The Convergence of Blockchain, NFTs, and Insurance: A New Era in Risk Management and Funding Innovation
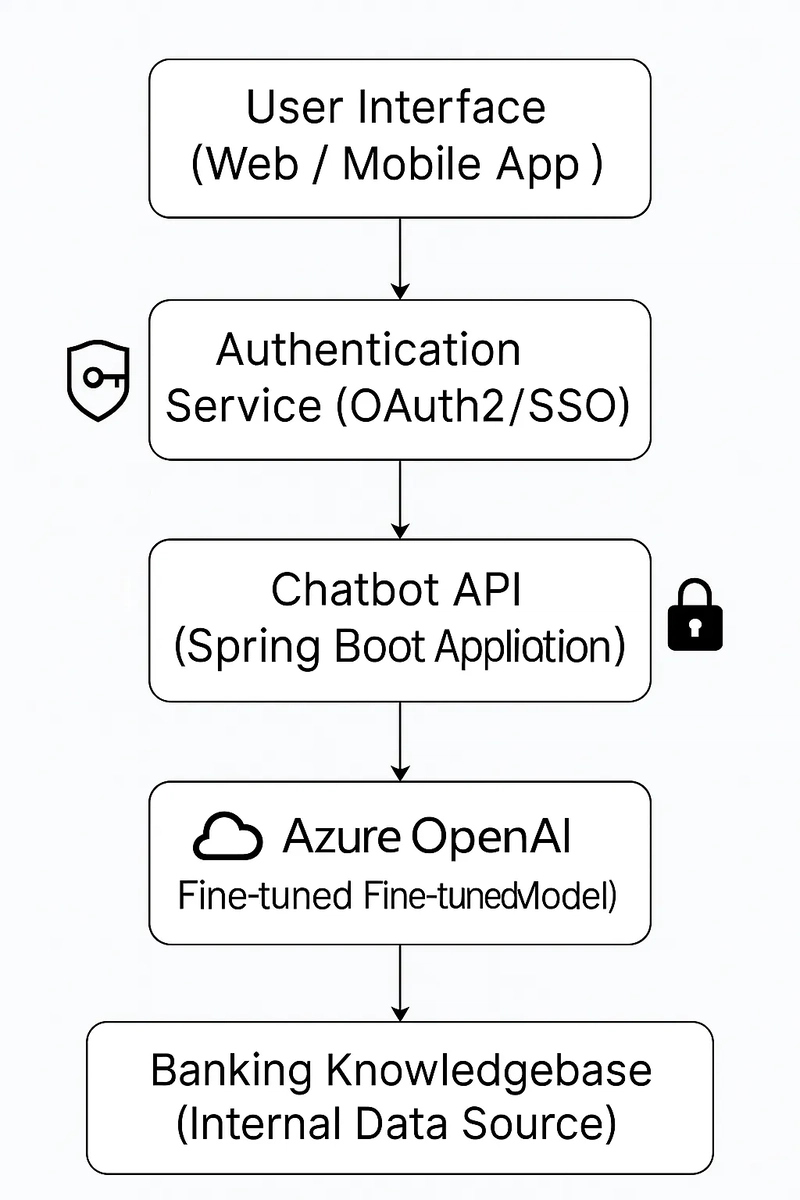
Abstract This post dives into the rapid convergence of blockchain technology, NFTs, and insurance. We explore how these emerging digital innovations are redefining risk management, streamlining funding strategies, and transforming traditional insurance practices. By examining blockchain’s immutable ledger, the uniqueness of NFT-backed policies, and the cutting-edge role of smart contracts, we offer technical insights into how these disruptive systems work. With detailed tables, bullet lists, and real-world use cases, this post is designed to be accessible to technical experts, developers, and industry professionals interested in the future of insurance. Introduction The insurance industry has long been associated with paper-based processes, opaque data management, and manual claim processing. Today, modern digital technologies—namely blockchain and non-fungible tokens (NFTs)—are challenging this status quo. From enhancing transparency with immutable ledgers to streamlining claims processing through automated smart contracts, these innovations are setting the stage for a radical transformation in risk management and funding strategies. Blockchain’s transparent and tamper-proof design, combined with NFTs’ ability to confer unique digital ownership, presents a compelling alternative to traditional insurance models. Furthermore, significant investments are fueling these improvements, as demonstrated by venture capital involvement and innovative funding approaches. This post will discuss the historical context, key technical features, practical applications, and future trends of this digital revolution within the insurance ecosystem. For a detailed examination of these topics as originally discussed in the Blockchain and Insurance article, read on to learn how technology is revolutionizing risk, funding, and operational efficiency. Background and Context A Brief History of Blockchain and NFTs Blockchain technology emerged with Bitcoin in 2009, revolutionizing the way we think about digital transactions. Its core characteristic—the immutable ledger—ensures that every transaction is permanently recorded and virtually impossible to tamper with. Over time, blockchain evolved beyond cryptocurrencies, providing a robust framework for secure data exchange, smart contracts, and decentralized applications. NFTs gained prominence as unique digital assets that verify authenticity and ownership, initially in the world of digital art and collectibles. Today, NFTs are finding innovative applications in insurance by digitizing policy ownership and preserving risk history on an immutable ledger. Ecosystem Context The integration of blockchain and NFTs into the insurance space has created an ecosystem that includes startups, traditional insurers, tech giants, and regulatory bodies. This diverse blend of stakeholders is working to overcome legacy system constraints while setting new industry standards for data security and transparency. Key players in this ecosystem focus on: Risk Management: Leveraging decentralized ledgers for fraud prevention and real-time risk assessment. Operational Efficiency: Utilizing smart contracts to automate claim settlements and policy renewals. Funding and Investment: Capital infusion from venture capitalists and corporate partnerships to develop cutting-edge, blockchain-based models. Important resources such as News AI Q1 2025 and KI Trends Deutschland Q1 2025 offer further insights into these transformative trends. Core Concepts and Features Blockchain Fundamentals Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that underpins the transparency and security of digital transactions. Its key aspects include: Immutable Ledger: Every transaction is securely recorded, reducing the risk of fraud. Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, enhancing resilience. Transparency: Open access to transaction data builds trust among stakeholders. Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements that automate processes such as claim settlements and policy updates. Below is a table summarizing these core features: Feature Description Relevance to Insurance Immutable Ledger Secure, unchangeable records of all transactions Enhances transparency and reduces fraud Decentralization Distributed network of nodes Eliminates single points of failure Transparency Open, verifiable records of transactions Builds trust with policyholders and regulators Smart Contracts Automated, self-executing contracts Streamlines claims processing and policy updates NFTs in Insurance NFTs—non-fungible tokens—are digital assets that confer unique ownership of an item or data record. In insurance, NFT-backed policies offer several groundbreaking benefits: Uniqueness: Each insurance policy token is distinct and verifiable. Interoperability: NFTs can interact with smart contracts, allowing real-time data updat

