Exploring Azure Blob Storage: Features, Redundancy, and Best Practices
Introduction Ever wondered where all that "stuff" on the internet lives? A lot of it, especially things like documents, images, and videos, ends up in places like Azure Blob Storage. Think of it as a giant, super-organized digital warehouse in the cloud. Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft's service that lets you store tons of this unstructured data. It's designed to grow as much as you need, keep your data safe, and not cost you a fortune. In this blog post, we'll break down Azure Blob Storage, its features, how it keeps your data safe (redundancy), and how to use it like a pro. What is Azure Blob Storage? Imagine you have a massive amount of stuff to store—way more than your computer could handle. Azure Blob Storage is like a limitless storage space in Microsoft's cloud where you can keep all that data. It's really good at handling all sorts of data, from text and pictures to videos and audio files. It's built to handle huge amounts of data, so you don't have to worry about running out of space. Plus, it's designed to be super reliable and fast. You can get to your data from anywhere with an internet connection using standard web addresses (HTTP or HTTPS). Types of Azure Blobs Okay, so Azure Blob Storage is the big warehouse. Now, let's talk about how things are organized inside. There are three main ways to store your data, and they're called "blobs": Block Blobs: These are your workhorse blobs. They're the best choice for storing most common file types, like documents, images, and videos. Think of them as being made up of smaller "blocks" that can be managed individually, which makes them really efficient for uploading and downloading large files. If you're streaming a video or backing up your data, you'll likely be using block blobs. Append Blobs: Imagine you're adding entries to a log file. You just keep adding to the end, right? That's what append blobs are for. They're optimized for adding data to the end of a blob, which makes them perfect for things like logging data from applications. Page Blobs: These are a bit more specialized. Think of them like the virtual hard drives for computers in the cloud. They're designed for storing files that need to be accessed randomly and frequently, and they can get pretty big (up to 8TB!). Azure Virtual Machines use page blobs to store their operating system disks. Keeping Your Data Safe: Redundancy Options Now, the really important stuff: how does Azure Blob Storage make sure your data doesn't disappear? That's where "redundancy" comes in. It's all about making extra copies of your data so that if something goes wrong, you don't lose anything. Azure gives you several ways to do this, and each one offers a different level of protection and cost: Locally Redundant Storage (LRS): This is the simplest option. It makes three copies of your data, but all within the same building (data center). It's the cheapest way to go, but it only protects you from problems within that single data center (like a hard drive failing). Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS): This is a step up in protection. It also makes three copies of your data, but it spreads those copies across three different buildings (availability zones) within the same geographic region. These buildings are independent, so if one loses power, your data is still safe. Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS): Now we're talking serious protection. GRS copies your data to a data center hundreds of miles away in a completely different region. This protects you from major disasters like a hurricane or an earthquake that could take out an entire region. Read-Access Geo-Redundant Storage (RA-GRS): This is like GRS, but with a bonus. Not only does it copy your data to that far-away data center, but it also lets you read that data from the remote location, even if everything is working fine in your primary location. This can be useful for certain situations. Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS): This option combines the best of both worlds. It spreads your data across multiple availability zones in the primary region and replicates it to a secondary region. This gives you excellent protection against both local and regional problems. Read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS): This is the ultimate in protection. It's like GZRS, but it also lets you read your data from the secondary region. It's the most resilient option Azure Blob Storage offers. Using Azure Blob Storage Like a Pro: Best Practices Okay, so you know what it is and how it keeps your data safe. Here's how to use it the right way: Keep it Secure: Always use the most secure way to transfer your data (HTTPS), and make sure you're using the latest security standards (TLS 1.2 or later). Also, only give people the minimum access they need to your data. Don't give everyone the keys to the whole warehouse! Clean Up Automatically: Azure has a cool feature called "lifecycle management." You can set up rules that automatically move your data to cheaper storage as it

