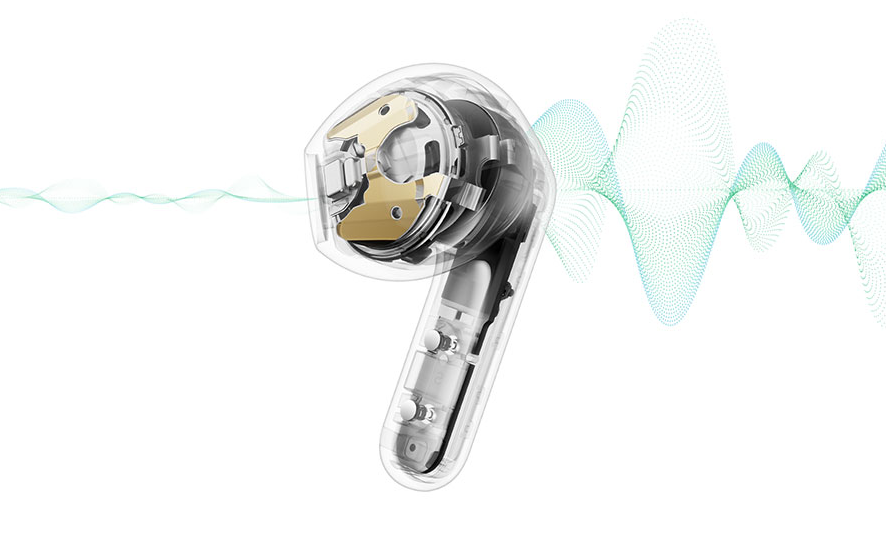
Brain-Like AI Model Learns More Efficiently by Mimicking Neural Spike Patterns
This is a Plain English Papers summary of a research paper called Brain-Like AI Model Learns More Efficiently by Mimicking Neural Spike Patterns. If you like these kinds of analysis, you should join AImodels.fyi or follow us on Twitter. Overview This paper proposes a novel architecture called the Poisson Variational Autoencoder (P-VAE) that combines principles of predictive coding with a VAE that encodes inputs into discrete spike counts. The P-VAE introduces a metabolic cost term in the model loss function, suggesting a relationship with sparse coding. The paper analyzes the geometry of the learned representations and finds that the P-VAE encodes its inputs in relatively higher dimensions, facilitating linear separability of categories in a downstream classification task with much better sample efficiency. Plain English Explanation The human brain is incredibly efficient at processing sensory information, and researchers are constantly seeking to understand the underlying mechanisms. [Variational autoencoders (VAEs)](https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/learning-multi-modal-generative-models-permutation-inva... Click here to read the full summary of this paper

This is a Plain English Papers summary of a research paper called Brain-Like AI Model Learns More Efficiently by Mimicking Neural Spike Patterns. If you like these kinds of analysis, you should join AImodels.fyi or follow us on Twitter.
Overview
- This paper proposes a novel architecture called the Poisson Variational Autoencoder (P-VAE) that combines principles of predictive coding with a VAE that encodes inputs into discrete spike counts.
- The P-VAE introduces a metabolic cost term in the model loss function, suggesting a relationship with sparse coding.
- The paper analyzes the geometry of the learned representations and finds that the P-VAE encodes its inputs in relatively higher dimensions, facilitating linear separability of categories in a downstream classification task with much better sample efficiency.
Plain English Explanation
The human brain is incredibly efficient at processing sensory information, and researchers are constantly seeking to understand the underlying mechanisms. [Variational autoencoders (VAEs)](https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/learning-multi-modal-generative-models-permutation-inva...








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)






























































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)










































































































































_Zoonar_GmbH_Alamy.jpg?#)



 (1).webp?#)





















































































![Are you buying a new Apple product to avoid tariffs? [Poll]](https://9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/03/tim-cook-apple-fifth-ave-joz.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=290&h=145&crop=1)



















![New iOS 19 Leak Allegedly Reveals Updated Icons, Floating Tab Bar, More [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96958/96958/96958-640.jpg)

![Apple to Source More iPhones From India to Offset China Tariff Costs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96954/96954/96954-640.jpg)