HarmonyOS NEXT Development Case: Tic-Tac-Toe Game Implementation
This article demonstrates a Tic-Tac-Toe game implementation using HarmonyOS NEXT's ArkUI framework, showcasing key features like reactive UI, animation handling, and game logic implementation. 1. Core Class Design 1.1 Cell Class - Game Piece Representation // Import prompt dialog module import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI'; // Utilize framework features like property tracking @ObservedV2 class Cell { // Define piece type: 0 for empty, 1 for black, 2 for white @Trace user: number = 0; // Piece identifier (e.g., "A", "B") name: string = ""; // Position coordinates x: number = 0; y: number = 0; // Piece dimensions width: number = 100; height: number = 100; // Constructor initializes piece state constructor(name: string, x: number, y: number, user: number) { this.user = user; this.name = name; this.x = x; this.y = y; } // Animation offset values @Trace animX: number = 0; @Trace animY: number = 0; // Calculate center coordinates getCenterX() { return this.x - this.width / 2; } getCenterY() { return this.y - this.height / 2; } // Handle piece movement animation moveAnimation(animationTime: number, toCell: Cell, callback?: () => void) { animateToImmediately({ duration: animationTime, iterations: 1, curve: Curve.Linear, onFinish: () => { animateToImmediately({ duration: 0, iterations: 1, curve: Curve.Linear, onFinish: () => { callback?.(); } }, () => { this.animX = 0; this.animY = 0; const temp = this.user; this.user = toCell.user; toCell.user = temp; }); } }, () => { this.animX = toCell.x - this.x; this.animY = toCell.y - this.y; }); } } 1.2 Connection Class - Piece Relationships class Connection { startName: string; endName: string; startX: number; startY: number; endX: number; endY: number; constructor(start: Cell, end: Cell) { this.startName = start.name; this.endName = end.name; this.startX = start.x; this.startY = start.y; this.endX = end.x; this.endY = end.y; } } 2. Game Implementation Logic 2.1 Main Game Component @Entry @Component struct TwoSonChessGame { @State isAnimationRunning: boolean = false; @State cells: Cell[] = []; @State connections: Connection[] = []; @State currentPlayer: number = 1; // Initialize game board aboutToAppear(): void { const cellA = new Cell("A", 180, 180, 2); const cellB = new Cell("B", 