Building an AI-Powered Web Data Pipeline with n8n, Scrapeless, and Claude
Introduction In today's data-driven landscape, organizations need efficient ways to extract, process, and analyze web content. Traditional web scraping faces numerous challenges: anti-bot protections, complex JavaScript rendering, and the need for constant maintenance. Furthermore, making sense of unstructured web data requires sophisticated processing. This guide demonstrates how to build a complete web data pipeline using n8n workflow automation, Scrapeless web scraping, Claude AI for intelligent extraction, and Qdrant vector database for semantic storage. Whether you're building a knowledge base, conducting market research, or developing an AI assistant, this workflow provides a powerful foundation. What You'll Build Our n8n workflow combines several cutting-edge technologies: Scrapeless Web Unlocker: Advanced web scraping with JavaScript rendering Claude 3.7 Sonnet: AI-powered data extraction and structuring Ollama Embeddings: Local vector embedding generation Qdrant Vector Database: Semantic storage and retrieval Notification System: Real-time monitoring via webhooks This end-to-end pipeline transforms messy web data into structured, vectorized information ready for semantic search and AI applications. Installation and Setup Installing n8n n8n requires Node.js v18, v20, or v22. If you encounter version compatibility issues: # Check your Node.js version node -v # If you have a newer unsupported version (e.g., v23+), install nvm curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.5/install.sh | bash # Or for Windows, use NVM for Windows installer # Install a compatible Node.js version nvm install 20 # Use the installed version nvm use 20 # Install n8n globally npm install n8n -g # Run n8n n8n Your n8n instance should now be available at http://localhost:5678. Setting up Claude API Visit Anthropic Console and create an account Navigate to API Keys section Click "Create Key" and set appropriate permissions Copy your API key for use in the n8n workflow (In AI Data Checker, Claude Data extractor and Claude AI Agent) Setting up Scrapeless Visit Scrapeless and create an account Navigate to the Universal Scraping API section in your dashboard https://app.scrapeless.com/exemple/overview Copy your token for use in the n8n workflow You can customize your Scrapeless web scraping request using this curl command and import it directly into the HTTP Request node in n8n: curl -X POST "https://api.scrapeless.com/api/v1/unlocker/request" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -H "x-api-token: scrapeless_api_key" \ -d '{ "actor": "unlocker.webunlocker", "proxy": { "country": "ANY" }, "input": { "url": "https://www.scrapeless.com", "method": "GET", "redirect": true, "js_render": true, "js_instructions": [{"wait":100}], "block": { "resources": ["image","font","script"], "urls": ["https://example.com"] } } }' Installing Qdrant with Docker # Pull Qdrant image docker pull qdrant/qdrant # Run Qdrant container with data persistence docker run -d \ --name qdrant-server \ -p 6333:6333 \ -p 6334:6334 \ -v $(pwd)/qdrant_storage:/qdrant/storage \ qdrant/qdrant Verify Qdrant is running: curl http://localhost:6333/healthz Installing Ollama macOS: brew install ollama Linux: curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh Windows: Download and install from Ollama's website. Start Ollama server: ollama serve Install the required embedding model: ollama pull all-minilm Verify model installation: ollama list Setting Up the n8n Workflow Workflow Overview Our workflow consists of these key components: Manual/Scheduled Trigger: Starts the workflow Collection Check: Verifies if Qdrant collection exists URL Configuration: Sets the target URL and parameters Scrapeless Web Request: Extracts HTML content Claude Data Extraction: Processes and structures the data Ollama Embeddings: Generates vector embeddings Qdrant Storage: Saves vectors and metadata Notification: Sends status updates via webhook Step 1: Configure Workflow Trigger and Collection Check Start by adding a Manual Trigger node, then add a HTTP Request node to check if your Qdrant collection exists. You can customize the collection name in this initial step - the workflow will automatically create the collection if it doesn't exist. Important Note: If you want to use a different collection name than the default "hacker-news", make sure to change it consistently in ALL nodes that reference Qdrant. Step 2: Configure Scrapeless Web Request Add an HTTP Request node for Scrapeless web scraping. Configure the node using the curl command provided earlier as a reference, replacing YOUR_API_TOKEN with your actual Scrapeless API token. You

