Migrating Hadoop Workloads to AWS: On-Premises HDFS, Spark, Kafka, Airflow to AWS S3, Iceberg, and EMR
Table of Contents Introduction Why Migrate from On-Premises Hadoop to AWS? Target AWS Architecture with Iceberg Step-by-Step Migration Process Code Snippets & Implementation Lessons Learned & Best Practices 1. Introduction Many enterprises still run on-premises Hadoop (HDFS, Spark, Kafka, Airflow) for big data processing. However, challenges like high operational costs, scalability bottlenecks, and maintenance overhead make cloud migration attractive. This blog provides a 6-step guide for migrating to AWS S3, Apache Iceberg, and EMR, including: ✔ Architecture diagrams ✔ Code snippets for Spark, Kafka, and Iceberg ✔ Lessons learned from real-world migrations 2. Why Migrate from On-Premises Hadoop to AWS? Challenges with On-Prem Hadoop Issue AWS Solution Expensive hardware & maintenance Pay-as-you-go pricing (EMR, S3) Manual scaling (YARN/HDFS) Auto-scaling EMR clusters HDFS limitations (durability, scaling) S3 (11 9’s durability) + Iceberg (ACID tables) Complex Kafka & Airflow management AWS MSK (Managed Kafka) & MWAA (Managed Airflow) Key Benefits of AWS + Iceberg Cost savings (no upfront hardware, spot instances) Modern table format (Iceberg for schema evolution, time travel) Serverless options (Glue, Athena, EMR Serverless) 3. Target AWS Architecture with Iceberg Current On-Premises Setup New AWS Architecture (Iceberg + EMR) Key AWS Services S3 – Data lake storage (replaces HDFS) EMR – Managed Spark with Iceberg support AWS Glue Data Catalog – Metastore for Iceberg tables MSK – Managed Kafka for streaming MWAA – Managed Airflow for orchestration 4. Step-by-Step Migration Process Phase 1: Assessment & Planning Inventory existing workloads (HDFS paths, Spark SQL, Kafka topics) Choose Iceberg for table format (supports schema evolution, upserts) Plan networking (VPC, security groups, IAM roles) Phase 2: Data Migration (HDFS → S3 + Iceberg) Option 1: Use distcp to copy data from HDFS to S3 hadoop distcp hdfs://namenode/path s3a://bucket/path Option 2: Use Spark to rewrite data as Iceberg df = spark.read.parquet("hdfs://path") df.write.format("iceberg").save("s3://bucket/iceberg_table") Phase 3: Compute Migration (Spark → EMR with Iceberg) Configure EMR with Iceberg (use bootstrap script): #!/bin/bash sudo pip install pyiceberg echo "spark.sql.catalog.glue_catalog=org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog" >> /etc/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf echo "spark.sql.catalog.glue_catalog.warehouse=s3://bucket/warehouse" >> /etc/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf Phase 4: Streaming Migration (Kafka → MSK) Mirror topics using Kafka Connect { "name": "msk-mirror", "config": { "connector.class": "org.apache.kafka.connect.mirror.MirrorSourceConnector", "source.cluster.bootstrap.servers": "on-prem-kafka:9092", "target.cluster.bootstrap.servers": "b-1.msk.aws:9092", "topics": ".*" } } Phase 5: Orchestration Migration (Airflow → MWAA) Export DAGs and update paths (replace hdfs:// with s3://) Use AWS Secrets Manager for credentials Phase 6: Validation & Optimization Verify data consistency (compare row counts, checksums) Optimize Iceberg (compact files, partition pruning) CALL glue_catalog.system.rewrite_data_files('db.table', strategy='binpack') 5. Code Snippets & Implementation 1. Reading/Writing Iceberg Tables in Spark # Read from HDFS (old) df = spark.read.parquet("hdfs:///data/transactions") # Write to Iceberg (new) df.write.format("iceberg").mode("overwrite").save("s3://bucket/iceberg_db/transactions") # Query with time travel spark.read.format("iceberg").option("snapshot-id", "12345").load("s3://bucket/iceberg_db/transactions") 2. Kafka to Iceberg (Structured Streaming) df = spark.readStream.format("kafka") \ .option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "b-1.msk.aws:9092") \ .option("subscribe", "transactions") \ .load() # Write to Iceberg in Delta Lake format df.writeStream.format("iceberg") \ .outputMode("append") \ .option("path", "s3://bucket/iceberg_db/streaming") \ .start() 3. Airflow DAG for Iceberg Maintenance from airflow import DAG from airflow.providers.amazon.aws.operators.emr import EmrAddStepsOperator dag = DAG("iceberg_maintenance", schedule_interval="@weekly") compact_task = EmrAddStepsOperator( task_id="compact_iceberg", job_flow_id="j-EMRCLUSTER", steps=[{ "Name": "Compact Iceberg", "HadoopJarStep": { "Jar": "command-runner.jar", "Args": ["spark-sql", "--executor-memory", "8G", "-e", "CALL glue_catalog.system.rewrite_data_files('db.
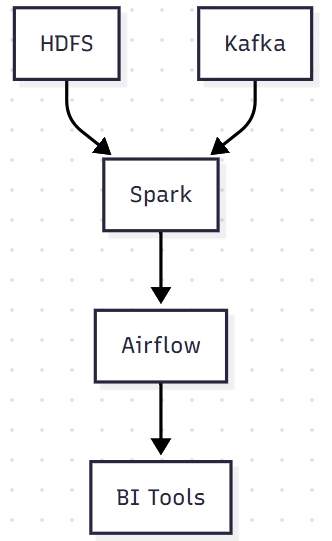
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Why Migrate from On-Premises Hadoop to AWS?
- Target AWS Architecture with Iceberg
- Step-by-Step Migration Process
- Code Snippets & Implementation
- Lessons Learned & Best Practices
1. Introduction
Many enterprises still run on-premises Hadoop (HDFS, Spark, Kafka, Airflow) for big data processing. However, challenges like high operational costs, scalability bottlenecks, and maintenance overhead make cloud migration attractive.
This blog provides a 6-step guide for migrating to AWS S3, Apache Iceberg, and EMR, including:
✔ Architecture diagrams
✔ Code snippets for Spark, Kafka, and Iceberg
✔ Lessons learned from real-world migrations
2. Why Migrate from On-Premises Hadoop to AWS?
Challenges with On-Prem Hadoop
| Issue | AWS Solution |
|---|---|
| Expensive hardware & maintenance | Pay-as-you-go pricing (EMR, S3) |
| Manual scaling (YARN/HDFS) | Auto-scaling EMR clusters |
| HDFS limitations (durability, scaling) | S3 (11 9’s durability) + Iceberg (ACID tables) |
| Complex Kafka & Airflow management | AWS MSK (Managed Kafka) & MWAA (Managed Airflow) |
Key Benefits of AWS + Iceberg
- Cost savings (no upfront hardware, spot instances)
- Modern table format (Iceberg for schema evolution, time travel)
- Serverless options (Glue, Athena, EMR Serverless)
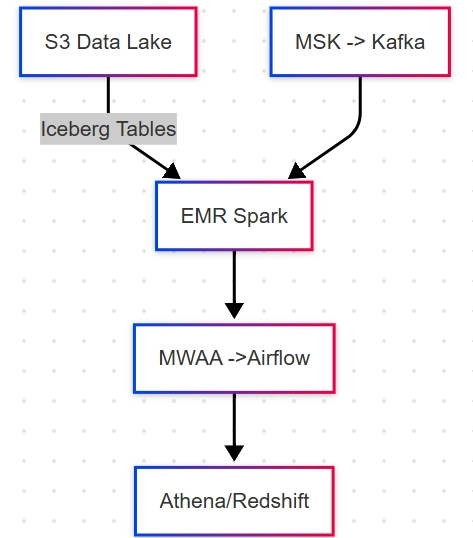
3. Target AWS Architecture with Iceberg
Current On-Premises Setup
New AWS Architecture (Iceberg + EMR)
Key AWS Services
- S3 – Data lake storage (replaces HDFS)
- EMR – Managed Spark with Iceberg support
- AWS Glue Data Catalog – Metastore for Iceberg tables
- MSK – Managed Kafka for streaming
- MWAA – Managed Airflow for orchestration
4. Step-by-Step Migration Process
Phase 1: Assessment & Planning
- Inventory existing workloads (HDFS paths, Spark SQL, Kafka topics)
- Choose Iceberg for table format (supports schema evolution, upserts)
- Plan networking (VPC, security groups, IAM roles)
Phase 2: Data Migration (HDFS → S3 + Iceberg)
-
Option 1: Use
distcpto copy data from HDFS to S3
hadoop distcp hdfs://namenode/path s3a://bucket/path
- Option 2: Use Spark to rewrite data as Iceberg
df = spark.read.parquet("hdfs://path")
df.write.format("iceberg").save("s3://bucket/iceberg_table")
Phase 3: Compute Migration (Spark → EMR with Iceberg)
- Configure EMR with Iceberg (use bootstrap script):
#!/bin/bash
sudo pip install pyiceberg
echo "spark.sql.catalog.glue_catalog=org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog" >> /etc/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf
echo "spark.sql.catalog.glue_catalog.warehouse=s3://bucket/warehouse" >> /etc/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf
Phase 4: Streaming Migration (Kafka → MSK)
- Mirror topics using Kafka Connect
{
"name": "msk-mirror",
"config": {
"connector.class": "org.apache.kafka.connect.mirror.MirrorSourceConnector",
"source.cluster.bootstrap.servers": "on-prem-kafka:9092",
"target.cluster.bootstrap.servers": "b-1.msk.aws:9092",