540, 180, 1); const cellC = new Cell("C", 360, 360, 0); const cellD = new Cell("D", 180, 540, 1); const cellE = new Cell("E", 540, 540, 2); this.cells.push(cellA, cellB, cellC, cellD, cellE); this.connections.push( new Connection(cellA, cellB), new Connection(cellA, cellC), new Connection(cellA, cellD), new Connection(cellB, cellC), new Connection(cellC, cellD), new Connection(cellC, cellE), new Connection(cellD, cellE) ); } // Game control methods resetGame() { this.currentPlayer = 1; this.cells[0].user = 2; this.cells[1].user = 1; this.cells[2].user = 0; this.cells[3].user = 1; this.cells[4].user = 2; } // Move validation and execution move(cell: Cell) { if (this.isCellValid(cell)) { const targetIndex = this.checkValidMove(cell); if (targetIndex !== -1) { this.isAnimationRunning = true; cell.moveAnimation(300, this.cells[targetIndex], () => { this.isAnimationRunning = false; this.moveCompleted(); }); } } } // Post-move handling moveCompleted() { this.currentPlayer = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? 2 : 1; if (this.isGameOver()) { const winner = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? 'White Wins' : 'Black Wins'; promptAction.showDialog({ title: 'Game Over', message: winner, buttons: [{ text: 'Restart', color: '#ffa500' }] }).then(() => this.resetGame()); } else if (this.currentPlayer === 2) { this.aiMove(); } } // AI implementation aiMove() { const whiteCells = this.cells.filter(cell => cell.user === 2 && this.checkValidMove(cell) !== -1); if (whiteCells.length === 1) { this.move(whiteCells[0]); } else if (whiteCells.length === 2) { const moveIndex = this.chooseBestMove(whiteCells); this.move(whiteCells[moveIndex]); } } } 3. UI Implementation build() { Column({ space: 10 }) { Stack() { // Draw connection lines ForEach(this.connections, (conn: Connection) => { Line() .width(5).height(5) .startPoint([`${conn.startX}lpx`, `${conn.startY}lpx`]) .endPoint([`${conn.endX}lpx`, `${conn.endY}lpx`]) .stroke(Color.Black) .fill(Color
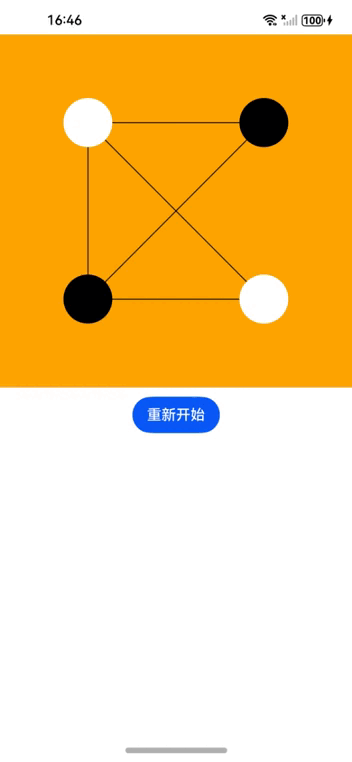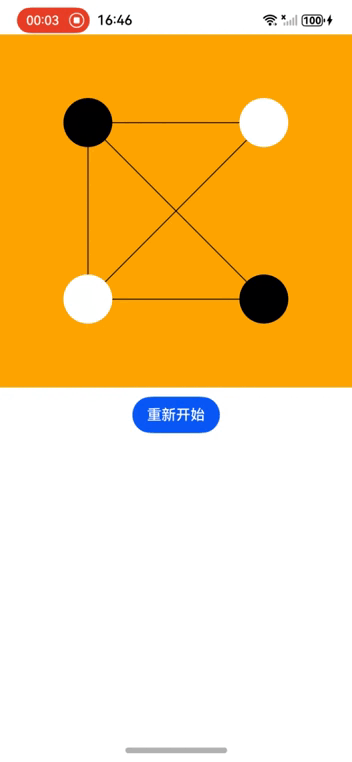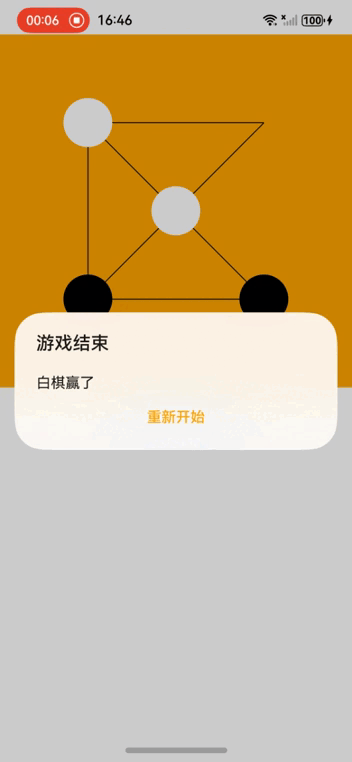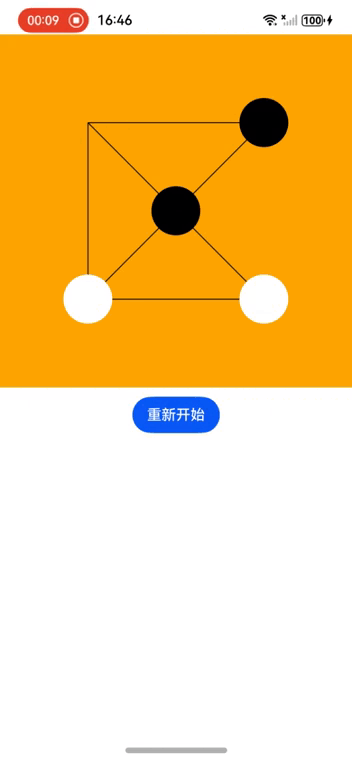
This article demonstrates a Tic-Tac-Toe game implementation using HarmonyOS NEXT's ArkUI framework, showcasing key features like reactive UI, animation handling, and game logic implementation.