Introduction
In today's data-driven landscape, organizations need efficient ways to extract, process, and analyze web content. Traditional web scraping faces numerous challenges: anti-bot protections, complex JavaScript rendering, and the need for constant maintenance. Furthermore, making sense of unstructured web data requires sophisticated processing.
This guide demonstrates how to build a complete web data pipeline using n8n workflow automation, Scrapeless web scraping, Claude AI for intelligent extraction, and Qdrant vector database for semantic storage. Whether you're building a knowledge base, conducting market research, or developing an AI assistant, this workflow provides a powerful foundation.
What You'll Build
Our n8n workflow combines several cutting-edge technologies:
- Scrapeless Web Unlocker: Advanced web scraping with JavaScript rendering
- Claude 3.7 Sonnet: AI-powered data extraction and structuring
- Ollama Embeddings: Local vector embedding generation
- Qdrant Vector Database: Semantic storage and retrieval
- Notification System: Real-time monitoring via webhooks
This end-to-end pipeline transforms messy web data into structured, vectorized information ready for semantic search and AI applications.

Installation and Setup
Installing n8n
n8n requires Node.js v18, v20, or v22. If you encounter version compatibility issues:
# Check your Node.js version
node -v
# If you have a newer unsupported version (e.g., v23+), install nvm
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.5/install.sh | bash
# Or for Windows, use NVM for Windows installer
# Install a compatible Node.js version
nvm install 20
# Use the installed version
nvm use 20
# Install n8n globally
npm install n8n -g
# Run n8n
n8n
Your n8n instance should now be available at http://localhost:5678.
Setting up Claude API
- Visit Anthropic Console and create an account
- Navigate to API Keys section
- Click "Create Key" and set appropriate permissions
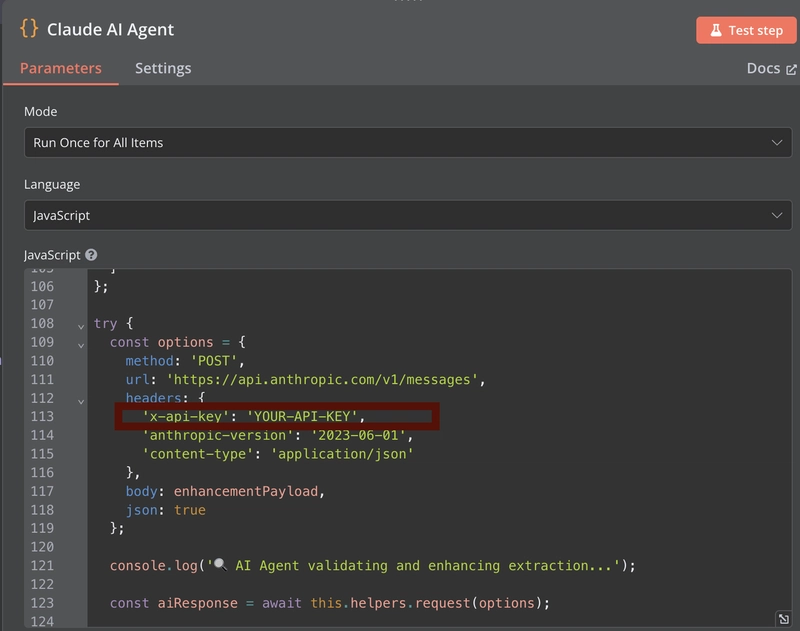
- Copy your API key for use in the n8n workflow (In AI Data Checker, Claude Data extractor and Claude AI Agent)
Setting up Scrapeless
- Visit Scrapeless and create an account
- Navigate to the Universal Scraping API section in your dashboard https://app.scrapeless.com/exemple/overview
- Copy your token for use in the n8n workflow
You can customize your Scrapeless web scraping request using this curl command and import it directly into the HTTP Request node in n8n:
curl -X POST "https://api.scrapeless.com/api/v1/unlocker/request" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "x-api-token: scrapeless_api_key" \
-d '{
"actor": "unlocker.webunlocker",
"proxy": {
"country": "ANY"
},
"input": {
"url": "https://www.scrapeless.com",
"method": "GET",
"redirect": true,
"js_render": true,
"js_instructions": [{"wait":100}],
"block": {
"resources": ["image","font","script"],
"urls": ["https://example.com"]
}
}
}'
Installing Qdrant with Docker
# Pull Qdrant image
docker pull qdrant/qdrant
# Run Qdrant container with data persistence
docker run -d \
--name qdrant-server \
-p 6333:6333 \
-p 6334:6334 \
-v $(pwd)/qdrant_storage:/qdrant/storage \
qdrant/qdrant
Verify Qdrant is running:
curl http://localhost:6333/healthz
Installing Ollama
macOS:
brew install ollama
Linux:
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
Windows: Download and install from Ollama's website.
Start Ollama server:
ollama serve
Install the required embedding model:
ollama pull all-minilm
Verify model installation:
ollama list
Setting Up the n8n Workflow
Workflow Overview
Our workflow consists of these key components:
- Manual/Scheduled Trigger: Starts the workflow
- Collection Check: Verifies if Qdrant collection exists
- URL Configuration: Sets the target URL and parameters
- Scrapeless Web Request: Extracts HTML content
- Claude Data Extraction: Processes and structures the data
- Ollama Embeddings: Generates vector embeddings
- Qdrant Storage: Saves vectors and metadata
- Notification: Sends status updates via webhook
Step 1: Configure Workflow Trigger and Collection Check
Start by adding a Manual Trigger node, then add a HTTP Request node to check if your Qdrant collection exists. You can customize the collection name in this initial step - the workflow will automatically create the collection if it doesn't exist.
Important Note: If you want to use a different collection name than the default "hacker-news", make sure to change it consistently in ALL nodes that reference Qdrant.
Step 2: Configure Scrapeless Web Request