"topics": ".*"
}
}
Phase 5: Orchestration Migration (Airflow → MWAA)
-
Export DAGs and update paths (replace
hdfs://withs3://) - Use AWS Secrets Manager for credentials
Phase 6: Validation & Optimization
- Verify data consistency (compare row counts, checksums)
- Optimize Iceberg (compact files, partition pruning)
CALL glue_catalog.system.rewrite_data_files('db.table', strategy='binpack')
5. Code Snippets & Implementation
1. Reading/Writing Iceberg Tables in Spark
# Read from HDFS (old)
df = spark.read.parquet("hdfs:///data/transactions")
# Write to Iceberg (new)
df.write.format("iceberg").mode("overwrite").save("s3://bucket/iceberg_db/transactions")
# Query with time travel
spark.read.format("iceberg").option("snapshot-id", "12345").load("s3://bucket/iceberg_db/transactions")
2. Kafka to Iceberg (Structured Streaming)
df = spark.readStream.format("kafka") \
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "b-1.msk.aws:9092") \
.option("subscribe", "transactions") \
.load()
# Write to Iceberg in Delta Lake format
df.writeStream.format("iceberg") \
.outputMode("append") \
.option("path", "s3://bucket/iceberg_db/streaming") \
.start()
3. Airflow DAG for Iceberg Maintenance
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.providers.amazon.aws.operators.emr import EmrAddStepsOperator
dag = DAG("iceberg_maintenance", schedule_interval="@weekly")
compact_task = EmrAddStepsOperator(
task_id="compact_iceberg",
job_flow_id="j-EMRCLUSTER",
steps=[{
"Name": "Compact Iceberg",
"HadoopJarStep": {
"Jar": "command-runner.jar",
"Args": ["spark-sql", "--executor-memory", "8G",
"-e", "CALL glue_catalog.system.rewrite_data_files('db.transactions')"]
}
}]
)
6. Lessons Learned & Best Practices
Key Challenges & Fixes
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Slow S3 writes | Use EMRFS S3-optimized committer |
| Hive metastore conflicts | Migrate to Glue Data Catalog |
| Kafka consumer lag | Increase MSK broker size & optimize partitions |
Best Practices
✅ Use EMR 6.8+ for native Iceberg support
✅ Partition Iceberg tables by time for better performance
✅ Enable S3 lifecycle policies to save costs
✅ Monitor MSK lag with CloudWatch
Final Thoughts
Migrating to AWS S3 + Iceberg + EMR modernizes data infrastructure, reduces costs, and improves scalability. By following this guide, enterprises can minimize downtime and maximize performance.
Next Steps
Would you like a deeper dive into Iceberg optimizations or Kafka migration strategies? Let me know in the comments!







































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)

































































































































































































![GrandChase tier list of the best characters available [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33057-1637756796/grandchase-ios-android-3rd-anniversary.jpg?#)












































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





































































































![Global security vulnerability database gets 11 more months of funding [u]](https://photos5.appleinsider.com/gallery/63338-131616-62453-129471-61060-125967-51013-100774-49862-97722-Malware-Image-xl-xl-xl-(1)-xl-xl.jpg)






















![Apple M4 13-inch iPad Pro On Sale for $200 Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97056/97056/97056-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares New 'Mac Does That' Ads for MacBook Pro [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97055/97055/97055-640.jpg)

![Apple Releases tvOS 18.4.1 for Apple TV [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97047/97047/97047-640.jpg)