1. Core Class Design
1.1 Cell Class - Game Piece Representation
// Import prompt dialog module
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI';
// Utilize framework features like property tracking
@ObservedV2
class Cell {
// Define piece type: 0 for empty, 1 for black, 2 for white
@Trace user: number = 0;
// Piece identifier (e.g., "A", "B")
name: string = "";
// Position coordinates
x: number = 0;
y: number = 0;
// Piece dimensions
width: number = 100;
height: number = 100;
// Constructor initializes piece state
constructor(name: string, x: number, y: number, user: number) {
this.user = user;
this.name = name;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// Animation offset values
@Trace animX: number = 0;
@Trace animY: number = 0;
// Calculate center coordinates
getCenterX() {
return this.x - this.width / 2;
}
getCenterY() {
return this.y - this.height / 2;
}
// Handle piece movement animation
moveAnimation(animationTime: number, toCell: Cell, callback?: () => void) {
animateToImmediately({
duration: animationTime,
iterations: 1,
curve: Curve.Linear,
onFinish: () => {
animateToImmediately({
duration: 0,
iterations: 1,
curve: Curve.Linear,
onFinish: () => {
callback?.();
}
}, () => {
this.animX = 0;
this.animY = 0;
const temp = this.user;
this.user = toCell.user;
toCell.user = temp;
});
}
}, () => {
this.animX = toCell.x - this.x;
this.animY = toCell.y - this.y;
});
}
}
1.2 Connection Class - Piece Relationships
class Connection {
startName: string;
endName: string;
startX: number;
startY: number;
endX: number;
endY: number;
constructor(start: Cell, end: Cell) {
this.startName = start.name;
this.endName = end.name;
this.startX = start.x;
this.startY = start.y;
this.endX = end.x;
this.endY = end.y;
}
}
2. Game Implementation Logic
2.1 Main Game Component
@Entry
@Component
struct TwoSonChessGame {
@State isAnimationRunning: boolean = false;
@State cells: Cell[] = [];
@State connections: Connection[] = [];
@State currentPlayer: number = 1;
// Initialize game board
aboutToAppear(): void {
const cellA = new Cell("A", 180, 180, 2);
const cellB = new Cell("B", 540, 180, 1);
const cellC = new Cell("C", 360, 360, 0);
const cellD = new Cell("D", 180, 540, 1);
const cellE = new Cell("E", 540, 540, 2);
this.cells.push(cellA, cellB, cellC, cellD, cellE);
this.connections.push(
new Connection(cellA, cellB),
new Connection(cellA, cellC),
new Connection(cellA, cellD),
new Connection(cellB, cellC),
new Connection(cellC, cellD),
new Connection(cellC, cellE),
new Connection(cellD, cellE)
);
}
// Game control methods
resetGame() {
this.currentPlayer = 1;
this.cells[0].user = 2;
this.cells[1].user = 1;
this.cells[2].user = 0;
this.cells[3].user = 1;
this.cells[4].user = 2;
}
// Move validation and execution
move(cell: Cell) {
if (this.isCellValid(cell)) {
const targetIndex = this.checkValidMove(cell);
if (targetIndex !== -1) {
this.isAnimationRunning = true;
cell.moveAnimation(300, this.cells[targetIndex], () => {
this.isAnimationRunning = false;
this.moveCompleted();
});
}
}
}
// Post-move handling
moveCompleted() {
this.currentPlayer = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? 2 : 1;
if (this.isGameOver()) {
const winner = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? 'White Wins' : 'Black Wins';
promptAction.showDialog({
title: 'Game Over',
message: winner,
buttons: [{ text: 'Restart', color: '#ffa500' }]
}).then(() => this.resetGame());
} else if (this.currentPlayer === 2) {
this.aiMove();
}
}
// AI implementation
aiMove() {
const whiteCells = this.cells.filter(cell =>
cell.user === 2 && this.checkValidMove(cell) !== -1);
if (whiteCells.length === 1) {
this.move(whiteCells[0]);
} else if (whiteCells.length === 2) {
const moveIndex = this.chooseBestMove(whiteCells);
this.move(whiteCells[moveIndex]);
}
}
}
3. UI Implementation
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Stack() {
// Draw connection lines
ForEach(this.connections, (conn: Connection) => {
Line()
.width(5).height(5)
.startPoint([`${conn.startX}lpx`, `${conn.startY}lpx`])
.endPoint([`${conn.endX}lpx`, `${conn.endY}lpx`])
.stroke(Color.Black)
.fill(Color.Green);
});
// Render game pieces
ForEach(this.cells, (cell: Cell) => {
Text()
.width(`${cell.width}lpx`)
.height(`${cell.height}lpx`)
.margin({
left: `${cell.getCenterX()}lpx`,
top: `${cell.getCenterY()}lpx`
})
.translate({ x: `${cell.animX}lpx`, y: `${cell.animY}lpx` })
.backgroundColor(cell.user === 0 ? Color.Transparent :
(cell.user === 1 ? Color.Black : Color.White))
.borderRadius('50%')
.onClick(() => {
if (!this.isAnimationRunning) this.move(cell);
});
});
}
.width('720lpx').height('720lpx')
.backgroundColor(Color.Orange);
// Restart button
Button('Restart').onClick(() => {
if (!this.isAnimationRunning) this.resetGame();
});
}
}
Key Features Demonstrated:
- Reactive UI Updates: Leveraging @ObservedV2 and @trace decorators for efficient state management
- Animation System: Smooth piece movement using animateToImmediately
-
Game Logic:
- Turn-based gameplay
- Move validation
- Win condition checking
- Basic AI implementation
- Component Composition: Effective use of Stack, Column, and ForEach for UI organization
- User Interaction: Click handling with animation state management
This implementation demonstrates fundamental HarmonyOS development patterns while maintaining clean architecture and responsive gameplay experience.




































