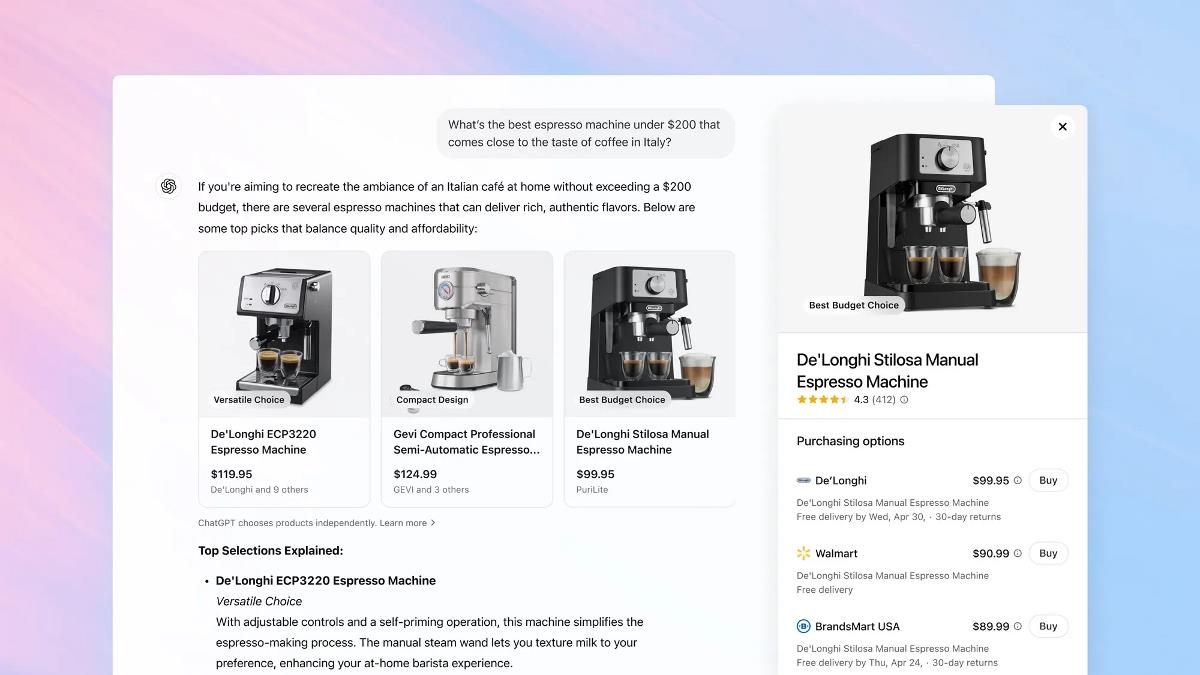
Securing Boardroom Buy-In for Your Cybersecurity Budget
Cybersecurity has evolved from a technical concern to a strategic business priority. With escalating regulatory requirements, sophisticated threat actors, and the rising financial and reputational costs of breaches, boards of directors are increasingly scrutinizing cybersecurity investments. However, securing budget approval remains a persistent challenge for CISOs. Board members often lack technical expertise, prioritize short-term financial […] The post Securing Boardroom Buy-In for Your Cybersecurity Budget appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Cybersecurity has evolved from a technical concern to a strategic business priority. With escalating regulatory requirements, sophisticated threat actors, and the rising financial and reputational costs of breaches, boards of directors are increasingly scrutinizing cybersecurity investments.
However, securing budget approval remains a persistent challenge for CISOs. Board members often lack technical expertise, prioritize short-term financial returns, and struggle to contextualize cyber risks within broader business objectives.
Success hinges on translating complex security concepts into actionable insights that resonate with executive priorities-protecting revenue, ensuring operational continuity, and maintaining stakeholder trust.
This article outlines strategies to bridge the communication gap, demonstrate tangible value, and foster long-term alignment between cybersecurity initiatives and boardroom expectations.
Bridging the Communication Gap
Cybersecurity leaders must reframe technical risks as business risks. Board members prioritize organizational resilience, regulatory compliance, and financial stability-not firewall configurations or malware detection rates.
Effective communication starts by abandoning jargon and focusing on outcomes.
For example, instead of detailing a phishing campaign’s technical mechanics, highlight how a $2.3M investment in employee training reduced simulated click-through rates by 62%, potentially averting a $20M ransomware incident.
Align proposals with strategic goals: A zero-trust architecture isn’t just about network segmentation; it’s about enabling secure hybrid work models that support revenue growth.
Proactively address how cybersecurity initiatives mitigate risks to mergers, product launches, or supply chain partnerships.
Five Key Strategies for Effective Advocacy
- Quantify Risk in Financial Terms
Translate threats into boardroom-ready metrics: Calculate the likelihood of a data breach (e.g., 28% annual probability) and its financial impact (e.g., $4.45M average cost). Use scenario analysis to show how a $1M investment in endpoint detection could reduce breach costs by 37%. - Demonstrate ROI Through Cyber Risk Quantification (CRQ)
CRQ platforms enable CISOs to model the ROI of security tools. For instance, a $500K cloud security investment might reduce financial exposure by $2.1M annually. Present these figures alongside traditional business KPIs like net present value (NPV) or internal rate of return (IRR). - Align with Regulatory and Industry Benchmarks
Map initiatives to frameworks like NIST or CIS Controls, emphasizing compliance with SEC disclosure rules or GDPR. Boards respond to peer pressure: Highlight that 73% of competitors in your sector have adopted similar measures. - Leverage Third-Party Risk Metrics
