Why is HL7 integration essential for modern healthcare systems?
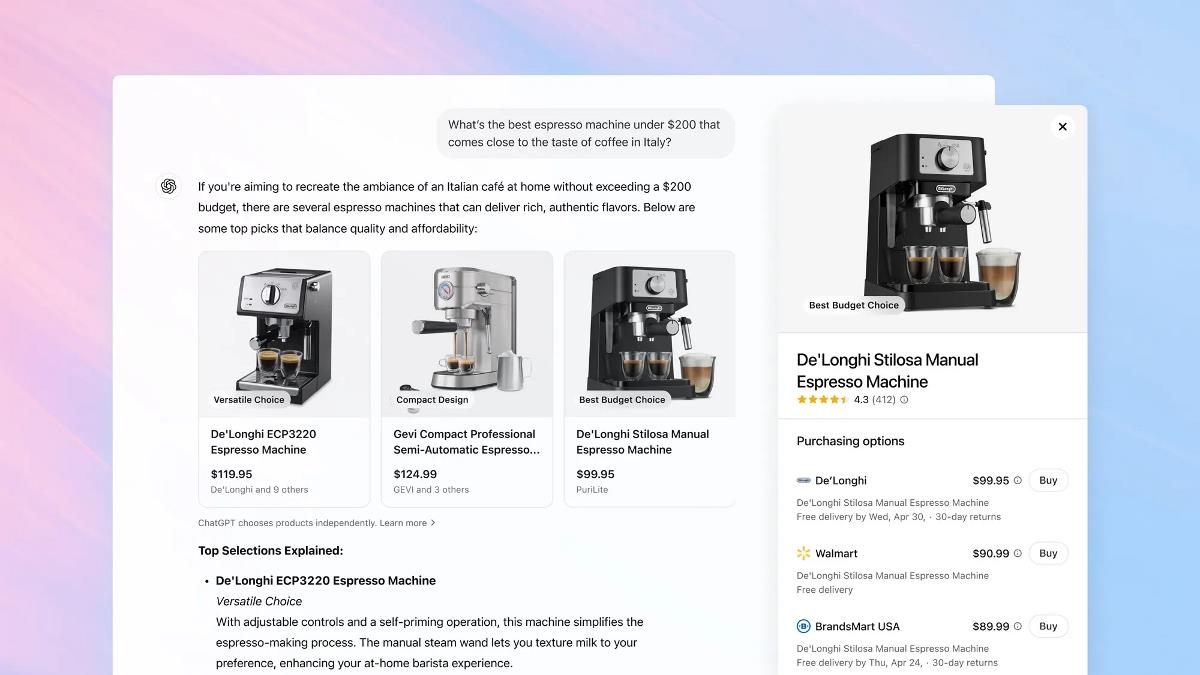
The U.S. healthcare system is currently changing, with 95% of healthcare organizations using HL7 standards to break data silos and improve operational efficiency. Interoperability, however, is another persistent problem costing the industry $30 billion every year due to added inefficiencies. For healthcare providers, payers, and IT leaders, HL7 integration is more than a technological improvement; it is also a strategic stance to improve patient care, cut costs, and secure operations for the foreseeable future. Understanding the market potential of this technology is very important. The worldwide healthcare data integration market was valued at $1.21 billion in 2023, according to Grand View Research. The market is expected to see significant growth at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period (2019-2032) and is anticipated to reach $3.11 billion by the year 2030. What is HL7? Health Level Seven (HL7) is a widely recognized framework of standards for interoperable exchange of clinical, administrative, and financial information among healthcare systems. As it were, “universal language” allows EHRs, lab systems, pharmacies, and telehealth platforms to communicate, hence breaking data silos and allowing interoperability. When for example the lab results of a patient get sent automatically from the Laboratory Information System to the EHR, HL7 standards provide a means of setting up the data in a way that both systems will understand it correctly. 95% of U.S. healthcare organizations make use of HL7 V2.x, which in effect establishes its position as the foundation of healthcare IT. Types of HL7 Standards HL7 encompasses a variety of standards tailored to different aspects of healthcare information exchange: HL7 Version 2 (V2): The V2 standard was founded in the late 1980s and has evidently become the most widely accepted standard, primarily directed toward how clinical data are exchanged (example: patient’s admissions, discharges, and lab results). HL7 Version 3 (V3): A much later version that was using a heavy data model to bring consistency and accuracy to interaction around very complex data. Clinical Document Architecture (CDA): A standard for the structures and semantics of clinical documents to make human-readable and machine-processable medical documents. Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR): A modern standard designed to enable rapid and efficient data exchange by means of web technologies. It is rapidly gaining importance, among other reasons, because it’s flexible and scalable. Read More :- Why is HL7 integration essential for modern healthcare systems?

