Glass Beads vs. Ceramic Beads: A Comparative Guide to Sandblasting Effects and Applications in Machining
In the field of machining and surface treatment, sandblasting is widely used for cleaning, strengthening, and refining metal surfaces. Glass beads and ceramic beads are two common blasting media, each offering distinct differences in blasting effects, durability, and suitable applications. This article provides a detailed comparison to help you choose the most suitable blasting material. 1. Hardness & Wear Resistance Glass Beads: With a Mohs hardness of 5-6, glass beads are relatively soft, making them ideal for gentle surface treatments such as removing dirt, light deburring, and achieving a satin finish. Ceramic Beads: With a Mohs hardness of 7-8, ceramic beads are harder and more wear-resistant, making them suitable for more aggressive sandblasting applications that require higher impact force, such as strengthening metal surfaces and improving wear resistance. 2. Blasting Effects & Surface Finish Glass bead blasting creates a uniform matte or semi-gloss finish, making it suitable for stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals. It effectively removes contaminants without significantly altering surface roughness. Ceramic bead blasting results in a smoother and more wear-resistant surface, making it ideal for high-precision applications such as aerospace and medical equipment manufacturing. 3. Suitable Materials & Applications Glass Beads: Best suited for stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper, and plastics, commonly used in automotive, mold making, and food processing equipment industries. Ceramic Beads: More suitable for steel, titanium alloys, and heat-resistant alloys, often used in aerospace, precision manufacturing, and turbine blade processing. 4. Cost & Service Life Glass Beads are more affordable but more fragile, leading to a shorter reuse cycle. Ceramic Beads are more expensive but significantly more durable, making them more cost-effective in the long run. 5. Environmental Impact & Safety Glass Beads are made from silicate glass and do not contain free silica, making them relatively eco-friendly, though they generate more dust. Ceramic Beads are composed of zirconia or alumina ceramics, producing less dust, creating a cleaner working environment, and being more operator-friendly. Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Blasting Media? ✅ Choose glass beads if you need a gentle cleaning effect that won’t damage the workpiece, especially for aluminum and stainless steel surface cleaning and polishing. ✅ Choose ceramic beads if you require stronger impact, longer service life, and enhanced durability, especially in high-end manufacturing, aerospace, and precision machining. The best choice depends on your workpiece material, processing requirements, and cost considerations. Hope this comparison helps you make the best decision!
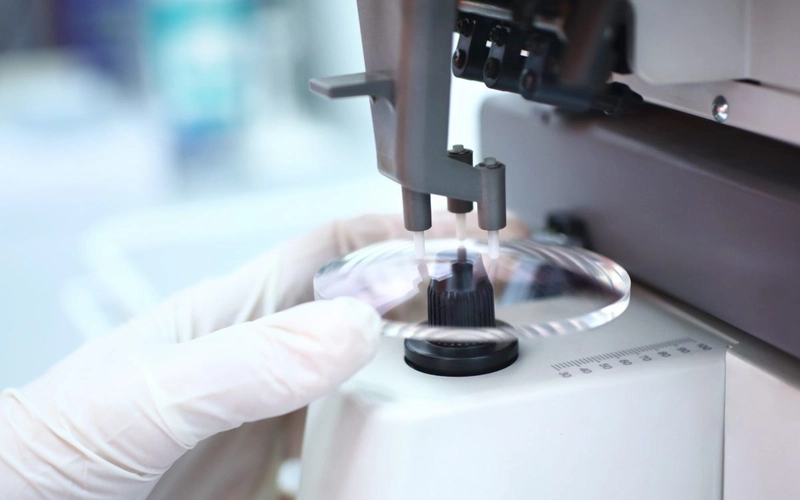

In the field of machining and surface treatment, sandblasting is widely used for cleaning, strengthening, and refining metal surfaces. Glass beads and ceramic beads are two common blasting media, each offering distinct differences in blasting effects, durability, and suitable applications. This article provides a detailed comparison to help you choose the most suitable blasting material.
Glass Beads: With a Mohs hardness of 5-6, glass beads are relatively soft, making them ideal for gentle surface treatments such as removing dirt, light deburring, and achieving a satin finish.
Ceramic Beads: With a Mohs hardness of 7-8, ceramic beads are harder and more wear-resistant, making them suitable for more aggressive sandblasting applications that require higher impact force, such as strengthening metal surfaces and improving wear resistance.
2. Blasting Effects & Surface Finish
Glass bead blasting creates a uniform matte or semi-gloss finish, making it suitable for stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals. It effectively removes contaminants without significantly altering surface roughness.
Ceramic bead blasting results in a smoother and more wear-resistant surface, making it ideal for high-precision applications such as aerospace and medical equipment manufacturing.
3. Suitable Materials & Applications
Glass Beads: Best suited for stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper, and plastics, commonly used in automotive, mold making, and food processing equipment industries.
Ceramic Beads: More suitable for steel, titanium alloys, and heat-resistant alloys, often used in aerospace, precision manufacturing, and turbine blade processing.
4. Cost & Service Life
Glass Beads are more affordable but more fragile, leading to a shorter reuse cycle.
Ceramic Beads are more expensive but significantly more durable, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
5. Environmental Impact & Safety
Glass Beads are made from silicate glass and do not contain free silica, making them relatively eco-friendly, though they generate more dust.
Ceramic Beads are composed of zirconia or alumina ceramics, producing less dust, creating a cleaner working environment, and being more operator-friendly.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Blasting Media?
✅ Choose glass beads if you need a gentle cleaning effect that won’t damage the workpiece, especially for aluminum and stainless steel surface cleaning and polishing.
✅ Choose ceramic beads if you require stronger impact, longer service life, and enhanced durability, especially in high-end manufacturing, aerospace, and precision machining.
The best choice depends on your workpiece material, processing requirements, and cost considerations. Hope this comparison helps you make the best decision!







































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)


































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)









































































































.jpg?#)




























_ArtemisDiana_Alamy.jpg?#)











































































-xl.jpg)











![Yes, the Gemini icon is now bigger and brighter on Android [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/02/Gemini-on-Galaxy-S25.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)