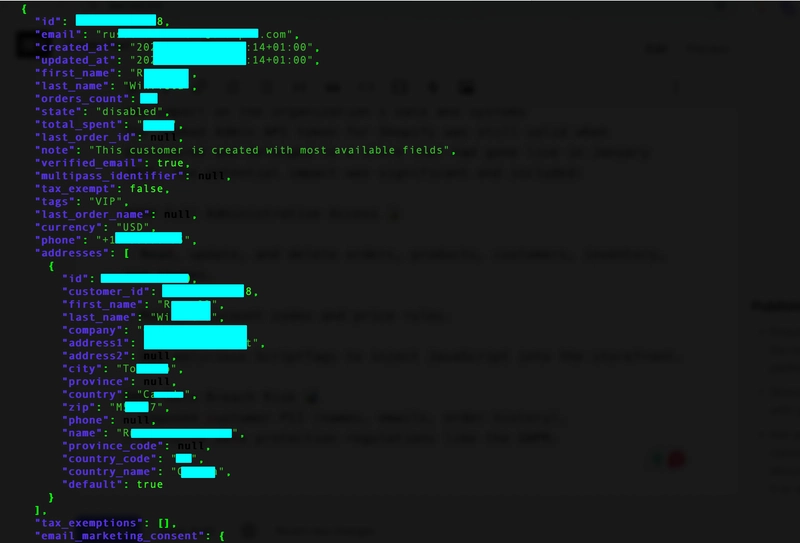
Java If ... Else
If: Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true else: Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false else if: Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false public class Triangle { //traingle check static int a = 60, b = 60, c = 60; public static void main(String[] args) { if (a + b + c == 180) { System.out.println("Traingle"); } else { System.out.println("its not traingle"); } } } Example 2: public class CharacterisVowelOrConstants { static char ch = 'w'; public static void main(String[] args) { if (ch == 'a' || ch == 'e' || ch == 'i' || ch == 'o' || ch == 'u') { System.out.println("Vowels"); } else { System.out.println("Constants"); } } } Example 3: package conditionalStatement; public class DayofTheWeek { static int day=3; public static void main(String[] args) { if (day == 1) { System.out.println("Sunday"); } else if (day == 2) { System.out.println("Monday"); } else if (day == 3) { System.out.println("TuesDay"); } else if (day == 4) { System.out.println("WednesDay"); } else if (day == 5) { System.out.println("ThursDay"); } else if (day == 6) { System.out.println("Friday"); } else if (day == 7) { System.out.println("Saturday"); } else { System.out.println("NoDays"); } } } Example 4: package conditionalStatement; public class EvenorOdd { static int number = 192; public static void main(String[] args) { if (number % 2 == 0) { System.out.println("Even"); } else { System.out.println("odd"); } } } Example 5: package conditionalStatement; public class GradingSystem { static int mark = 70; public static void main(String[] args) { if (mark >= 70 || mark==100) { //50 big 70 and 50 equal 100 System.out.println("A Grade"); } else if(mark>60&&mark==70) { System.out.println("B Grade"); } else if (mark>35||mark==60) { System.out.println("C Grade"); } else if(mark>101) { System.out.println("Wrong Input"); } else { System.out.println("Fail"); } } } Example 6: public class LargestOfThreeNumber { static int a = 1180; static int b = 1180; static int c = 11830; public static void main(String[] args) { if (a > b && a > c) {// 100 big 90 t 100>80 t System.out.println("a is greater"); } else if (b > c && b > a) { //90 big 80 =true 100 big 90 true System.out.println("B is greater"); } else if (c > a && c > b) { System.out.println("C is greater"); } else { System.out.println("all are equal"); } } } Example 7: package conditionalStatement; public class LargestOfTwoNumbers { static int a = 30; static int b = 30; public static void main(String[] args) { if (a > b) { // 10 big 110 System.out.println("a is largest"); } else if (a == b) { System.out.println("a and b is equals"); } else { System.out.println("b is largest"); } } } Example 8: package conditionalStatement; public class LeapYearCheck { static int year = 2824; public static void main(String[] args) { LeapYearCheck lp = new LeapYearCheck(); if (lp.year % 4 == 0 && (lp.year % 400 == 0 || lp.year != 0)) { System.out.println("leap year"); } else { System.out.println("this is Not Leap Year"); } } } //100 diviede 0 numbers and 400 divede panna 0 Example 9: package conditionalStatement; public class MonthCheck { static int month=4; public static void main(String[] args) { if(month>1) { System.out.println(""); } } } Example 10: package conditionalStatement; public class SimpleNumberComparision { int number = -90; public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleNumberComparision numbers=new SimpleNumberComparision(); if(numbers.number>0) { System.out.println("positive"); } if (numbers.number==0) { System.out.println("Equeal"); } else if(numbers.number