The U.S. healthcare system is currently changing, with 95% of healthcare organizations using HL7 standards to break data silos and improve operational efficiency. Interoperability, however, is another persistent problem costing the industry $30 billion every year due to added inefficiencies. For healthcare providers, payers, and IT leaders, HL7 integration is more than a technological improvement; it is also a strategic stance to improve patient care, cut costs, and secure operations for the foreseeable future. Understanding the market potential of this technology is very important. The worldwide healthcare data integration market was valued at $1.21 billion in 2023, according to Grand View Research. The market is expected to see significant growth at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period (2019-2032) and is anticipated to reach $3.11 billion by the year 2030.
What is HL7?
Health Level Seven (HL7) is a widely recognized framework of standards for interoperable exchange of clinical, administrative, and financial information among healthcare systems. As it were, “universal language” allows EHRs, lab systems, pharmacies, and telehealth platforms to communicate, hence breaking data silos and allowing interoperability.
When for example the lab results of a patient get sent automatically from the Laboratory Information System to the EHR, HL7 standards provide a means of setting up the data in a way that both systems will understand it correctly. 95% of U.S. healthcare organizations make use of HL7 V2.x, which in effect establishes its position as the foundation of healthcare IT.
Types of HL7 Standards
HL7 encompasses a variety of standards tailored to different aspects of healthcare information exchange:
HL7 Version 2 (V2): The V2 standard was founded in the late 1980s and has evidently become the most widely accepted standard, primarily directed toward how clinical data are exchanged (example: patient’s admissions, discharges, and lab results).
HL7 Version 3 (V3): A much later version that was using a heavy data model to bring consistency and accuracy to interaction around very complex data.
Clinical Document Architecture (CDA): A standard for the structures and semantics of clinical documents to make human-readable and machine-processable medical documents.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR): A modern standard designed to enable rapid and efficient data exchange by means of web technologies. It is rapidly gaining importance, among other reasons, because it’s flexible and scalable.
Read More :- Why is HL7 integration essential for modern healthcare systems?





























![[Free Webinar] Guide to Securing Your Entire Identity Lifecycle Against AI-Powered Threats](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjqbZf4bsDp6ei3fmQ8swm7GB5XoRrhZSFE7ZNhRLFO49KlmdgpIDCZWMSv7rydpEShIrNb9crnH5p6mFZbURzO5HC9I4RlzJazBBw5aHOTmI38sqiZIWPldRqut4bTgegipjOk5VgktVOwCKF_ncLeBX-pMTO_GMVMfbzZbf8eAj21V04y_NiOaSApGkM/s1600/webinar-play.jpg?#)





































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)









































































































































































































































































_Jochen_Tack_Alamy.png?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)






























































































![Apple testing Stage Manager for iPhone, Photographic Styles for video, and more [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/iOS-Decoded-iOS-18.5.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

















![New Hands-On iPhone 17 Dummy Video Shows Off Ultra-Thin Air Model, Updated Pro Designs [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97171/97171/97171-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares Trailer for First Immersive Feature Film 'Bono: Stories of Surrender' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97168/97168/97168-640.jpg)
![Apple Restructures Global Affairs and Apple Music Teams [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97162/97162/97162-640.jpg)