3342. Find Minimum Time to Reach Last Room II
3342. Find Minimum Time to Reach Last Room II Difficulty: Medium Topics: Array, Graph, Heap (Priority Queue), Matrix, Shortest Path There is a dungeon with n x m rooms arranged as a grid. You are given a 2D array moveTime of size n x m, where moveTime[i][j] represents the minimum time in seconds when you can start moving to that room. You start from the room (0, 0) at time t = 0 and can move to an adjacent room. Moving between adjacent rooms takes one second for one move and two seconds for the next, alternating between the two. Return the minimum time to reach the room (n - 1, m - 1). Two rooms are adjacent if they share a common wall, either horizontally or vertically. Example 1: Input: moveTime = [[0,4],[4,4]] Output: 7 Explanation: The minimum time required is 7 seconds. At time t == 4, move from room (0, 0) to room (1, 0) in one second. At time t == 5, move from room (1, 0) to room (1, 1) in two seconds. Example 2: Input: moveTime = [[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0]] Output: 6 Explanation: The minimum time required is 6 seconds. At time t == 0, move from room (0, 0) to room (1, 0) in one second. At time t == 1, move from room (1, 0) to room (1, 1) in two seconds. At time t == 3, move from room (1, 1) to room (1, 2) in one second. At time t == 4, move from room (1, 2) to room (1, 3) in two seconds. Example 3: Input: moveTime = [[0,1],[1,2]] Output: 4 Constraints: 2 Explanation: Initialization: The distance array dist is initialized to infinity for all positions and parities, except the starting position (0, 0) with parity 0, which is set to 0. Priority Queue: The priority queue is initialized with the starting position and time 0. The queue is ordered to always process the smallest time first by using negative priorities. Processing Nodes: For each node extracted from the queue, check if it is the target. If not, explore all adjacent nodes, calculate the departure and arrival times considering the minimum start time of the destination node, and update the priority queue if a shorter path is found. Dynamic Adjustment: The cost of each move alternates between 1 and 2 seconds based on the parity of moves taken so far. The departure time is adjusted to ensure it meets the minimum start time of the destination node. This approach efficiently finds the shortest path using Dijkstra's algorithm with state tracking for move parity, ensuring optimal time complexity and handling the constraints effectively. Contact Links If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks
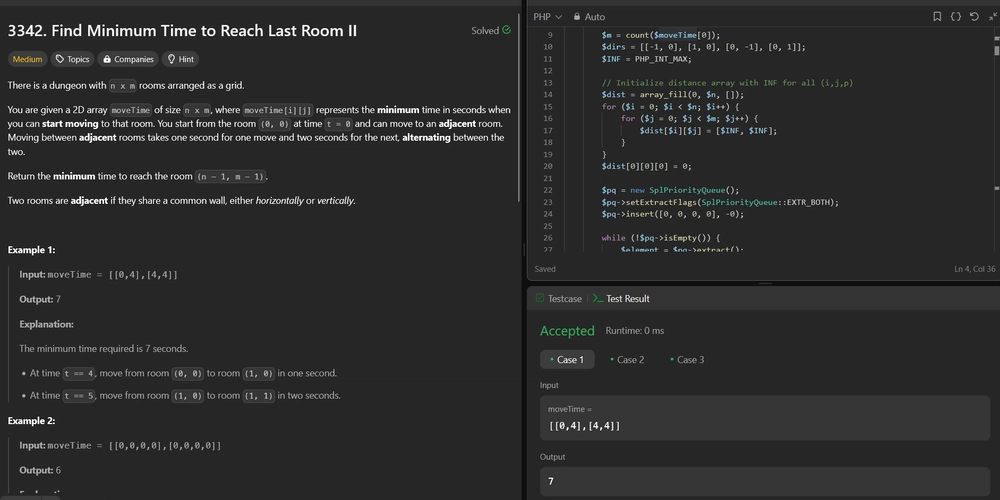
3342. Find Minimum Time to Reach Last Room II
Difficulty: Medium
Topics: Array, Graph, Heap (Priority Queue), Matrix, Shortest Path
There is a dungeon with n x m rooms arranged as a grid.
You are given a 2D array moveTime of size n x m, where moveTime[i][j] represents the minimum time in seconds when you can start moving to that room. You start from the room (0, 0) at time t = 0 and can move to an adjacent room. Moving between adjacent rooms takes one second for one move and two seconds for the next, alternating between the two.
Return the minimum time to reach the room (n - 1, m - 1).
Two rooms are adjacent if they share a common wall, either horizontally or vertically.
Example 1:
- Input: moveTime = [[0,4],[4,4]]
- Output: 7
-
Explanation: The minimum time required is 7 seconds.
- At time
t == 4, move from room(0, 0)to room(1, 0)in one second. - At time
t == 5, move from room(1, 0)to room(1, 1)in two seconds.
- At time
Example 2:
- Input: moveTime = [[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0]]
- Output: 6
-
Explanation: The minimum time required is 6 seconds.
- At time
t == 0, move from room(0, 0)to room(1, 0)in one second. - At time
t == 1, move from room(1, 0)to room(1, 1)in two seconds. - At time
t == 3, move from room(1, 1)to room(1, 2)in one second. - At time
t == 4, move from room(1, 2)to room(1, 3)in two seconds.
- At time
Example 3:
- Input: moveTime = [[0,1],[1,2]]
- Output: 4
Constraints:
2 <= n == moveTime.length <= 7502 <= m == moveTime[i].length <= 7500 <= moveTime[i][j] <= 109
