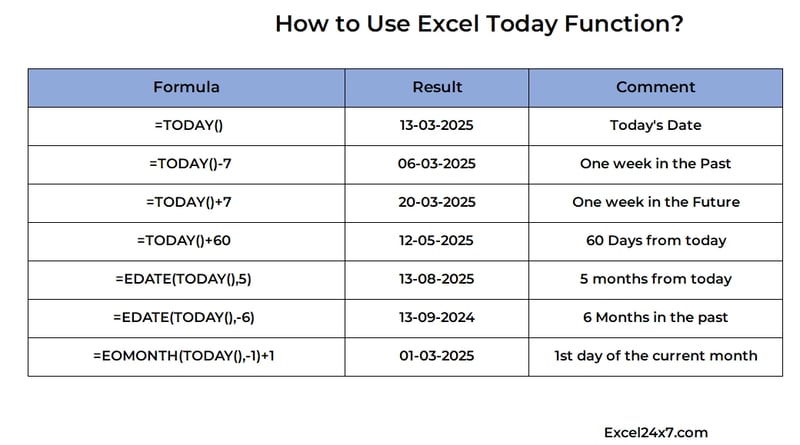
Setting Up a Production-Ready CI/CD Pipeline with Jenkins & Docker
Introduction: Why CI/CD Matters in DevOps Imagine you're working on a critical software project, and every time a developer pushes new code, it has to be manually tested and deployed. This process is slow, error-prone, and hinders rapid releases. Now, imagine automating this with a Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline using Jenkins and Docker—ensuring that every code change is automatically tested, built, and deployed. This blog will walk you through setting up a production-ready CI/CD pipeline using Jenkins & Docker, helping you streamline your DevOps workflow. By the end, you'll have a fully functional pipeline that automates the process from code commit to deployment. (Image source: Official Jenkins Website) Step-by-Step Guide: Building the CI/CD Pipeline Prerequisites Before we start, ensure you have: A Linux server (Ubuntu 22.04 recommended) Docker and Docker Compose installed Jenkins installed and running A GitHub repository with sample code (Node.js application for this tutorial) Step 1: Install and Configure Jenkins 1. Install Jenkins sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y openjdk-11-jdk wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y jenkins 2. Start and Enable Jenkins sudo systemctl start jenkins sudo systemctl enable jenkins 3. Access Jenkins Dashboard Open your browser and go to http://your-server-ip:8080 to complete the setup. Step 2: Install Required Plugins Navigate to Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins and install: Pipeline Docker Pipeline Git Plugin Blue Ocean (for visualization) Step 3: Configure Docker in Jenkins 1. Install Docker sudo apt install -y docker.io sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable docker 2. Add Jenkins to Docker Group sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins sudo systemctl restart jenkins Step 4: Create a Jenkins Pipeline 1. Create a Jenkinsfile in Your Project Repository pipeline { agent any stages { stage('Checkout') { steps { git 'https://github.com/your-repo/sample-app.git' } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { sh 'docker build -t myapp:latest .' } } stage('Run Tests') { steps { sh 'docker run myapp:latest npm test' } } stage('Deploy') { steps { sh 'docker-compose up -d' } } } } 2. Create a New Pipeline in Jenkins Go to Jenkins Dashboard > New Item Select Pipeline, name it, and click OK Under Pipeline Definition, choose Pipeline script from SCM Enter your GitHub repository URL Save and Build Now Troubleshooting Common Issues Jenkins can't access Docker? Run sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sock Pipeline fails at docker build? Ensure the Dockerfile is present in the repo. Permission denied errors? Run sudo chown -R jenkins:jenkins /var/lib/jenkins Real-World Use Cases & Comparisons How Companies Use Jenkins & Docker Company Use Case Netflix Automates deployments to Kubernetes clusters Spotify Manages microservices with Docker and Jenkins Airbnb Uses CI/CD for seamless feature rollouts Docker vs. Virtual Machines Feature Docker Containers Virtual Machines Performance Lightweight, fast Heavy, slower Isolation Process-level Full OS emulation Resource Usage Minimal High Interactive Learning & Resources Watch this tutorial: CI/CD with Jenkins & Docker Take this quiz: Jenkins & Docker Quiz Read more: Jenkins Official Docs Engaging Conclusion & Call-to-Action Setting up a Jenkins & Docker CI/CD pipeline is a game-changer for any DevOps engineer. It improves efficiency, reliability, and scalability, ensuring your deployments are smooth and automated. What do you think? Comment below with your thoughts or challenges! Don’t forget to subscribe for more DevOps content and follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.

