Meet Sdelete, the obscure Microsoft tool that wipes data for good
When you delete a file from your computer, it’s not really gone. In fact, it can often be recovered with the right tools. That’s where Sdelete comes in. Sdelete is short for Secure Delete and it permanently wipes files by overwriting them–sometimes multiple times, which makes recovery virtually impossible. This tool is part of the Sysinternals suite from Mark Russinovich, which now belongs to Microsoft. It works according to the Clearing and Sanitizing standard DOD 5220.22-M of the US Department of Defense. This is how it works via the command line: The tool comes in a zip archive and offers the command sdelete after unpacking. For this command to work in the Windows command prompt in any directory, it must be located in a folder that is part of the Windows path variable Path. The easiest way is to copy the contents of the archive to the folder C:\Windows. Now call up the command prompt by pressing the key combination Win-R and entering cmd. This action starts the command prompt, in which you enter the command sdelete to delete files or folders. The Sdelete command line program from Sysinternals Tools allows you to permanently delete files and folders.IDG For example, if you want to delete the file “Document1.docx, enter the following: sdelete -p 3 [path]\Document1.docx Please replace [path] with the location of the file, including the drive letter, such as N:\files. The -p 3 indicates the number of overwrites. In this case, there are three. If you want to delete a folder, including all subfolders and files contained in it, such as the Temp folder, specify your parameters as follows: sdelete -p 3 -s [path]\Temp The -s parameter also deletes the subfolders. The -r parameter is also interesting: this removes the write protection attribute before deleting the file. Otherwise, there would be error messages for protected files. The freeware Sdelete-Gui offers simple user guidance for the command line tool Sdelete. It adds the “Secure Delete” command to the Windows Explorer context menu.IDG Sdelete can also overwrite the entire free space on a drive. The process securely deletes all remaining files. You can perform the deletion by using the parameter -z. If the free space on drive C: is to be overwritten, the command looks like this: sdelete -z C: Depending on the size of the drive, it may take some time for the command to complete. Delete with user guidance: For those who find the command prompt too cumbersome, there is user guidance for the sdelete command. We call the tool Sdelete-Gui. When you start it for the first time, it asks you how often you want sdelete to overwrite a file and then suggests ten times. That’s a lot. Three times is also very reliable. Click on Enable to set the desired number and close the window with the X in the top right-hand corner. You will now find the Secure delete command in the Windows Explorer context menu. Select the file or files you want to securely delete and right-click on them. In Windows 11, first select Show more options and then Secure delete. Attention: Sdelete will immediately delete the data without prompting you. Please note that Sdelete deletes your data reliably. Once you use the command, there is no way to restore them. You should therefore use Sdelete with caution.