Abstract
This post dives into the rapid convergence of blockchain technology, NFTs, and insurance. We explore how these emerging digital innovations are redefining risk management, streamlining funding strategies, and transforming traditional insurance practices. By examining blockchain’s immutable ledger, the uniqueness of NFT-backed policies, and the cutting-edge role of smart contracts, we offer technical insights into how these disruptive systems work. With detailed tables, bullet lists, and real-world use cases, this post is designed to be accessible to technical experts, developers, and industry professionals interested in the future of insurance.
Introduction
The insurance industry has long been associated with paper-based processes, opaque data management, and manual claim processing. Today, modern digital technologies—namely blockchain and non-fungible tokens (NFTs)—are challenging this status quo. From enhancing transparency with immutable ledgers to streamlining claims processing through automated smart contracts, these innovations are setting the stage for a radical transformation in risk management and funding strategies.
Blockchain’s transparent and tamper-proof design, combined with NFTs’ ability to confer unique digital ownership, presents a compelling alternative to traditional insurance models. Furthermore, significant investments are fueling these improvements, as demonstrated by venture capital involvement and innovative funding approaches. This post will discuss the historical context, key technical features, practical applications, and future trends of this digital revolution within the insurance ecosystem.
For a detailed examination of these topics as originally discussed in the Blockchain and Insurance article, read on to learn how technology is revolutionizing risk, funding, and operational efficiency.
Background and Context
A Brief History of Blockchain and NFTs
Blockchain technology emerged with Bitcoin in 2009, revolutionizing the way we think about digital transactions. Its core characteristic—the immutable ledger—ensures that every transaction is permanently recorded and virtually impossible to tamper with. Over time, blockchain evolved beyond cryptocurrencies, providing a robust framework for secure data exchange, smart contracts, and decentralized applications.
NFTs gained prominence as unique digital assets that verify authenticity and ownership, initially in the world of digital art and collectibles. Today, NFTs are finding innovative applications in insurance by digitizing policy ownership and preserving risk history on an immutable ledger.
Ecosystem Context
The integration of blockchain and NFTs into the insurance space has created an ecosystem that includes startups, traditional insurers, tech giants, and regulatory bodies. This diverse blend of stakeholders is working to overcome legacy system constraints while setting new industry standards for data security and transparency.
Key players in this ecosystem focus on:
- Risk Management: Leveraging decentralized ledgers for fraud prevention and real-time risk assessment.
- Operational Efficiency: Utilizing smart contracts to automate claim settlements and policy renewals.
- Funding and Investment: Capital infusion from venture capitalists and corporate partnerships to develop cutting-edge, blockchain-based models.
Important resources such as News AI Q1 2025 and KI Trends Deutschland Q1 2025 offer further insights into these transformative trends.
Core Concepts and Features
Blockchain Fundamentals
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that underpins the transparency and security of digital transactions. Its key aspects include:
- Immutable Ledger: Every transaction is securely recorded, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, enhancing resilience.
- Transparency: Open access to transaction data builds trust among stakeholders.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements that automate processes such as claim settlements and policy updates.
Below is a table summarizing these core features:
| Feature | Description | Relevance to Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Immutable Ledger | Secure, unchangeable records of all transactions | Enhances transparency and reduces fraud |
| Decentralization | Distributed network of nodes | Eliminates single points of failure |
| Transparency | Open, verifiable records of transactions | Builds trust with policyholders and regulators |
| Smart Contracts | Automated, self-executing contracts | Streamlines claims processing and policy updates |
NFTs in Insurance
NFTs—non-fungible tokens—are digital assets that confer unique ownership of an item or data record. In insurance, NFT-backed policies offer several groundbreaking benefits:
- Uniqueness: Each insurance policy token is distinct and verifiable.
- Interoperability: NFTs can interact with smart contracts, allowing real-time data updates.
- Customization: Policies can be tailored to individual risk profiles and digitally represented.
- Tradability: NFT-backed policies open the possibility of secondary markets for risk exchange.
A bullet list of overlapping benefits includes:
- Reduced Fraud: Immutable blockchain records minimize claim falsification.
- Operational Efficiency: Automated smart contracts reduce the need for intermediaries.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined processes translate to lower administrative expenses.
