Gridiron Survivor's Elfgorithm: Introduction and Team Installation
This article introduces Gridiron Survivor's Elfgorithm, an AI-powered Secret Santa app currently in production, and it also serves as an installation guide using Git and pnpm for project team members! What is the Elfgorithm App? Elfgorithm is an AI-powered Secret Santa app currently in production, scheduled for release in winter 2025. It simplifies the management of gift exchanges by eliminating the guesswork involved in Secret Santa and gift exchanges! This app handles the details of gift-giving and offers personalized gift ideas, helping you find the perfect gifts for everyone on your list. How Elfgorithm works: Create a group, invite participants, and let the intelligent algorithm match you with the perfect gifts, ensuring everyone experiences the joy of giving and receiving! The Elfgorithm App features: Smart Gifting: AI-powered gift suggestions tailored to each recipient Easy Organizing: Effortlessly manage groups and participants Scheduling: Set draw dates and exchange dates with reminders Personalization: Customize your exchange details Check out the deployed in-progress project: Deployed project: https://elfgorithm.vercel.app/ GitHub: https://github.com/LetsGetTechnical/elecretanta What is Gridiron Survivor Gridiron Survivor is an apprenticeship program initiated by Shashi Lo, Senior UX Engineer at Microsoft, designed to provide essential work experience for developers entering the tech industry. The program offers practical training in project management, coding practices, and team collaboration, equipping aspiring developers with the mentorship and skills needed to succeed in their first tech jobs. Prerequisite For Gridiron Survivor team members, the following sections provide a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you get onboarded. ⚠ Note: You will need to have Node.js installed as a prerequisite. The onboarding steps include: Cloning the project Navigating to the project directory Opening the project in VS Code Creating and verifying the .env file in VS Code Adding the environment variables Installing project dependencies using pnpm Running the development server Cloning the project The following elecretanta link will bring you to the project page. Once there, follow the instructions to clone the project. The GitHub repo: elecretanta Click on the green “Code” button Choose “clone using the web URL” by clicking on the copy URL to clipboard icon. VS Code In VS Code’s Bash terminal, navigate to a location of your choice to download the project into. Then type the command git clone, followed by the copied elecretanta URL (Ctrl + v): git clone https://github.com/LetsGetTechnical/elecretanta.git Navigate to the Project Directory Once the project is downloaded, use the ls command to list the files and directories in the current directory, allowing you to verify that the project files have been successfully downloaded (your file path will vary from mine). Then use the cd command to change into the directory of the downloaded project, allowing you to navigate to the project's root folder and begin working with its files. Note that you are starting on the (develop) branch. More on this branch later. Open the Project in VS Code Now that you have the ( develop ) branch open in the Bash terminal, it is time to open the elecretanta project folder in VS Code. In the VS Code File Explorer, click the blue Open Folder button, and then navigate to and select the elecretanta project folder, which has been downloaded to your computer. Once you have the elecretanta project folder selected, click the Select Folder button, which opens the project in VS Code. Note: You may need to reopen your Bash terminal. Once reopened, you should already be on the (develop) branch. Create and Verify the .env File in VS Code In the project’s root directory folder (ELECRETANTA) in the VS Code Explorer, right-click the New File icon (the first icon) and create an .env file. ⚠ Important: Make sure to add the dot(.) when creating the env file. You will know you have successfully created the env file by verifying that it is represented with a gear icon, as depicted in the image below. Adding the Environment Variables Once you have successfully created the .env file, you will need to contact a GIS team member to retrieve the necessary data to add to this file. At the time of writing this article, Alex is the primary point of contact. Alternatively, you can reach out to Team Lead Shashi for instructions. GOOGLE_API_KEY= GOOGLE_CSE_ID= NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_URL= NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY= OPENAI_API_KEY= Installation To install the project, it is important to note that we are exclusively using pnpm. Performant npm (pnpm), is a fast, efficient package manager for JavaScript. It saves disk space by storing a single vers

This article introduces Gridiron Survivor's Elfgorithm, an AI-powered Secret Santa app currently in production, and it also serves as an installation guide using Git and pnpm for project team members!
What is the Elfgorithm App?
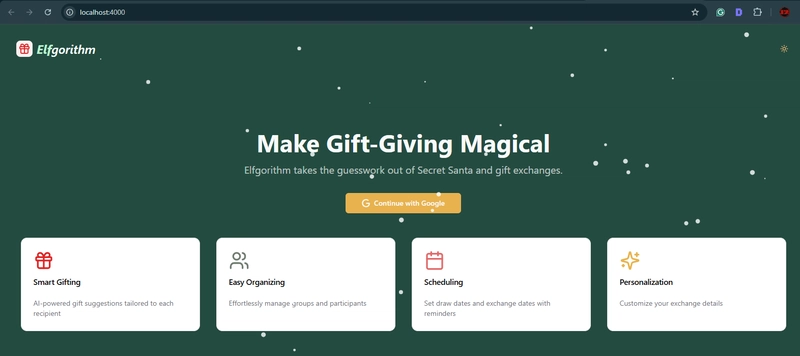
Elfgorithm is an AI-powered Secret Santa app currently in production, scheduled for release in winter 2025. It simplifies the management of gift exchanges by eliminating the guesswork involved in Secret Santa and gift exchanges! This app handles the details of gift-giving and offers personalized gift ideas, helping you find the perfect gifts for everyone on your list.