Supply chain breaches account for 62% of incidents. Show how vendor risk management programs reduce third-party vulnerabilities, protecting partnerships and avoiding contractual penalties. - Create a Board-Level Cyber Task Force
Establish a subcommittee chaired by the CFO or COO to review cyber strategies quarterly. This ensures continuous dialogue, demystifies security operations, and distributes accountability beyond the CISO.
Sustaining Engagement Measures
Cybersecurity budgeting isn’t a one-time negotiation-it requires ongoing collaboration. Implement a quarterly reporting cadence that tracks progress against agreed-upon metrics, such as reduced incident response times or improved audit scores.
For example, a manufacturing firm reduced its mean time to detect (MTTD) threats from 72 hours to 14 hours post-investment, slashing potential downtime costs by $8M annually.
Integrate cybersecurity into enterprise risk management (ERM) frameworks to ensure it’s reviewed alongside financial, operational, and reputational risks.
- Adopt a “Cyber Resilience Scorecard”
Develop a dashboard that grades organizational preparedness across domains like incident response, patching cadence, and employee awareness. Tie improvements directly to risk reduction. - Conduct Tabletop Exercises with Board Participation
Simulate ransomware attacks or data breaches during board meetings to contextualize decision-making under pressure. Post-exercise reviews clarify how budget allocations enhance crisis readiness.
By embedding cybersecurity into strategic planning and demonstrating measurable impact, CISOs can transform boardroom skepticism into sustained advocacy.
The goal isn’t just to secure funding-it’s to position cybersecurity as a competitive differentiator that enables innovation, trust, and growth.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!
The post Securing Boardroom Buy-In for Your Cybersecurity Budget appeared first on Cyber Security News.





























![[Free Webinar] Guide to Securing Your Entire Identity Lifecycle Against AI-Powered Threats](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjqbZf4bsDp6ei3fmQ8swm7GB5XoRrhZSFE7ZNhRLFO49KlmdgpIDCZWMSv7rydpEShIrNb9crnH5p6mFZbURzO5HC9I4RlzJazBBw5aHOTmI38sqiZIWPldRqut4bTgegipjOk5VgktVOwCKF_ncLeBX-pMTO_GMVMfbzZbf8eAj21V04y_NiOaSApGkM/s1600/webinar-play.jpg?#)





































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)









































































































































































































































































_Jochen_Tack_Alamy.png?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)





























































































![Apple testing Stage Manager for iPhone, Photographic Styles for video, and more [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/iOS-Decoded-iOS-18.5.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

















![New Hands-On iPhone 17 Dummy Video Shows Off Ultra-Thin Air Model, Updated Pro Designs [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97171/97171/97171-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares Trailer for First Immersive Feature Film 'Bono: Stories of Surrender' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97168/97168/97168-640.jpg)
![Apple Restructures Global Affairs and Apple Music Teams [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97162/97162/97162-640.jpg)