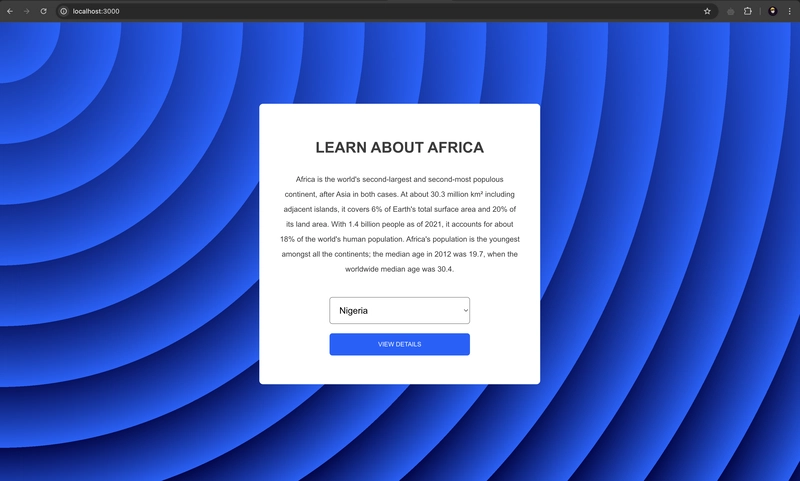
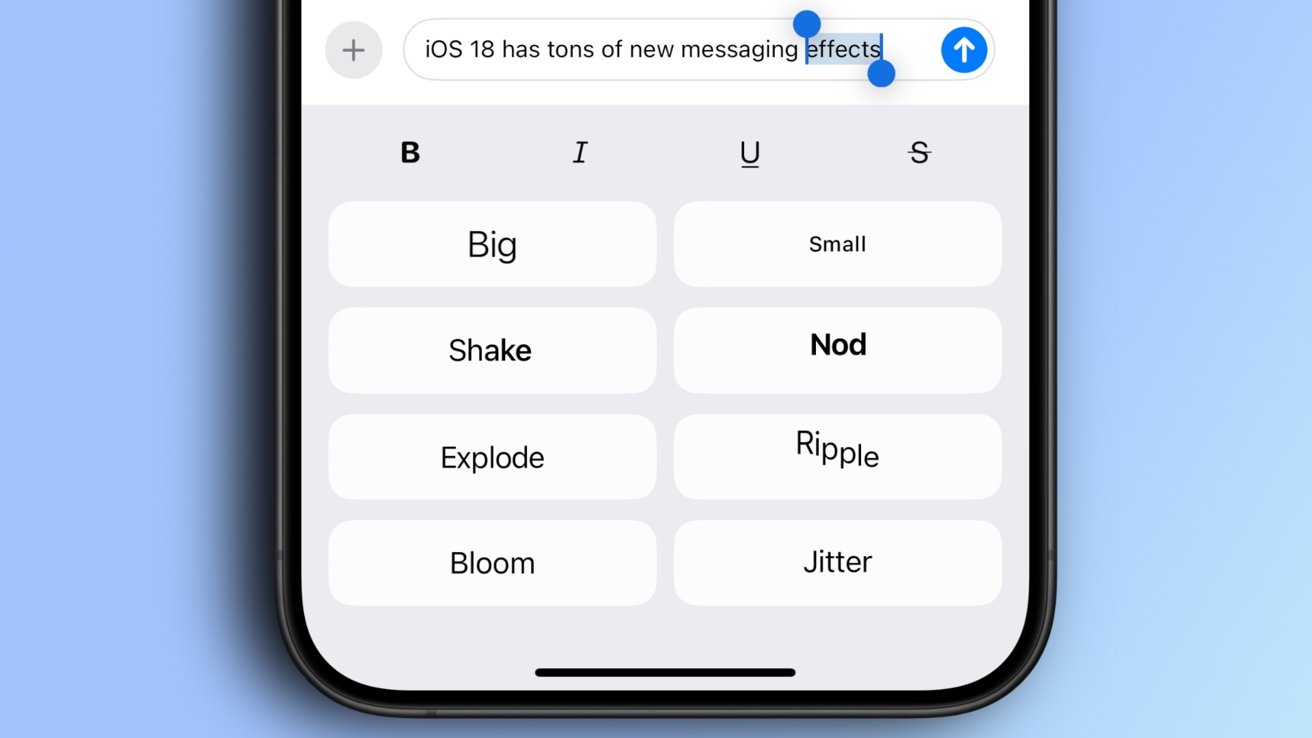
[Part 1]Setting Up Your TypeScript Environment for Test Automation
Introduction Setting up a well-structured TypeScript environment is essential for efficient test automation. This module will guide you through installing necessary tools, configuring your development setup, and understanding TypeScript compilation. Lesson 1: Introduction to TypeScript and Its Advantages for QA Automation Concept: TypeScript enhances test automation by adding static typing, better code maintainability, and improved debugging capabilities. Key Topics: TypeScript Basics: Understanding its syntax and structure. Advantages in QA: Why TypeScript improves automation reliability. Practical Applications: Real-world use cases in test automation. Example: let testStatus: string = "Passed"; console.log("Test result:", testStatus); Pro Tip: TypeScript helps catch errors at compile-time, reducing runtime failures. Lesson 2: Installing Node.js, npm, and TypeScript Concept: Node.js provides the runtime for executing JavaScript and TypeScript, while npm manages dependencies. Key Topics: Installing Node.js: Downloading and setting up Node.js. Verifying npm Installation: Checking npm version in the terminal. Installing TypeScript: Using npm to install TypeScript globally. Example: # Install TypeScript globally npm install -g typescript # Verify installation tsc -v Pro Tip: Use Node Version Manager (NVM) to manage multiple Node.js versions. Lesson 3: Configuring Your TypeScript Development Environment Concept: Setting up an optimized development environment improves productivity and ease of coding. Key Topics: Choosing an IDE: Using Visual Studio Code for TypeScript development. Configuring tsconfig.json: Setting up TypeScript compilation options. Installing Extensions: Adding TypeScript-specific extensions to enhance development. Example: Creating a tsconfig.json file: { "compilerOptions": { "target": "ES6", "module": "CommonJS", "strict": true, "outDir": "dist" } } Pro Tip: Enable strict mode in tsconfig.json for better type safety. Lesson 4: Understanding TypeScript Compilation and JavaScript Output Concept: TypeScript must be compiled into JavaScript before execution. Key Topics: Writing TypeScript: Creating .ts files with TypeScript code. Compiling TypeScript: Using the TypeScript Compiler (tsc). Analyzing JavaScript Output: Understanding the transpiled JavaScript. Running JavaScript: Executing compiled JavaScript in Node.js. Example: # Compile TypeScript tsc example.ts # Run the generated JavaScript node example.js Pro Tip: Use tsc --watch for automatic compilation on file changes. Conclusion This module covered the foundational setup for using TypeScript in test automation, from installation to compilation. Key Takeaways: TypeScript enhances test automation with strong typing and better debugging. Node.js and npm are essential for managing TypeScript dependencies. Configuring tsconfig.json optimizes the development environment. Understanding TypeScript compilation helps in debugging JavaScript output. What’s Next? In the next module, we will explore TypeScript Fundamentals: Syntax, Data Types, and Operators for QA, covering the essential programming concepts required for writing effective test automation scripts. Visit us at Testamplify | X | Instagram | LinkedIn
![[Part 1]Setting Up Your TypeScript Environment for Test Automation](https://media2.dev.to/dynamic/image/width=800%2Cheight=%2Cfit=scale-down%2Cgravity=auto%2Cformat=auto/https%3A%2F%2Fdev-to-uploads.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fuploads%2Farticles%2Ft8kbjtr43le4x9cer1rn.png)
Introduction
Setting up a well-structured TypeScript environment is essential for efficient test automation. This module will guide you through installing necessary tools, configuring your development setup, and understanding TypeScript compilation.