Introduction
Ever wondered where all that "stuff" on the internet lives? A lot of it, especially things like documents, images, and videos, ends up in places like Azure Blob Storage. Think of it as a giant, super-organized digital warehouse in the cloud. Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft's service that lets you store tons of this unstructured data. It's designed to grow as much as you need, keep your data safe, and not cost you a fortune. In this blog post, we'll break down Azure Blob Storage, its features, how it keeps your data safe (redundancy), and how to use it like a pro.
What is Azure Blob Storage?
Imagine you have a massive amount of stuff to store—way more than your computer could handle. Azure Blob Storage is like a limitless storage space in Microsoft's cloud where you can keep all that data. It's really good at handling all sorts of data, from text and pictures to videos and audio files. It's built to handle huge amounts of data, so you don't have to worry about running out of space. Plus, it's designed to be super reliable and fast. You can get to your data from anywhere with an internet connection using standard web addresses (HTTP or HTTPS).
Okay, so Azure Blob Storage is the big warehouse. Now, let's talk about how things are organized inside. There are three main ways to store your data, and they're called "blobs":
Block Blobs: These are your workhorse blobs. They're the best choice for storing most common file types, like documents, images, and videos. Think of them as being made up of smaller "blocks" that can be managed individually, which makes them really efficient for uploading and downloading large files. If you're streaming a video or backing up your data, you'll likely be using block blobs.
Append Blobs: Imagine you're adding entries to a log file. You just keep adding to the end, right? That's what append blobs are for. They're optimized for adding data to the end of a blob, which makes them perfect for things like logging data from applications.
Page Blobs: These are a bit more specialized. Think of them like the virtual hard drives for computers in the cloud. They're designed for storing files that need to be accessed randomly and frequently, and they can get pretty big (up to 8TB!). Azure Virtual Machines use page blobs to store their operating system disks.
Keeping Your Data Safe: Redundancy Options
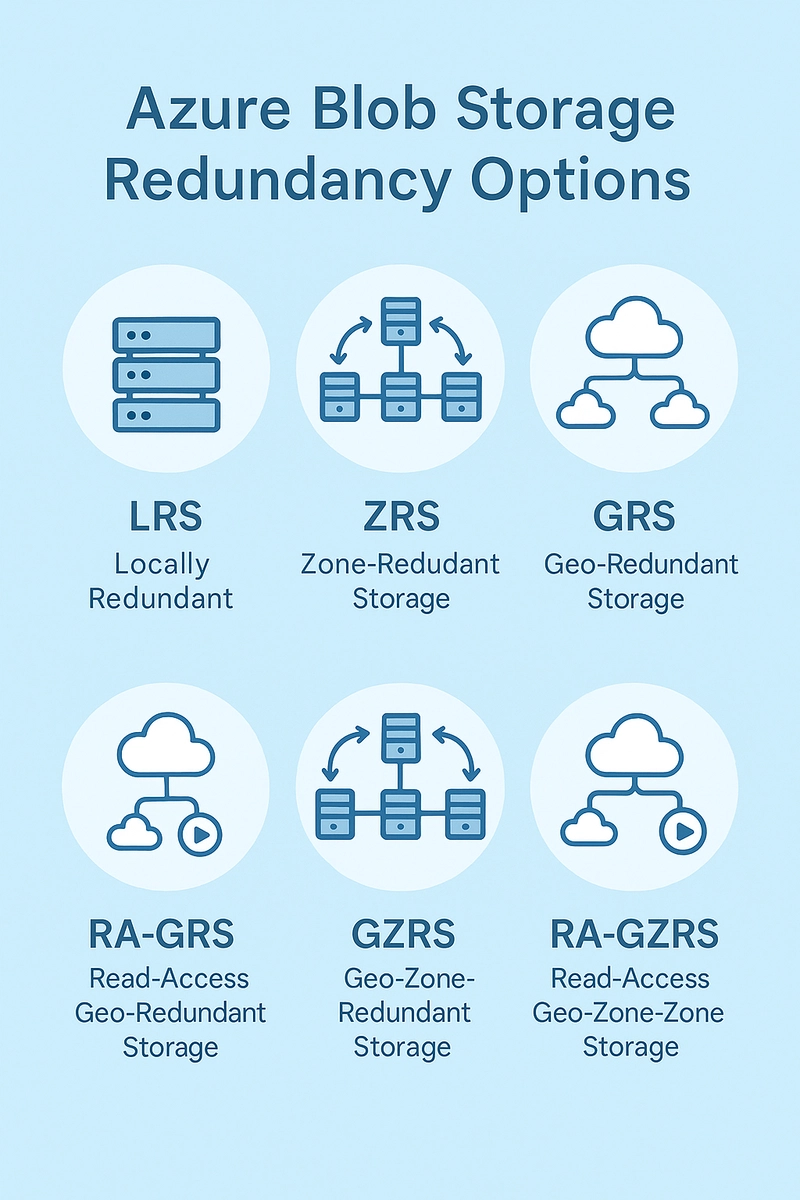
Now, the really important stuff: how does Azure Blob Storage make sure your data doesn't disappear? That's where "redundancy" comes in. It's all about making extra copies of your data so that if something goes wrong, you don't lose anything. Azure gives you several ways to do this, and each one offers a different level of protection and cost:
Locally Redundant Storage (LRS): This is the simplest option. It makes three copies of your data, but all within the same building (data center). It's the cheapest way to go, but it only protects you from problems within that single data center (like a hard drive failing).
Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS): This is a step up in protection. It also makes three copies of your data, but it spreads those copies across three different buildings (availability zones) within the same geographic region. These buildings are independent, so if one loses power, your data is still safe.
Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS): Now we're talking serious protection. GRS copies your data to a data center hundreds of miles away in a completely different region. This protects you from major disasters like a hurricane or an earthquake that could take out an entire region.
Read-Access Geo-Redundant Storage (RA-GRS): This is like GRS, but with a bonus. Not only does it copy your data to that far-away data center, but it also lets you read that data from the remote location, even if everything is working fine in your primary location. This can be useful for certain situations.
Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS): This option combines the best of both worlds. It spreads your data across multiple availability zones in the primary region and replicates it to a secondary region. This gives you excellent protection against both local and regional problems.