- Customer Trust: Transparent recording fosters stronger relationships with policyholders.
Funding Innovations
The insurance sector is witnessing an influx of capital aimed at developing blockchain-based solutions. Funding innovations include:
- Venture Capital Investment: Tech startups receive substantial capital to innovate.
- Corporate Partnerships: Collaborations between insurers and major tech companies spur integrated solutions.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): New funding models enable tokenized equity and risk-sharing platforms.
- Ecosystem Collaboration: Consortiums such as B3i foster shared standards and regulatory compliance.
These trends are documented in resources like Berita NFT Indonesia 2025 Q1 and further supported by perspectives on alternative funding models from platforms like Copyleft Licenses Ultimate Guide.
Applications and Use Cases
Blockchain and NFT innovations are not just theoretical—they are yielding practical benefits across multiple applications in insurance and reinsurance.
Automated Claims Processing
Imagine a scenario where natural disaster sensors detect property damage and automatically trigger a smart contract. In such a system:
- Sensors relay damage data to the blockchain in real time.
- Smart contracts validate whether claim conditions are met.
- Funds are disbursed automatically, reducing delays and manual intervention.
This use case illustrates how automation dramatically improves efficiency, accuracy, and trust in the claims process.
NFT-Backed Insurance Policies
High-value assets, such as luxury art or collectibles, can be insured using NFT-backed policies. Benefits include:
- Digital Authentication: Ownership and policy terms are verified in real time.
- Enhanced Resale Value: Policy tokens can be transferred or traded on secure secondary markets.
- Fraud Prevention: Recorded on an immutable ledger, the NFT ensures that claims and ownership history remains unaltered.
This application highlights how blockchain and NFT integration can reduce administrative costs and improve risk assessment.
Parametric Insurance and Reinsurance
Parametric insurance uses predefined metrics (e.g., seismic activity, weather conditions) to process claims automatically. In this model:
- Predefined triggers automatically execute smart contracts.
- Claims are processed rapidly, minimizing manual approvals.
- Reinsurance data is shared securely between multiple parties, improving risk modeling accuracy.
The combination of blockchain and smart contracts not only streamlines traditional insurance processes but also facilitates reinsurance efficiency by offering a secure platform for data sharing and risk modeling.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promise of blockchain and NFT technology in insurance, several challenges remain:
Technical Challenges
- Scalability: Increased transaction volumes can tax blockchain networks, potentially slowing down processing times.
- Interoperability: Combining disparate blockchain systems and ensuring standardized NFT protocols is complex.
- Security Risks: Although blockchain is highly secure, vulnerabilities in smart contracts can expose systems to attacks.
- Data Privacy: Balancing the transparency of blockchain with the need to protect sensitive personal data is an ongoing challenge.
Regulatory and Compliance Barriers
- Jurisdictional Differences: Varying international standards complicate cross-border blockchain implementations.
- Dynamic Regulations: Rapid technological advancements may outpace existing regulatory frameworks, leading to uncertainties.
- Compliance Risks: Non-compliance with evolving legal standards can result in severe penalties.
Market Adoption
- Legacy Systems: Traditional insurers often face difficulty integrating modern blockchain technologies with their established IT infrastructures.
- Cultural Shifts: Resistance to change from employees and customers accustomed to conventional practices can slow adoption.
- Talent Shortage: There is a significant demand for blockchain and NFT experts, which can create talent gaps and hinder growth.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Emerging Trends
As the technology matures, several trends are expected to drive further adoption of blockchain and NFT applications in insurance:
- Enhanced Automation: Further integration of smart contracts will accelerate claims processing and policy management.
- Interoperable Ecosystems: Development of industry-wide standards will enable seamless cross-chain communication.
- Advanced Cybersecurity: Regular audits and robust security protocols will ensure the integrity of blockchain systems.
- Real-Time Data Integration: The synthesis of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with blockchain will provide near-instant risk adjustments and premium updates.
Innovative Funding Models
Funding strategies are poised to evolve as well, with a focus on decentralization and sustainability:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms are exploring tokenized risk and equity funding models.
- Tokenization of Assets: The practice of issuing digital tokens to represent insurance policies is likely to expand, offering liquidity and new revenue streams.
- Collaborative Research: Increased investment in R&D will drive prototypes and pilot projects that test integrated blockchain solutions.