Lesson 1: Introduction to TypeScript and Its Advantages for QA Automation
Concept:
TypeScript enhances test automation by adding static typing, better code maintainability, and improved debugging capabilities.
Key Topics:
- TypeScript Basics: Understanding its syntax and structure.
- Advantages in QA: Why TypeScript improves automation reliability.
- Practical Applications: Real-world use cases in test automation.
Example:
let testStatus: string = "Passed";
console.log("Test result:", testStatus);
Pro Tip: TypeScript helps catch errors at compile-time, reducing runtime failures.
Lesson 2: Installing Node.js, npm, and TypeScript
Concept:
Node.js provides the runtime for executing JavaScript and TypeScript, while npm manages dependencies.
Key Topics:
- Installing Node.js: Downloading and setting up Node.js.
- Verifying npm Installation: Checking npm version in the terminal.
- Installing TypeScript: Using npm to install TypeScript globally.
Example:
# Install TypeScript globally
npm install -g typescript
# Verify installation
tsc -v
Pro Tip: Use Node Version Manager (NVM) to manage multiple Node.js versions.
Lesson 3: Configuring Your TypeScript Development Environment
Concept:
Setting up an optimized development environment improves productivity and ease of coding.
Key Topics:
- Choosing an IDE: Using Visual Studio Code for TypeScript development.
-
Configuring
tsconfig.json: Setting up TypeScript compilation options. - Installing Extensions: Adding TypeScript-specific extensions to enhance development.
Example:
Creating a tsconfig.json file:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES6",
"module": "CommonJS",
"strict": true,
"outDir": "dist"
}
}
Pro Tip: Enable strict mode in tsconfig.json for better type safety.
Lesson 4: Understanding TypeScript Compilation and JavaScript Output
Concept:
TypeScript must be compiled into JavaScript before execution.
Key Topics:
-
Writing TypeScript: Creating
.tsfiles with TypeScript code. -
Compiling TypeScript: Using the TypeScript Compiler (
tsc). - Analyzing JavaScript Output: Understanding the transpiled JavaScript.
- Running JavaScript: Executing compiled JavaScript in Node.js.
Example:
# Compile TypeScript
tsc example.ts
# Run the generated JavaScript
node example.js
Pro Tip: Use tsc --watch for automatic compilation on file changes.
Conclusion
This module covered the foundational setup for using TypeScript in test automation, from installation to compilation.
Key Takeaways:
- TypeScript enhances test automation with strong typing and better debugging.
- Node.js and npm are essential for managing TypeScript dependencies.
- Configuring
tsconfig.jsonoptimizes the development environment. - Understanding TypeScript compilation helps in debugging JavaScript output.
What’s Next?
In the next module, we will explore TypeScript Fundamentals: Syntax, Data Types, and Operators for QA, covering the essential programming concepts required for writing effective test automation scripts.
Visit us at Testamplify | X | Instagram | LinkedIn





































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)



































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)







































































































.jpg?#)





.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
























_ArtemisDiana_Alamy.jpg?#)













































































-xl.jpg)












![Yes, the Gemini icon is now bigger and brighter on Android [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/02/Gemini-on-Galaxy-S25.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)