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)
























































































































![Ditching a Microsoft Job to Enter Startup Purgatory with Lonewolf Engineer Sam Crombie [Podcast #171]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1746753508177/0cd57f66-fdb0-4972-b285-1443a7db39fc.png?#)



































































































































_Piotr_Adamowicz_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)






































































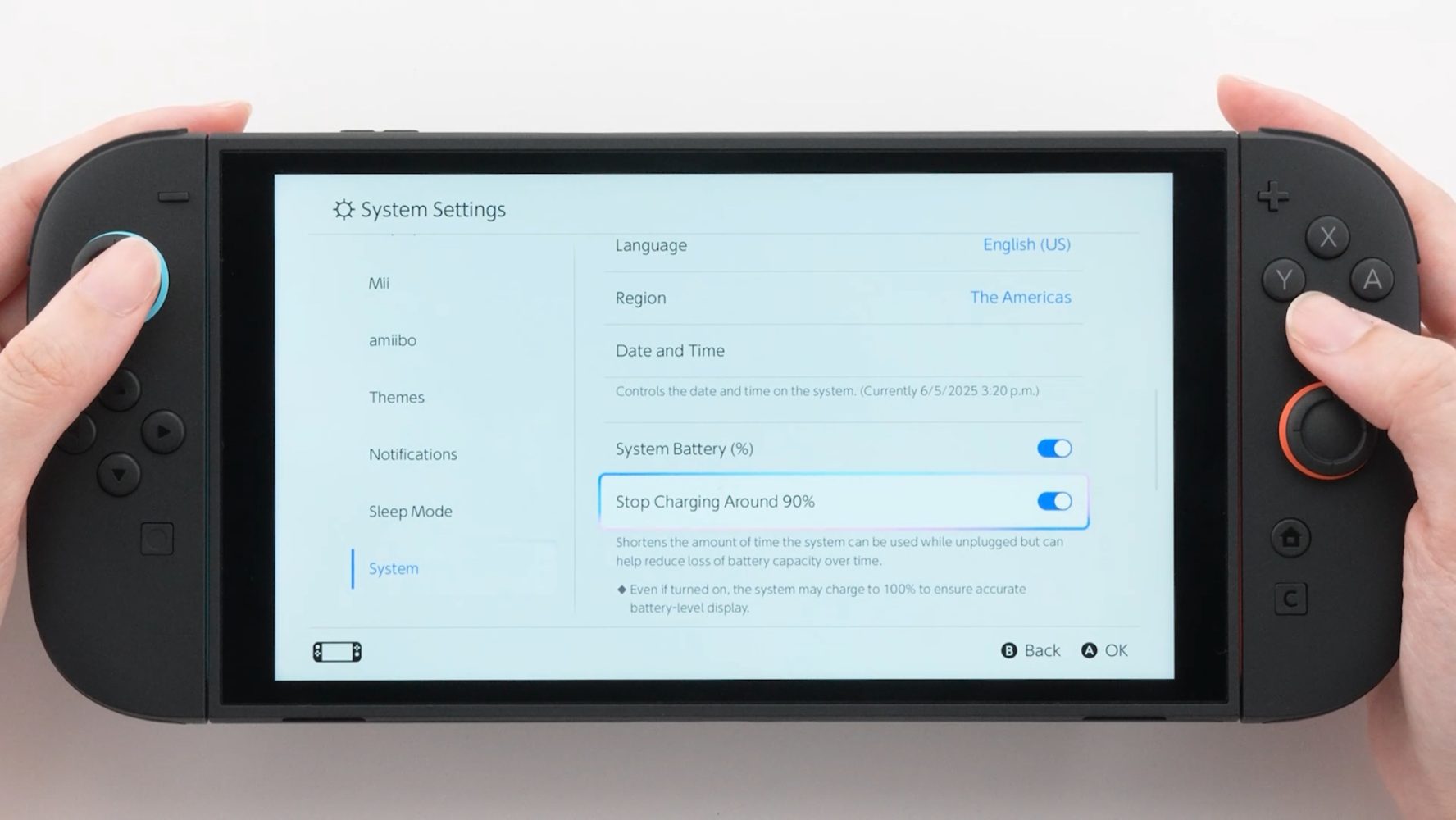


































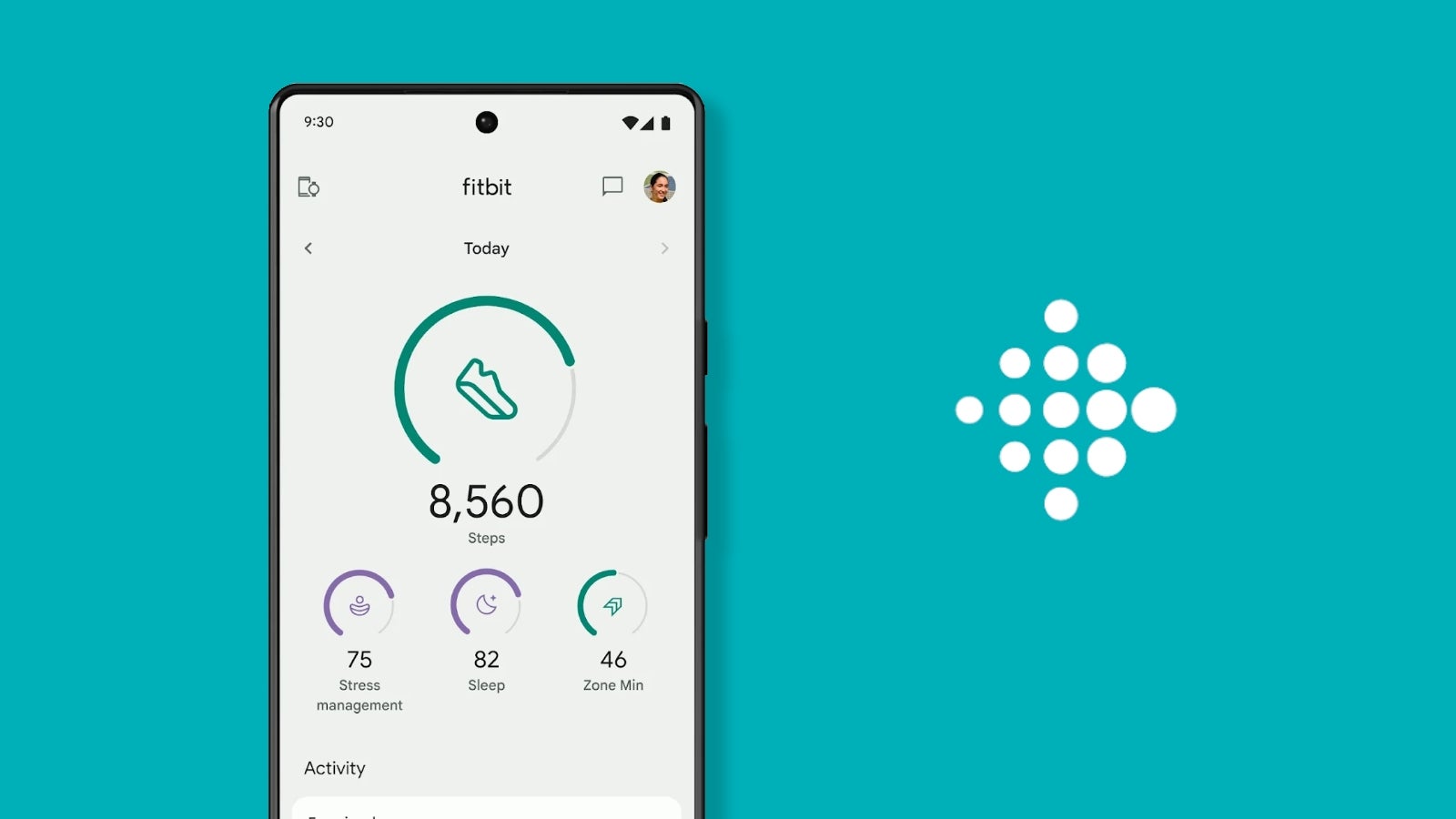
![Apple to Launch AI-Powered Battery Saver Mode in iOS 19 [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97309/97309/97309-1280.jpg)

![Apple Officially Releases macOS Sequoia 15.5 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97308/97308/97308-640.jpg)