Read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS): This is the ultimate in protection. It's like GZRS, but it also lets you read your data from the secondary region. It's the most resilient option Azure Blob Storage offers.
Using Azure Blob Storage Like a Pro: Best Practices
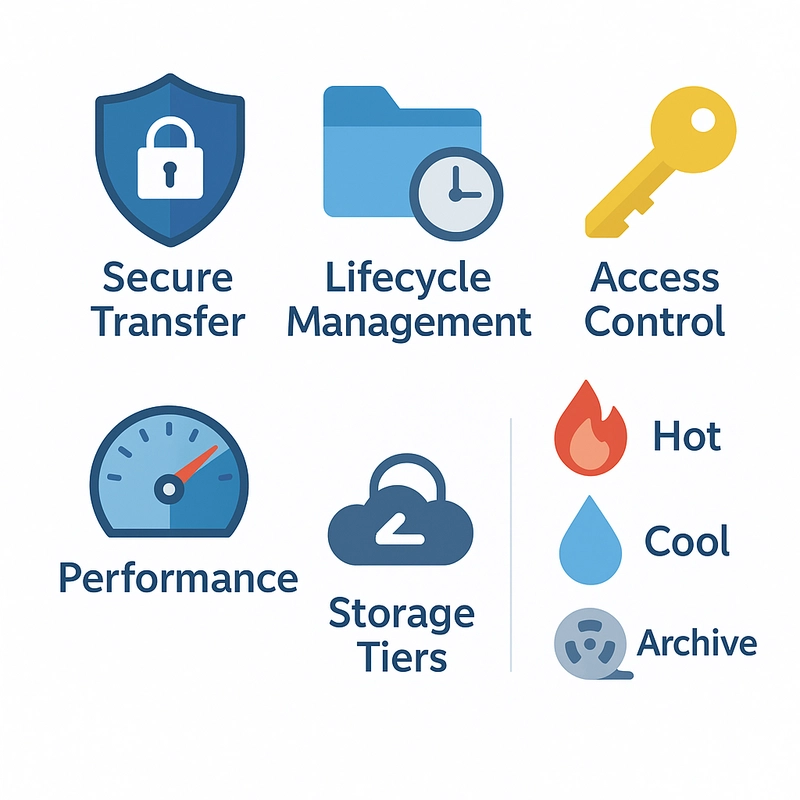
Okay, so you know what it is and how it keeps your data safe. Here's how to use it the right way:
Keep it Secure: Always use the most secure way to transfer your data (HTTPS), and make sure you're using the latest security standards (TLS 1.2 or later). Also, only give people the minimum access they need to your data. Don't give everyone the keys to the whole warehouse!
Clean Up Automatically: Azure has a cool feature called "lifecycle management." You can set up rules that automatically move your data to cheaper storage as it gets older (if you're not accessing it as often) or delete it altogether when you don't need it anymore. This can save you a lot of money!
Choose the Right Redundancy: Don't just pick the most expensive option by default. Think about how important your data is. If it's super critical (like customer data for a major application), use RA-GRS or RA-GZRS. If it's less important (like temporary files), LRS might be fine. For most applications, ZRS or GZRS are great choices.
Control Who Can Get In: Use Azure's built-in security tools (Azure Active Directory) to manage who can access your data. You can also use special "keys" (Shared Access Signatures, or SAS) to give someone limited access to specific data for a specific amount of time. It's like giving someone a temporary key to one specific room in the warehouse.
Use the Right Tools for the Job: If you're moving a lot of data, especially big files, use a tool called AzCopy. It's designed to be super-fast and efficient for transferring data to and from Azure Blob Storage.
Keep Things Organized: Just like you organize files into folders on your computer, organize your blobs into "containers" in Azure Blob Storage. This helps you keep things tidy and makes it easier to manage security settings.
Keep an Eye on Things: Azure gives you tools to monitor how much storage you're using and how well it's performing. Use these tools to make sure everything is running smoothly and to keep your costs under control.
Pick the Right Storage Tier: Azure Blob Storage has different "tiers" with different prices and performance. "Hot" is for data you access frequently (like active project files), "Cool" is for data you access less often (like backups), and "Archive" is for data you almost never access (like old records). Choosing the right tier can save you a lot of money.
Conclusion
Azure Blob Storage is a really powerful and flexible way to store all sorts of data in the cloud. Whether you're storing website content, backing up your data, or building a data-intensive application, Azure Blob Storage can handle it. By understanding how it works, how to keep your data safe, and how to use it efficiently, you can take full advantage of what it has to offer. It's like having a giant, secure, and well-organized warehouse for all your digital stuff!


































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)




































































































































































































































.jpg?#)































_NicoElNino_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)





























































































![Craft adds Readwise integration for working with book notes and highlights [50% off]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/craft3.jpg.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)















![Apple Restructures Global Affairs and Apple Music Teams [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97162/97162/97162-640.jpg)
![New iPhone Factory Goes Live in India, Another Just Days Away [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97165/97165/97165-640.jpg)