When you delete a file from your computer, it’s not really gone. In fact, it can often be recovered with the right tools. That’s where Sdelete comes in.
Sdelete is short for Secure Delete and it permanently wipes files by overwriting them–sometimes multiple times, which makes recovery virtually impossible. This tool is part of the Sysinternals suite from Mark Russinovich, which now belongs to Microsoft. It works according to the Clearing and Sanitizing standard DOD 5220.22-M of the US Department of Defense.
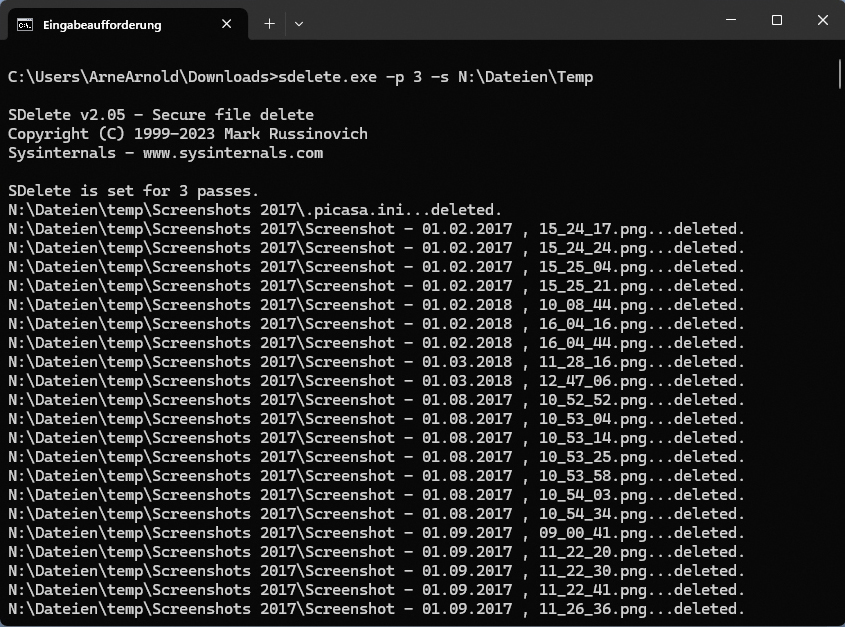
This is how it works via the command line: The tool comes in a zip archive and offers the command sdelete after unpacking. For this command to work in the Windows command prompt in any directory, it must be located in a folder that is part of the Windows path variable Path.
The easiest way is to copy the contents of the archive to the folder C:\Windows. Now call up the command prompt by pressing the key combination Win-R and entering cmd. This action starts the command prompt, in which you enter the command sdelete to delete files or folders.
IDG
For example, if you want to delete the file “Document1.docx, enter the following:
sdelete -p 3 [path]\Document1.docx
Please replace [path] with the location of the file, including the drive letter, such as N:\files. The -p 3 indicates the number of overwrites. In this case, there are three. If you want to delete a folder, including all subfolders and files contained in it, such as the Temp folder, specify your parameters as follows:
sdelete -p 3 -s [path]\Temp
The -s parameter also deletes the subfolders. The -r parameter is also interesting: this removes the write protection attribute before deleting the file. Otherwise, there would be error messages for protected files.
IDG
Sdelete can also overwrite the entire free space on a drive. The process securely deletes all remaining files. You can perform the deletion by using the parameter -z. If the free space on drive C: is to be overwritten, the command looks like this:
sdelete -z C:
Depending on the size of the drive, it may take some time for the command to complete.
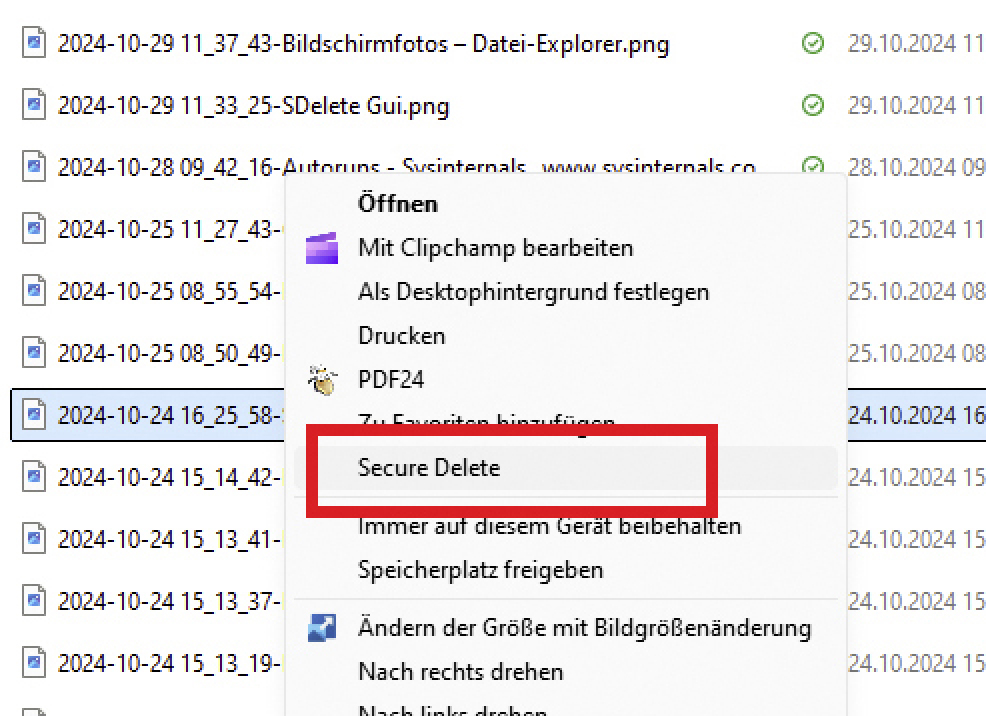
Delete with user guidance: For those who find the command prompt too cumbersome, there is user guidance for the sdelete command. We call the tool Sdelete-Gui. When you start it for the first time, it asks you how often you want sdelete to overwrite a file and then suggests ten times. That’s a lot. Three times is also very reliable.
Click on Enable to set the desired number and close the window with the X in the top right-hand corner. You will now find the Secure delete command in the Windows Explorer context menu. Select the file or files you want to securely delete and right-click on them. In Windows 11, first select Show more options and then Secure delete.
Attention: Sdelete will immediately delete the data without prompting you. Please note that Sdelete deletes your data reliably. Once you use the command, there is no way to restore them. You should therefore use Sdelete with caution.



































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)




























































































































![[DEALS] Microsoft 365: 1-Year Subscription (Family/Up to 6 Users) (23% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)









































































































.jpg?#)
.jpg?#)

































_Inge_Johnsson-Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)












































































































![New Powerbeats Pro 2 Wireless Earbuds On Sale for $199.95 [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97217/97217/97217-640.jpg)
![Alleged iPhone 17-19 Roadmap Leaked: Foldables and Spring Launches Ahead [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97214/97214/97214-640.jpg)

![New Apple iPad mini 7 On Sale for $399! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96096/96096/96096-640.jpg)