For further reading on innovative funding and network upgrades, check resources like Arbitrum Smart Contracts: Revolutionizing the Blockchain Landscape and Navigating the Future of Decentralized Decision Making: Arbitrum and On-Chain Governance.
Research and Development
Ongoing technical research is crucial to overcoming current challenges. Areas of focus include:
- Scalability solutions such as layer-2 protocols.
- Cross-chain interoperability standards.
- Advanced smart contract auditing tools.
These investments are expected to drive a future in which the insurance value chain is not only more secure but also significantly more efficient.
Summary
The convergence of blockchain, NFTs, and insurance represents a transformative leap in risk management and funding innovation. By harnessing blockchain’s immutable, decentralized nature along with NFT-backed policy automation, the insurance industry can:
- Reduce fraudulent activities.
- Provide frictionless claims processing.
- Offer scalable, cost-efficient solutions.
Despite technical, regulatory, and cultural challenges, the future holds immense promise for these innovations. As funding inflows and collaborative R&D efforts continue, we can expect a more transparent, efficient, and customer-centric insurance ecosystem.
Insurance professionals who embrace blockchain and NFT-based solutions will not only gain a competitive edge but also build trust by delivering superior value to policyholders. The journey ahead is filled with both challenges and transformative opportunities that could redefine traditional insurance and reinsurance practices for years to come.
For readers interested in further exploring the intersection of finance, technology, and open source, additional insights can be found in posts like Exploring Open Source Funding: Fueling Innovation and Sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of blockchain and NFTs into the insurance industry is paving the way for a revolutionary approach to risk management and funding strategies. This convergence not only improves operational efficiency by automating claims and policy management through smart contracts but also opens up innovative pathways for securing capital through tokenization and decentralized finance. As technical barriers are gradually overcome and regulatory frameworks evolve, the digital transformation of insurance is set to redefine market practices and customer experiences.
By combining detailed industry knowledge with lessons from real-world applications, this post has underscored the importance of adopting blockchain and NFT technologies as a pathway towards a more resilient and sustainable insurance ecosystem. Stakeholders across the industry are encouraged to explore pilot projects, invest in R&D, and engage with regulators to ensure that these innovations are implemented in an ethical, transparent, and secure manner.
Embracing this digital transformation today is key to ensuring long-term success, improved risk assessment, and the development of new revenue streams for the future of insurance.
Keywords: blockchain, NFTs, insurance innovation, risk management, digital assets, funding strategies, smart contracts, decentralized, transparency, automated claims processing.
With the abundant resources and collaborative efforts shaping the future, the convergence of these technologies heralds a significant evolution in how the insurance industry manages risk and funds its operations. Stay tuned as we continue to monitor these trends and share insights on this rapidly developing landscape.
Happy innovating!

































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)































































































































































































































































![What’s new in Android’s April 2025 Google System Updates [U: 4/28]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-3.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)










_Muhammad_R._Fakhrurrozi_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_NicoElNino_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)




















































































![macOS 15.5 beta 4 now available for download [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/macOS-Sequoia-15.5-b4.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)













![AirPods Pro 2 With USB-C Back On Sale for Just $169! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96315/96315/96315-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases iOS 18.5 Beta 4 and iPadOS 18.5 Beta 4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97145/97145/97145-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97147/97147/97147-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97150/97150/97150-640.jpg)




































![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of iOS 18.5 to Developers [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/uSxxRefnKz3z3MK1y_CnFxSg8Ak=/2500x/article-new/2025/04/iOS-18.5-Feature-Real-Mock.jpg)
![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of macOS Sequoia 15.5 [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/ne62qbjm_V5f4GG9UND3WyOAxE8=/2500x/article-new/2024/08/macOS-Sequoia-Night-Feature.jpg)























