Add an HTTP Request node for Scrapeless web scraping. Configure the node using the curl command provided earlier as a reference, replacing YOUR_API_TOKEN with your actual Scrapeless API token.
You can configure more advanced scraping parameters at Scrapeless Web Unlocker.
Step 3: Claude Data Extraction
Add a node to process the HTML content using Claude. You'll need to provide your Claude API key for authentication. The Claude extractor analyzes the HTML content and returns structured data in JSON format.
Step 4: Format Claude Output
This node takes Claude's response and prepares it for vectorization by extracting the relevant information and formatting it appropriately.
Step 5: Ollama Embeddings Generation
This node sends the structured text to Ollama for embedding generation. Make sure your Ollama server is running and the all-minilm model is installed.
Step 6: Qdrant Vector Storage
This node takes the generated embeddings and stores them in your Qdrant collection along with relevant metadata.
Step 7: Notification System
The final node sends a notification with the status of the workflow execution via your configured webhook.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
n8n Node.js Version Issues
If you see an error like:
Your Node.js version X is currently not supported by n8n.
Please use Node.js v18.17.0 (recommended), v20, or v22 instead!
Fix by installing nvm and using a compatible Node.js version as described in the setup section.
Scrapeless API Connection Issues
- Verify your API token is correct
- Check if you're hitting API rate limits
- Ensure proper URL formatting
Ollama Embedding Errors
Common error: connect ECONNREFUSED ::1:11434
Fix:
- Ensure Ollama is running: ollama serve
- Verify model is installed: ollama pull all-minilm
- Use direct IP (127.0.0.1) instead of localhost
- Check if another process is using port 11434
Advanced Usage Scenarios
Batch Processing Multiple URLs
To process multiple URLs in one workflow execution:
- Use a Split In Batches node to process URLs in parallel
- Configure proper error handling for each batch
-
Use the Merge node to combine results
Scheduled Data Updates
Keep your vector database current with scheduled updates:
Replace manual trigger with Schedule node
Configure update frequency (daily, weekly, etc.)
-
Use the If node to process only new or changed content
Custom Extraction Templates
Adapt Claude's extraction for different content types:
Create specific prompts for news articles, product pages, documentation, etc.
Use the Switch node to select the appropriate prompt
-
Store extraction templates as environment variables
Conclusion
This n8n workflow creates a powerful data pipeline combining the strengths of Scrapeless web scraping, Claude AI extraction, vector embeddings, and Qdrant storage. By automating these complex processes, you can focus on using the extracted data rather than the technical challenges of obtaining it.
The modular nature of n8n allows you to extend this workflow with additional processing steps, integration with other systems, or custom logic to meet your specific needs. Whether you're building an AI knowledge base, conducting competitive analysis, or monitoring web content, this workflow provides a solid foundation.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)























































































































![[DEALS] The ChatGPT & AI Super Bundle (91% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)

![How to make Developer Friends When You Don't Live in Silicon Valley, with Iraqi Engineer Code;Life [Podcast #172]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1747360508340/f07040cd-3eeb-443c-b4fb-370f6a4a14da.png?#)







































































































































































































































![A rare look inside the TSMC Arizona plant making chips for Apple [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/05/A-look-inside-the-TSMC-Arizona-plant-making-chips-for-Apple.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

















![Why Apple Still Can't Catch Up in AI and What It's Doing About It [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97352/97352/97352-640.jpg)
![Sonos Move 2 On Sale for 25% Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97355/97355/97355-640.jpg)
![Apple May Not Update AirPods Until 2026, Lighter AirPods Max Coming in 2027 [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97350/97350/97350-640.jpg)