How Elfgorithm works: Create a group, invite participants, and let the intelligent algorithm match you with the perfect gifts, ensuring everyone experiences the joy of giving and receiving!
The Elfgorithm App features:
Smart Gifting: AI-powered gift suggestions tailored to each recipient
Easy Organizing: Effortlessly manage groups and participants
Scheduling: Set draw dates and exchange dates with reminders
Personalization: Customize your exchange details
Check out the deployed in-progress project:
Deployed project: https://elfgorithm.vercel.app/
What is Gridiron Survivor
Gridiron Survivor is an apprenticeship program initiated by Shashi Lo, Senior UX Engineer at Microsoft, designed to provide essential work experience for developers entering the tech industry. The program offers practical training in project management, coding practices, and team collaboration, equipping aspiring developers with the mentorship and skills needed to succeed in their first tech jobs.
Prerequisite
For Gridiron Survivor team members, the following sections provide a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you get onboarded.
⚠ Note: You will need to have Node.js installed as a prerequisite.
The onboarding steps include:
Cloning the project
Navigating to the project directory
Opening the project in VS Code
Creating and verifying the .env file in VS Code
Adding the environment variables
Installing project dependencies using pnpm
Running the development server
Cloning the project
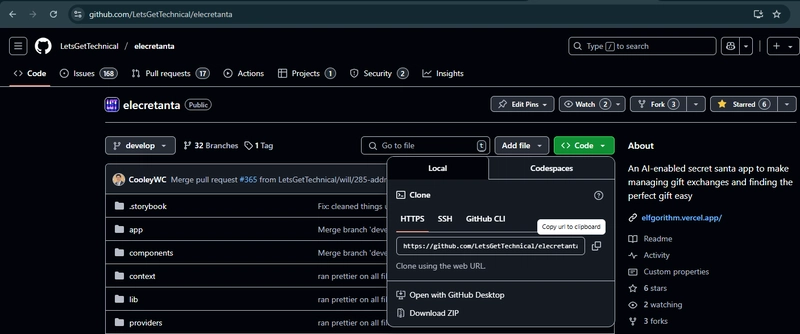
The following elecretanta link will bring you to the project page. Once there, follow the instructions to clone the project.
The GitHub repo: elecretanta
Click on the green “Code” button
Choose “clone using the web URL” by clicking on the copy URL to clipboard icon.
VS Code
In VS Code’s Bash terminal, navigate to a location of your choice to download the project into. Then type the command git clone, followed by the copied elecretanta URL (Ctrl + v):
git clone https://github.com/LetsGetTechnical/elecretanta.git
Navigate to the Project Directory
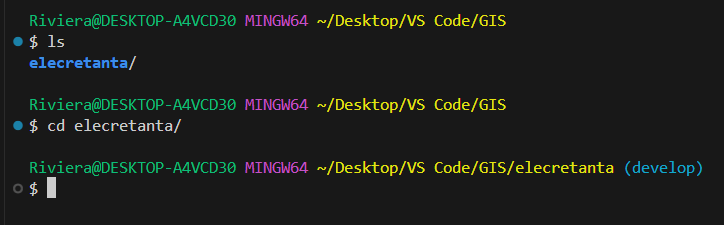
Once the project is downloaded, use the ls command to list the files and directories in the current directory, allowing you to verify that the project files have been successfully downloaded (your file path will vary from mine).
Then use the cd command to change into the directory of the downloaded project, allowing you to navigate to the project's root folder and begin working with its files.
Note that you are starting on the (develop) branch. More on this branch later.
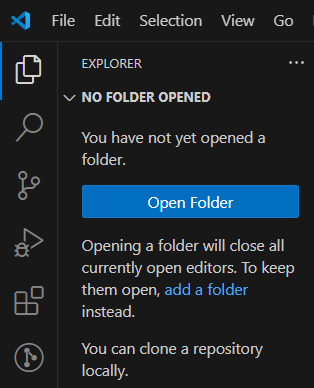
Open the Project in VS Code
Now that you have the ( develop ) branch open in the Bash terminal, it is time to open the elecretanta project folder in VS Code.
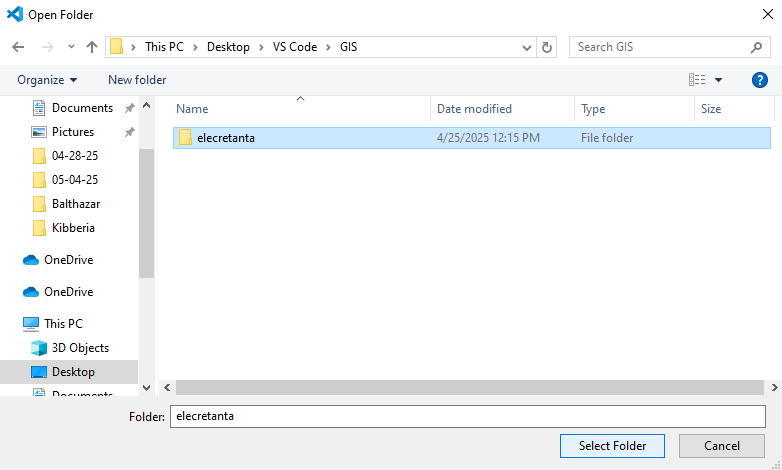
In the VS Code File Explorer, click the blue Open Folder button, and then navigate to and select the elecretanta project folder, which has been downloaded to your computer.