Hint:
- Use shortest path algorithms with a state for the last move being odd or even indexed.
Solution:
We need to find the minimum time required to reach the last room in a grid-based dungeon where each move alternates between taking 1 second and 2 seconds. Additionally, each room has a minimum time before you can start moving into it. The solution involves using a modified Dijkstra's algorithm to handle the alternating move times and the minimum start times for each room.
Approach
- Graph Representation: Treat the grid as a graph where each cell is a node, and edges exist between adjacent cells. The movement between nodes alternates between 1 and 2 seconds based on the number of moves made so far.
- State Tracking: Track the state of each node using both its position and the parity (even or odd) of the number of moves taken to reach it. This helps determine the cost of the next move.
- Priority Queue: Use a priority queue (min-heap) to always expand the node with the smallest current time. This ensures that we process nodes in the order of their earliest possible arrival times.
- Dynamic Adjustment: For each move, calculate the departure time from the current node, considering the minimum start time of the destination node. Adjust the arrival time based on the move cost (1 or 2 seconds) and update the priority queue accordingly.
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 3342. Find Minimum Time to Reach Last Room II
/**
* @param Integer[][] $moveTime
* @return Integer
*/
function minTimeToReach($moveTime) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
// Example usage:
$moveTime = [[0, 4], [4, 4]];
echo minTimeToReach($moveTime); // Output: 7
$moveTime = [[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0]];
echo minTimeToReach($moveTime); // Output: 6
$moveTime = [[0,1],[1,2]];
echo minTimeToReach($moveTime); // Output: 4
?>
Explanation:
-
Initialization: The distance array
distis initialized to infinity for all positions and parities, except the starting position(0, 0)with parity 0, which is set to 0. - Priority Queue: The priority queue is initialized with the starting position and time 0. The queue is ordered to always process the smallest time first by using negative priorities.
- Processing Nodes: For each node extracted from the queue, check if it is the target. If not, explore all adjacent nodes, calculate the departure and arrival times considering the minimum start time of the destination node, and update the priority queue if a shorter path is found.
- Dynamic Adjustment: The cost of each move alternates between 1 and 2 seconds based on the parity of moves taken so far. The departure time is adjusted to ensure it meets the minimum start time of the destination node.
This approach efficiently finds the shortest path using Dijkstra's algorithm with state tracking for move parity, ensuring optimal time complexity and handling the constraints effectively.
Contact Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)

























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Python Programming PCEP Certification Prep Bundle (67% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)















































.jpg?#)

































































-Mafia-The-Old-Country---The-Initiation-Trailer-00-00-54.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
-Nintendo-Switch-2---Reveal-Trailer-00-01-52.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)























_Aleksey_Funtap_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Sergey_Tarasov_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)















































































































![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Stick' Starring Owen Wilson [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97264/97264/97264-640.jpg)


![Beats Studio Pro Wireless Headphones Now Just $169.95 - Save 51%! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97258/97258/97258-640.jpg)