Single phase Half wave controlled rectifier
In power electronics, controlled rectifiers are circuits used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), with the ability to control the output voltage. One of the simplest types is the half-wave controlled rectifier, which employs a thyristor (usually an SCR) instead of a diode. Working principle In a standard half-wave rectifier, a diode conducts during the positive half cycle of the AC input. However, in a controlled rectifier, the diode is replaced with an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier). The SCR remains off until a gate pulse is applied. Once triggered, it conducts for the remainder of the positive half cycle. This gives us control over the firing angle (α)—the point in the AC cycle when the SCR is turned on. By adjusting this angle, we control the average output voltage delivered to the load. Highlights: *Only positive half cycles are rectified. *Output voltage can be controlled by varying the firing angle. Useful in light dimmers, speed control of DC motors, and heating applications. Some Applications *DC motor speed control *Heater control circuits *Power supplies for variable DC loads Understanding half-wave controlled rectifiers is a foundational step toward mastering more complex AC-DC conversion and power control systems in electronics. Written by Silas Madubuihe
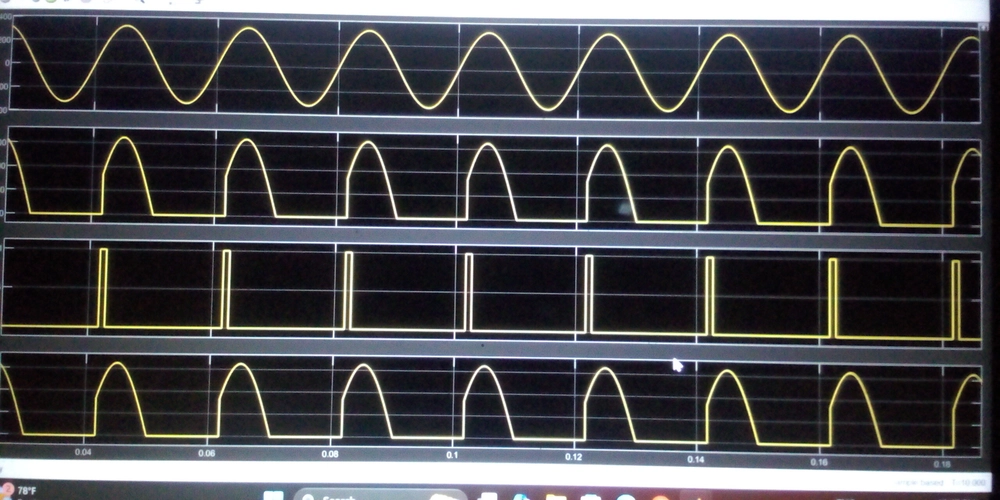
In power electronics, controlled rectifiers are circuits used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), with the ability to control the output voltage. One of the simplest types is the half-wave controlled rectifier, which employs a thyristor (usually an SCR) instead of a diode.
Working principle
In a standard half-wave rectifier, a diode conducts during the positive half cycle of the AC input. However, in a controlled rectifier, the diode is replaced with an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier). The SCR remains off until a gate pulse is applied. Once triggered, it conducts for the remainder of the positive half cycle.
This gives us control over the firing angle (α)—the point in the AC cycle when the SCR is turned on. By adjusting this angle, we control the average output voltage delivered to the load.
Highlights:
*Only positive half cycles are rectified.
*Output voltage can be controlled by varying the firing angle.
Useful in light dimmers, speed control of DC motors, and heating applications.
Some Applications
*DC motor speed control
*Heater control circuits
*Power supplies for variable DC loads
Understanding half-wave controlled rectifiers is a foundational step toward mastering more complex AC-DC conversion and power control systems in electronics.
Written by Silas Madubuihe











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)











































































































































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
























































.png?#)



































.webp?#)


























































































![[Fixed] Gemini app is failing to generate Audio Overviews](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/03/Gemini-Audio-Overview-cover.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

![What’s new in Android’s April 2025 Google System Updates [U: 4/14]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-3.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)













![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 Beta 2 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97011/97011/97011-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases macOS Sequoia 15.5 Beta 2 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97014/97014/97014-640.jpg)