Once you have the elecretanta project folder selected, click the Select Folder button, which opens the project in VS Code.
Note: You may need to reopen your Bash terminal. Once reopened, you should already be on the (develop) branch.
Create and Verify the .env File in VS Code
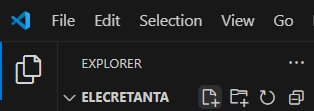
In the project’s root directory folder (ELECRETANTA) in the VS Code Explorer, right-click the New File icon (the first icon) and create an .env file.
⚠ Important: Make sure to add the dot(.) when creating the env file.
You will know you have successfully created the env file by verifying that it is represented with a gear icon, as depicted in the image below.
Adding the Environment Variables
Once you have successfully created the .env file, you will need to contact a GIS team member to retrieve the necessary data to add to this file. At the time of writing this article, Alex is the primary point of contact.
Alternatively, you can reach out to Team Lead Shashi for instructions.
GOOGLE_API_KEY=
GOOGLE_CSE_ID=
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_URL=
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY=
OPENAI_API_KEY=
Installation
To install the project, it is important to note that we are exclusively using pnpm. Performant npm (pnpm), is a fast, efficient package manager for JavaScript. It saves disk space by storing a single version of each package globally and using hard links for projects. This approach speeds up installations and enforces strict dependency management, making it a powerful alternative to npm and Yarn.
When you run pnpm, it installs the packages your project needs. It checks if the packages are already stored globally on your computer. If not, it downloads them. Instead of copying, it links these packages to your project, saving space and speeding up the process. This method also ensures that each package only uses its specified dependencies, reducing errors.
Install project dependencies using pnpm:
pnpm install
⚠ Once installed: run git pull to make sure your local repository is up to date with the latest changes from the remote repository.
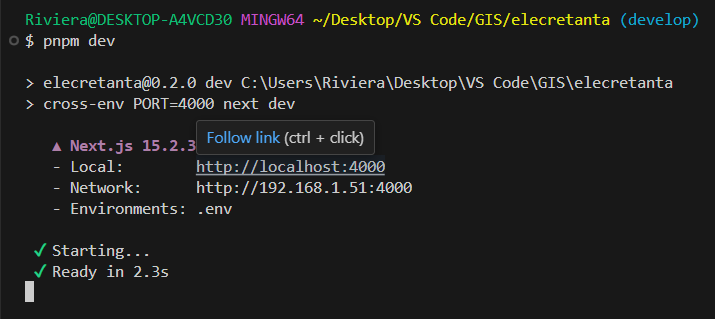
Run the development server
To run the project, use the pnpm dev command to start the development server.
pnpm dev
Once the development server is running, hover over the localhost URL and press (Ctrl + click) to open it in your browser.
Congratulations! You have successfully cloned the repository, navigated to the project directory, and opened it in VS Code. You created and verified the .env file, installed the necessary project dependencies using pnpm, and ensured your local repository is up to date. Finally, you started the development server and accessed the project in your browser!
Creating and Managing Your Own Branch
It is important to note that you do not work in the (develop) branch. You must create your own branch to work from and then push it to the GitHub repository. This process is beyond the scope of this article, but don't worry! GIS team member Danielle Lindblom has you covered! She recorded the following thorough video on this entire process.
Example: creating your branch includes
Your name (in camelCase)
Issue number
Issue description
I created a branch for writing a Story for the Avatar component as follows:
git checkout -b michaelL/303-add-story-avatar
git: Version control tool used to track changes in code.checkout: Command to switch between branches.-b: Option to create a new branch.michaelL/303-add-story-avatar: Name of the new branch, allowing separate work from the main codebase.
The complete process covered in Danielle’s instructional video includes:
Creating a working branch
Committing your code
Creating a pull request (PR)
Gridiron Survivor Sponsors
My other related articles
Bridging the Skills Gap: Empowering Junior Developers Through Apprenticeship Programs
How Learning in Public and Networking Can Advance Your Career
Thriving in Tech: Securing Your First Job, Leveraging Side Hustles, and Overcoming Layoffs
From Skillset to Networking: Tactics for Standing Out in a Challenging Job Market

































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)




































































































































































































































































_NicoElNino_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)













































































































![Standalone Meta AI App Released for iPhone [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97157/97157/97157-640.jpg)