If:
Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true
else:
Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false
else if:
Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false
public class Triangle {
//traingle check
static int a = 60, b = 60, c = 60;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (a + b + c == 180) {
System.out.println("Traingle");
}
else {
System.out.println("its not traingle");
}
}
}
Example 2:
public class CharacterisVowelOrConstants {
static char ch = 'w';
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (ch == 'a' || ch == 'e' || ch == 'i' || ch == 'o' || ch == 'u') {
System.out.println("Vowels");
} else {
System.out.println("Constants");
}
}
}
Example 3:
package conditionalStatement;
public class DayofTheWeek {
static int day=3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (day == 1) {
System.out.println("Sunday");
} else if (day == 2) {
System.out.println("Monday");
} else if (day == 3) {
System.out.println("TuesDay");
} else if (day == 4) {
System.out.println("WednesDay");
} else if (day == 5) {
System.out.println("ThursDay");
} else if (day == 6) {
System.out.println("Friday");
} else if (day == 7) {
System.out.println("Saturday");
} else {
System.out.println("NoDays");
}
}
}
Example 4:
package conditionalStatement;
public class EvenorOdd {
static int number = 192;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("Even");
} else {
System.out.println("odd");
}
}
}
Example 5:
package conditionalStatement;
public class GradingSystem {
static int mark = 70;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (mark >= 70 || mark==100) { //50 big 70 and 50 equal 100
System.out.println("A Grade");
}
else if(mark>60&&mark==70) {
System.out.println("B Grade");
}
else if (mark>35||mark==60) {
System.out.println("C Grade");
}
else if(mark>101) {
System.out.println("Wrong Input");
}
else {
System.out.println("Fail");
}
}
}
Example 6:
public class LargestOfThreeNumber {
static int a = 1180;
static int b = 1180;
static int c = 11830;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (a > b && a > c) {// 100 big 90 t 100>80 t
System.out.println("a is greater");
} else if (b > c && b > a) { //90 big 80 =true 100 big 90 true
System.out.println("B is greater");
} else if (c > a && c > b) {
System.out.println("C is greater");
}
else {
System.out.println("all are equal");
}
}
}
Example 7:
package conditionalStatement;
public class LargestOfTwoNumbers {
static int a = 30;
static int b = 30;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (a > b) { // 10 big 110
System.out.println("a is largest");
} else if (a == b) {
System.out.println("a and b is equals");
} else {
System.out.println("b is largest");
}
}
}
Example 8:
package conditionalStatement;
public class LeapYearCheck {
static int year = 2824;
public static void main(String[] args) {
LeapYearCheck lp = new LeapYearCheck();
if (lp.year % 4 == 0 && (lp.year % 400 == 0 || lp.year != 0)) {
System.out.println("leap year");
} else {
System.out.println("this is Not Leap Year");
}
}
}
//100 diviede 0 numbers and 400 divede panna 0
Example 9:
package conditionalStatement;
public class MonthCheck {
static int month=4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(month>1) {
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
Example 10:
package conditionalStatement;
public class SimpleNumberComparision {
int number = -90;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleNumberComparision numbers=new SimpleNumberComparision();
if(numbers.number>0) {
System.out.println("positive");
}
if (numbers.number==0) {
System.out.println("Equeal");
}
else if(numbers.number<0) {
System.out.println("negative");
}
}
}

















































.jpg)










![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)




































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)











































































































































































































































.jpg?#)




.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)























_Muhammad_R._Fakhrurrozi_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)













































































































![AirPods Pro 2 With USB-C Back On Sale for Just $169! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96315/96315/96315-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases iOS 18.5 Beta 4 and iPadOS 18.5 Beta 4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97145/97145/97145-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97147/97147/97147-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97150/97150/97150-640.jpg)







































![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of iOS 18.5 to Developers [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/uSxxRefnKz3z3MK1y_CnFxSg8Ak=/2500x/article-new/2025/04/iOS-18.5-Feature-Real-Mock.jpg)