Introduction: Why CI/CD Matters in DevOps
Imagine you're working on a critical software project, and every time a developer pushes new code, it has to be manually tested and deployed. This process is slow, error-prone, and hinders rapid releases. Now, imagine automating this with a Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline using Jenkins and Docker—ensuring that every code change is automatically tested, built, and deployed.
This blog will walk you through setting up a production-ready CI/CD pipeline using Jenkins & Docker, helping you streamline your DevOps workflow. By the end, you'll have a fully functional pipeline that automates the process from code commit to deployment.

Step-by-Step Guide: Building the CI/CD Pipeline
Prerequisites
Before we start, ensure you have:
- A Linux server (Ubuntu 22.04 recommended)
- Docker and Docker Compose installed
- Jenkins installed and running
- A GitHub repository with sample code (Node.js application for this tutorial)
Step 1: Install and Configure Jenkins
1. Install Jenkins
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y openjdk-11-jdk
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y jenkins
2. Start and Enable Jenkins
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
3. Access Jenkins Dashboard
Open your browser and go to http://your-server-ip:8080 to complete the setup.
Step 2: Install Required Plugins
Navigate to Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins and install:
- Pipeline
- Docker Pipeline
- Git Plugin
- Blue Ocean (for visualization)
Step 3: Configure Docker in Jenkins
1. Install Docker
sudo apt install -y docker.io
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
2. Add Jenkins to Docker Group
sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins
sudo systemctl restart jenkins
Step 4: Create a Jenkins Pipeline
1. Create a Jenkinsfile in Your Project Repository
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
git 'https://github.com/your-repo/sample-app.git'
}
}
stage('Build Docker Image') {
steps {
sh 'docker build -t myapp:latest .'
}
}
stage('Run Tests') {
steps {
sh 'docker run myapp:latest npm test'
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
sh 'docker-compose up -d'
}
}
}
}
2. Create a New Pipeline in Jenkins
- Go to Jenkins Dashboard > New Item
- Select Pipeline, name it, and click OK
- Under Pipeline Definition, choose Pipeline script from SCM
- Enter your GitHub repository URL
- Save and Build Now
Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
Jenkins can't access Docker? Run
sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sock -
Pipeline fails at
docker build? Ensure theDockerfileis present in the repo. -
Permission denied errors? Run
sudo chown -R jenkins:jenkins /var/lib/jenkins
Real-World Use Cases & Comparisons
How Companies Use Jenkins & Docker
| Company | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Netflix | Automates deployments to Kubernetes clusters |
| Spotify | Manages microservices with Docker and Jenkins |
| Airbnb | Uses CI/CD for seamless feature rollouts |
Docker vs. Virtual Machines
| Feature | Docker Containers | Virtual Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Lightweight, fast | Heavy, slower |
| Isolation | Process-level | Full OS emulation |
| Resource Usage | Minimal | High |
Interactive Learning & Resources
- Watch this tutorial: CI/CD with Jenkins & Docker
- Take this quiz: Jenkins & Docker Quiz
- Read more: Jenkins Official Docs
Engaging Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Setting up a Jenkins & Docker CI/CD pipeline is a game-changer for any DevOps engineer. It improves efficiency, reliability, and scalability, ensuring your deployments are smooth and automated.
What do you think? Comment below with your thoughts or challenges! Don’t forget to subscribe for more DevOps content and follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.







































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)

































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.jpg?#)






























_ArtemisDiana_Alamy.jpg?#)


 (1).webp?#)





































































-xl.jpg)











![Yes, the Gemini icon is now bigger and brighter on Android [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/02/Gemini-on-Galaxy-S25.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)










![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)