP, developed by Anthropic, allows AI models to connect with external data systems and services. Google and OpenAI are also backing MCP.
Together, these protocols are part of a larger effort among major technology firms to build open and interoperable AI ecosystems. These standards are aimed at making it easier for companies to mix and match AI services without being locked into a single provider.
Enterprise demand for AI agents is growing
Interest in AI agents is on the rise across industries. A KPMG survey cited by TechCrunch found that 65% of companies are currently testing or using agents to streamline business operations. These tools are often deployed in areas like customer support, scheduling, and internal workflow management.
Research firm Markets and Markets estimates that the global market for AI agents will increase from $7.84 billion in 2025 to $52.62 billion by 2030, signaling strong demand for agent-based automation.






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)

























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Python Programming PCEP Certification Prep Bundle (67% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)















































.jpg?#)
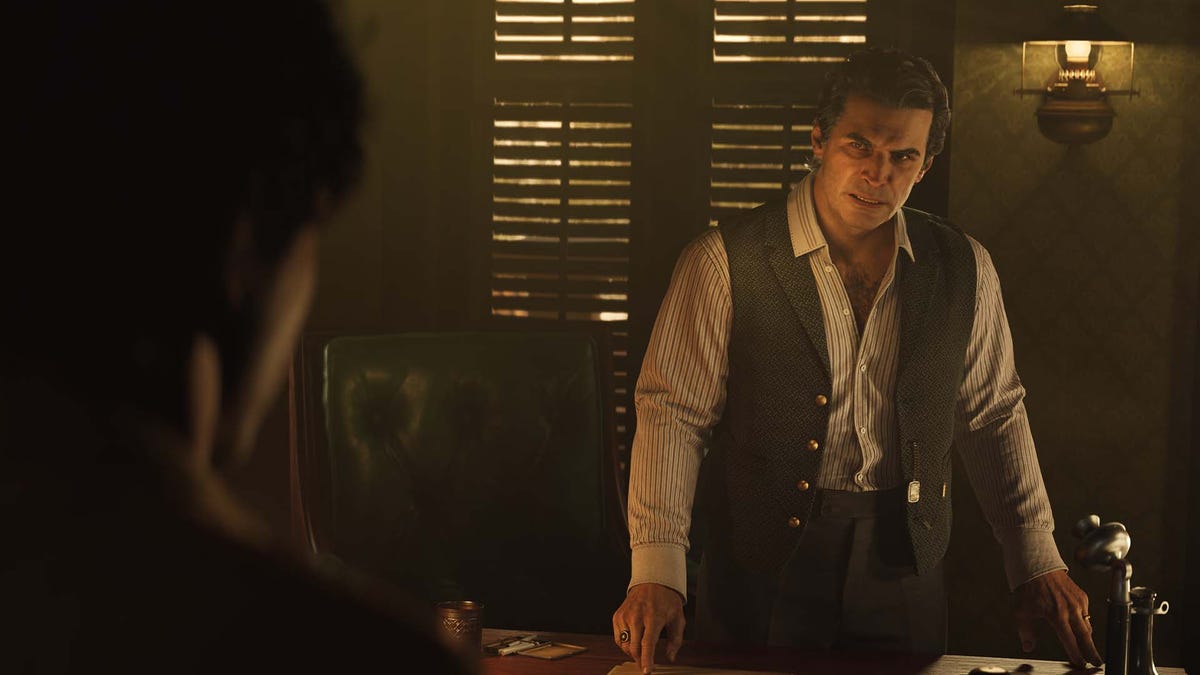

































































-Mafia-The-Old-Country---The-Initiation-Trailer-00-00-54.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
-Nintendo-Switch-2---Reveal-Trailer-00-01-52.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)























_Aleksey_Funtap_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Sergey_Tarasov_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)















































































































![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Stick' Starring Owen Wilson [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97264/97264/97264-640.jpg)


![Beats Studio Pro Wireless Headphones Now Just $169.95 - Save 51%! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97258/97258/97258-640.jpg)